1. Spring 基本概念
AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming)称为面向切面编程,在程序开发中主要用来解决一些系统层面上的问题,比如日志,事务,权限等待,Struts2的拦截器设计就是基于AOP的思想,是个比较经典的例子。
在不改变原有的逻辑的基础上,增加一些额外的功能。代理也是这个功能,读写分离也能用aop来做。
2. 原理图:
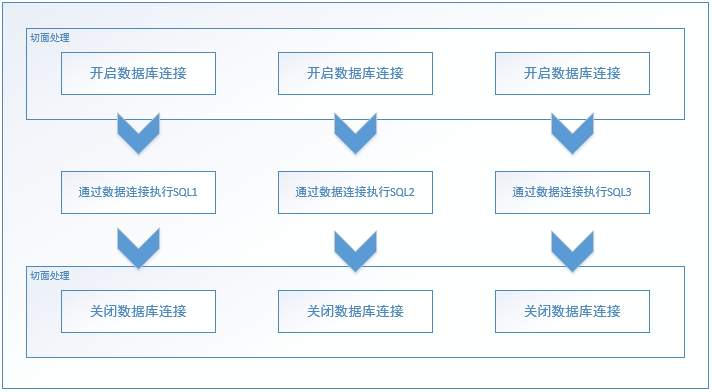
我们希望业务开发人员只关心中间部分,不再需要关系开启和关闭数据库连接的情况,同时也避免了代码重复和可能出现的问题。
3. 代码
public interface UserService { //删 void save(); String getStr(); void setStr(String str); }
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { private String str = "0"; public String getStr() { return str; } public void setStr(String str) { this.str = str; } @Override public void save() { System.out.println("--------- save --------------"); } }
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; /** * 自定义通知类 */ public class MyAdvice { //before 前置通知 在目标方法前调用 public void before() { System.out.println("before"); } //after 最终通知(后置通知)在目标方法后调用,无论是否出现异常都会执行 finally public void after() { System.out.println("after"); } //afterReturning 成功通知(后置通知)在目标方法执行后,并且执行成功,如果方法出现异常则不调用 public void afterReturning() { System.out.println("afterReturning"); } //afterThrowing 异常通知(后置通知)在目标方法执行出现异常的时候才会调用 public void afterThrowing() { System.out.println("afterThrowing"); } //around 环绕通知 需要我们手动调用目标方法,并且可以设置通知 public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { System.out.println("around before"); Object proceed = pjp.proceed(); System.out.println("around after"); return proceed; } }
import com.bing.aop.service.UserService; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import javax.annotation.Resource; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext_aop.xml") public class AopTest { @Resource(name="userService") UserService us; @Test public void Test2() { us.save(); } }
配置文件:文件名(applicationContext_aop.xml)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd"> <!-- 目标对象 --> <bean name="userService" class="com.bing.aop.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean> <!-- 通知对象 --> <bean name="myAdvice" class="com.bing.aop.MyAdvice"></bean> <aop:config> <!-- 切入点 expression 切入点表达式 可以配置要增强的方法 public void com.bing.aop.service.UserServiceImpl.save() * com.bing.aop.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..) id 就是唯一标识 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.bing.aop.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))" id="servicePc"/> <!-- 切面 通知+切入点 --> <aop:aspect ref="myAdvice"> <!-- 通知类型 --> <aop:before method="before" pointcut-ref="servicePc"/> <!-- 最终通知 后置通知 --> <aop:after method="after" pointcut-ref="servicePc"/> <!-- 成功通知 后置通知 --> <aop:after-returning method="afterReturning" pointcut-ref="servicePc"/> <!-- 异常通知 后置通知 --> <aop:after-throwing method="afterThrowing" pointcut-ref="servicePc"/> <!-- 环绕通知--> <aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="servicePc"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
运行结果:

到这里其实发现这个AOP没有什么实际用处,前后中间执行的东西都没有关系,并不能体现真正的AOP思想。
我们将上述代码修改一下:修改环绕通知的方法。
import com.bing.aop.service.UserService; import com.bing.aop.service.UserServiceImpl; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; /** * 自定义通知类 */ public class MyAdvice { //before 前置通知 在目标方法前调用 public void before() { System.out.println("before"); } //after 最终通知(后置通知)在目标方法后调用,无论是否出现异常都会执行 finally public void after() { System.out.println("after"); } //afterReturning 成功通知(后置通知)在目标方法执行后,并且执行成功,如果方法出现异常则不调用 public void afterReturning() { System.out.println("afterReturning"); } //afterThrowing 异常通知(后置通知)在目标方法执行出现异常的时候才会调用 public void afterThrowing() { System.out.println("afterThrowing"); } //around 环绕通知 需要我们手动调用目标方法,并且可以设置通知 public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { UserService userService = (UserServiceImpl)pjp.getTarget(); Object proceed = null; if("1".equals(userService.getStr()) || "setStr".equals(pjp.getSignature().getName())){ proceed = pjp.proceed(); } return proceed; } }
import com.bing.aop.service.UserService; import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import javax.annotation.Resource; @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration("classpath:applicationContext_aop.xml") public class AopTest { @Resource(name="userService") UserService us; @Test public void Test2() { System.out.println("设置前:------------Str == 0"); us.save(); us.setStr("1"); System.out.println("设置前:------------Str == 1"); us.save(); } }
然后将配置文件的其他通知都去掉:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-4.3.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop-4.3.xsd"> <!-- 目标对象 --> <bean name="userService" class="com.bing.aop.service.UserServiceImpl"></bean> <!-- 通知对象 --> <bean name="myAdvice" class="com.bing.aop.MyAdvice"></bean> <aop:config> <!-- 切入点 expression 切入点表达式 可以配置要增强的方法 public void com.bing.aop.service.UserServiceImpl.save() * com.bing.aop.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..) id 就是唯一标识 --> <aop:pointcut expression="execution(* com.bing.aop.service.*ServiceImpl.*(..))" id="servicePc"/> <!-- 切面 通知+切入点 --> <aop:aspect ref="myAdvice"> <!-- 环绕通知--> <aop:around method="around" pointcut-ref="servicePc"/> </aop:aspect> </aop:config> </beans>
运行效果:

把实体类和MyAdvice 结合起来,可以更加方便的写你想要处理的逻辑。
XML 用的越来越少了,现在大部分都使用注解了,下面是使用注解的Demo
import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; import org.springframework.context.annotation.EnableAspectJAutoProxy; @ComponentScan("com.hundsun.cop.aop") @Configuration @EnableAspectJAutoProxy public class AppConfig { }
import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.After; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterThrowing; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Aspect @Component public class MyAdvice { //设置切点 @Pointcut("execution(public * com.hundsun.cop.aop.UserService.*(..))") public void execution(){ } // 执行前 @Before("MyAdvice.execution()") public void before(){ } // 执行后 @After("MyAdvice.execution()") public void after() { System.out.println("after"); } //afterReturning 成功通知(后置通知)在目标方法执行后,并且执行成功,如果方法出现异常则不调用 @AfterReturning("MyAdvice.execution()") public void afterReturning() { System.out.println("afterReturning"); } //afterThrowing 异常通知(后置通知)在目标方法执行出现异常的时候才会调用 @AfterThrowing("MyAdvice.execution()") public void afterThrowing() { System.out.println("afterThrowing"); } //around 环绕通知 需要我们手动调用目标方法,并且可以设置通知 @Around("MyAdvice.execution()") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { System.out.println("around before"); Object proceed = pjp.proceed(); System.out.println("around after"); return proceed; } }
public interface UserService { void save(); String getStr(); void setStr(String str); }
@Component public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService { private String str = "0"; public String getStr() { return str; } public void setStr(String str) { this.str = str; } @Override public void save() { System.out.println("--------- save --------------"); } }
import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext annotationConfigApplicationContext = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class); UserService userService = annotationConfigApplicationContext.getBean(UserService.class); userService.save(); } }
运行结果

通过注解来表示切点的方式:
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j; import org.aspectj.lang.ProceedingJoinPoint; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Around; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect; import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Slf4j @Aspect @Component public class ExecTimeAdvice { //设置切点(设置成注解类,后面需要的地方加上注解即可) @Pointcut("@annotation(com.hundsun.o45.repeat.advice.ExecTimeMonitor)") public void execution(){ } @Around("ExecTimeAdvice.execution()") public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable { System.out.println("AOP测试"); return null; } }
注解:
import java.lang.annotation.Documented; import java.lang.annotation.ElementType; import java.lang.annotation.Retention; import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy; import java.lang.annotation.Target; @Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD}) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented public @interface ExecTimeMonitor { }
不喜欢夸夸奇谈,实战才是真理。代码是说明原理的最可靠的方式。