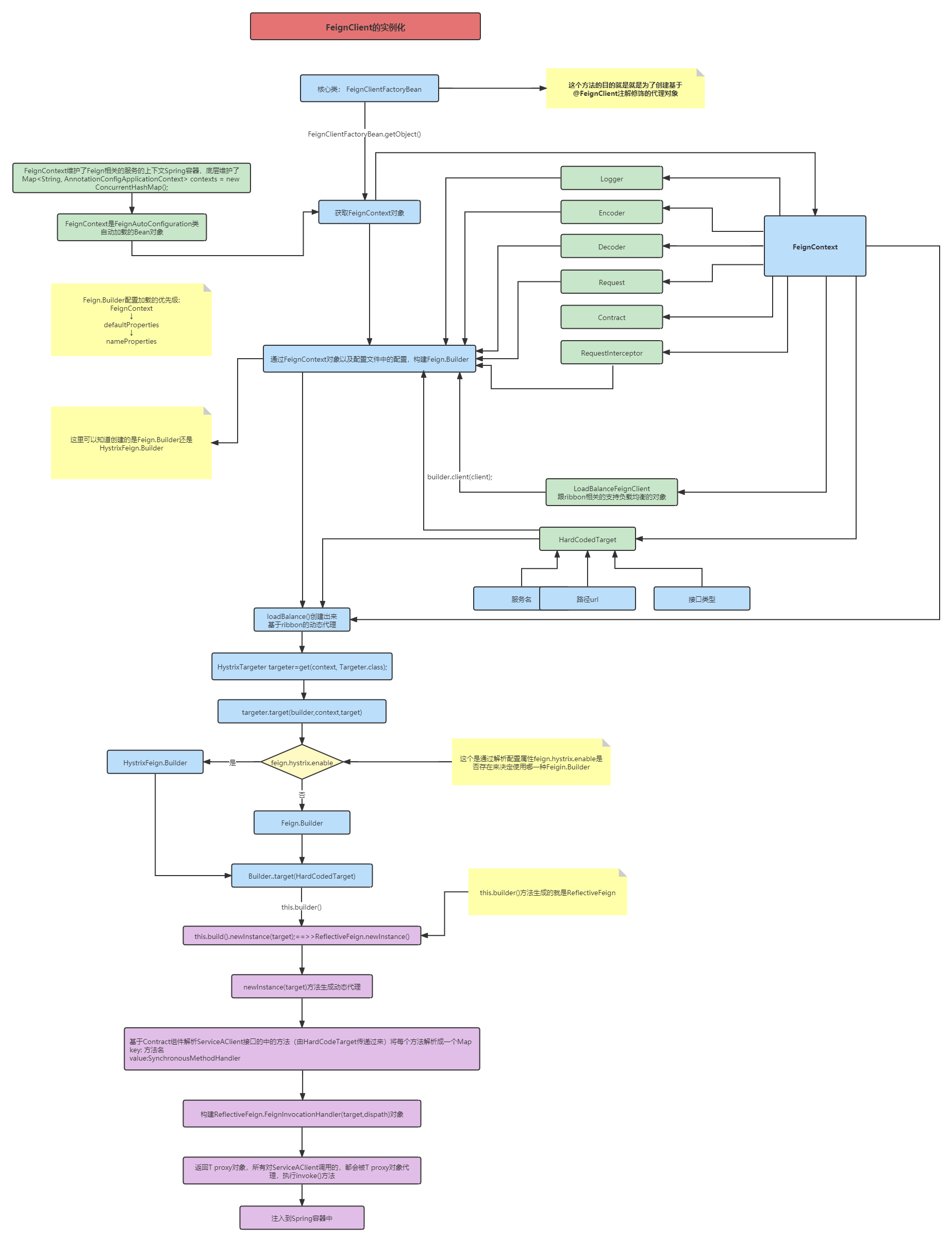
FeignClient实例化的主要目的是为了项目中使用@AutoWired 注解注入的被@FeignClient修饰的接口的实现类,显然这里是通过动态代理的方式生成接口的动态代理对象,将生成动态代理对象放入Spring容器中
这里的触发点也就是在FeignClientFactoryBean的getObject()方法中,
一.源码分析入口
1.FeignClientFactoryBean.getObject()
//获取@FeignClient修饰接口的代理对象,注入到Spring容器中 public Object getObject() throws Exception { return getTarget(); }
2.进入getTarget()方法中
<T> T getTarget() {
//从Spring容器中,获取FeignContext上下文的容器,该容器是和Feign相关服务相关的容器,
//每个服务都对应了一个了一个FeignContext,这个FeignContext主要是封装了FeignClient相关的配置信息;
//FeignContext的初始化操作在@FeignAutoConfiguration中,主要是加载了FeignClientSpecification(注解中的配置信息)和FeignClientsConfiguration(默认的组件Encoder,Decoder,等等)
//因此 FeignContext中具备和动态代理Bean相关的很多属性
FeignContext context = this.applicationContext.getBean(FeignContext.class);
//通过FeignContext上下文获取Feign.Builder对象,FeignBuilder对象也就是创建Feign的构建者对象,源码解析,参考 2.1 Feign.Builder builder = feign(context); if (!StringUtils.hasText(this.url)) { if (!this.name.startsWith("http")) { this.url = "http://" + this.name; } else { this.url = this.name; } this.url += cleanPath();
//通过HardCodedTarget对象,Feign.Builder,上下文对象构建LoadBalanceFeignClient对象(负载均衡的FeignClient对象) 参考2.2 return (T) loadBalance(builder, context,
//将1.name(服务名) 2.url(http://服务名) 3.@FeignClient修饰的接口类型构建 HardCodedTarget对象
new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type, this.name, this.url));
}
if (StringUtils.hasText(this.url) && !this.url.startsWith("http")) { this.url = "http://" + this.url; } String url = this.url + cleanPath(); Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class); if (client != null) { if (client instanceof LoadBalancerFeignClient) { // not load balancing because we have a url, // but ribbon is on the classpath, so unwrap client = ((LoadBalancerFeignClient) client).getDelegate(); } if (client instanceof FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) { // not load balancing because we have a url, // but Spring Cloud LoadBalancer is on the classpath, so unwrap client = ((FeignBlockingLoadBalancerClient) client).getDelegate(); } builder.client(client); } Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class); return (T) targeter.target(this, builder, context, new HardCodedTarget<>(this.type, this.name, url)); }
2.1创建 Feign.Builder 的过程如下代码
protected Feign.Builder feign(FeignContext context) { FeignLoggerFactory loggerFactory = get(context, FeignLoggerFactory.class); Logger logger = loggerFactory.create(this.type); // @formatter:off //从上下文中获取日志工厂,Encoder,Decoder,Contract组件,通过这些组件封装到Feign.Builder中,注意:这里如果配置了feign.hystrix.enable=true,
//则返回的是HystrixFeign.builder,否则为Feign.Builder
Feign.Builder builder = get(context, Feign.Builder.class) // required values .logger(logger) .encoder(get(context, Encoder.class)) .decoder(get(context, Decoder.class)) .contract(get(context, Contract.class)); // @formatter:on // 从配置属性FeignClientProperties中加载配置,如果存在用户属性,覆盖默认的配置 源码参考2.1.1 configureFeign(context, builder); return builder; }
2.1.1 configureFeign()配置Feign.Builder,同时指定上下文环境
protected void configureFeign(FeignContext context, Feign.Builder builder) {
//从上下文中获取配置属性相关的类FeignClientProperties FeignClientProperties properties = this.applicationContext .getBean(FeignClientProperties.class);
//如果属性不为空 if (properties != null) {
//判断默认配置文件的加载顺序 全局上下文->默认上下文->指定FeignClient上下文 if (properties.isDefaultToProperties()) {
//读取全局上下文的配置 configureUsingConfiguration(context, builder);
//先读取默认的配置 configureUsingProperties( properties.getConfig().get(properties.getDefaultConfig()), builder);
//再读取FeignClient上下文中自定义的配置 configureUsingProperties(properties.getConfig().get(this.contextId), builder); } else {
//非默认的配置文件加载顺序 默认上下文->指定FeignClient上下文->全局上下文顺序加载 configureUsingProperties( properties.getConfig().get(properties.getDefaultConfig()), builder); configureUsingProperties(properties.getConfig().get(this.contextId), builder); configureUsingConfiguration(context, builder); } } else {
//如果没有配置指定的用户属性feign.client ,则直接使用全局的上下文环境 configureUsingConfiguration(context, builder); } }
2.2 loadBalance() 方法
protected <T> T loadBalance(Feign.Builder builder, FeignContext context, HardCodedTarget<T> target) {
//从上下文中获取LoadBalanceFeignClient对象 Client client = getOptional(context, Client.class);
//将LoadBalanceFeignClient对象放入Feign.builder中 if (client != null) { builder.client(client);
//从上下文中获取Target对象 Targeter targeter = get(context, Targeter.class);
//通过Target.target()方法,获取Feign动态代理的实例 这段代码很重要,见2.2.1 return targeter.target(this, builder, context, target); } throw new IllegalStateException( "No Feign Client for loadBalancing defined. Did you forget to include spring-cloud-starter-netflix-ribbon?"); }
2.2.1 targeter.target()
@Override public <T> T newInstance(Target<T> target) {
Map<String, MethodHandler> nameToHandler = targetToHandlersByName.apply(target);
//将@FeignClient中的方法名和SynchronizedMethodHandler映射 Map<Method, MethodHandler> methodToHandler = new LinkedHashMap<Method, MethodHandler>(); List<DefaultMethodHandler> defaultMethodHandlers = new LinkedList<DefaultMethodHandler>();
//通过HardCodeTarget(具有服务名,http+服务名,接口类型),获取接口中的方法列表
for (Method method : target.type().getMethods()) { if (method.getDeclaringClass() == Object.class) { continue; } else if(Util.isDefault(method)) { DefaultMethodHandler handler = new DefaultMethodHandler(method); defaultMethodHandlers.add(handler); methodToHandler.put(method, handler); } else { methodToHandler.put(method, nameToHandler.get(Feign.configKey(target.type(), method))); } }
//这里生成的是FeignInvocationHandler(实现了InvocationHandler),里面重写了invoke()方法,也就是Feign发送http请求的逻辑,在下一部分,Feign源码分析三说明
//也就是说在HardCodeTarget中对应的接口类型中的方法,都会找到对应的SynchronizeMethodHanlder,最终执行到FeignInvocationHanlder里面的invoke()方法 InvocationHandler handler = factory.create(target, methodToHandler);
//基于JDK的动态代理生成动态代理的对象(动态代理三要素,类加载器,实现InvocationHandler的接口实现,被代理的类型) T proxy = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(target.type().getClassLoader(), new Class<?>[]{target.type()}, handler); for(DefaultMethodHandler defaultMethodHandler : defaultMethodHandlers) { defaultMethodHandler.bindTo(proxy); } return proxy; }
二.流程图