一:优化的概述
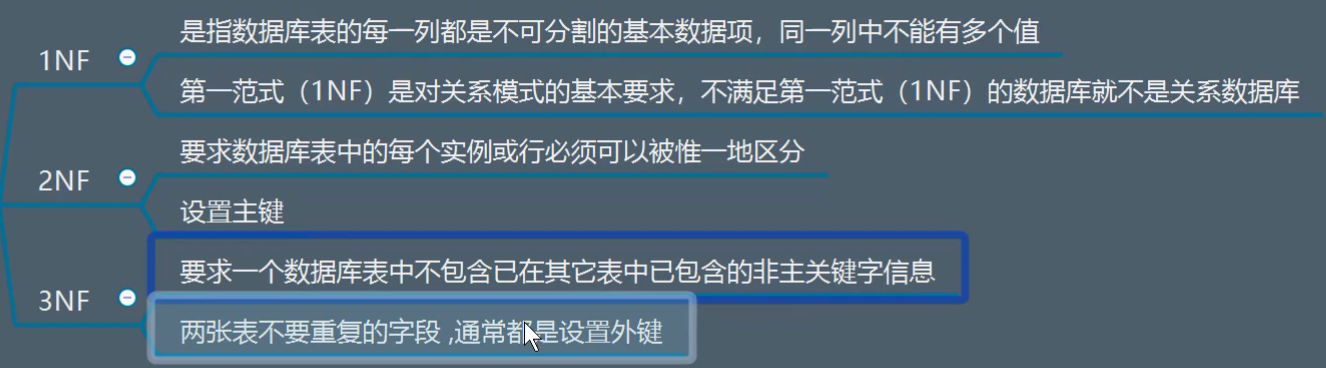
1.表的设计准则
满足三范式
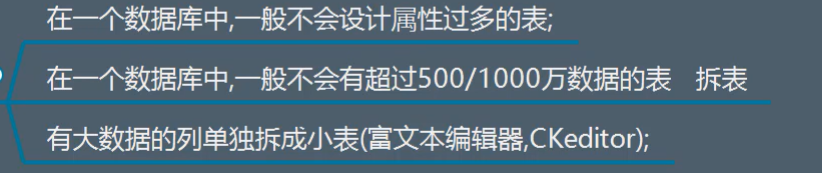
大表拆小标
2.dql的执行过程
可以参考:https://www.cnblogs.com/juncaoit/p/13269848.html

3.sql优化器

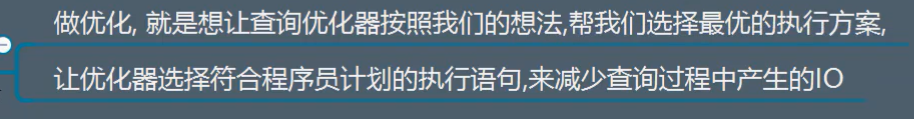
4.做优化做的是什么
二:Explain
1.查询执行计划

2.作用

3.使用方法
explain sql
4.sql
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `customer`;
CREATE TABLE `customer` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of customer
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `customer` VALUES ('1', 'zs');
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for employee
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `employee`;
CREATE TABLE `employee` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`dep_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`salary` decimal(10,2) DEFAULT NULL,
`cus_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=109 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of employee
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES ('1', '鲁班', '1', '10', '1000.00', '1');
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES ('2', '后裔', '1', '20', '2000.00', '1');
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES ('3', '孙尚香', '1', '20', '2500.00', '1');
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES ('4', '凯', '4', '20', '3000.00', '1');
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES ('5', '典韦', '4', '40', '3500.00', '2');
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES ('6', '貂蝉', '6', '20', '5000.00', '1');
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES ('7', '孙膑', '6', '50', '5000.00', '1');
INSERT INTO `employee` VALUES ('8', '蔡文姬', '30', '35', '4000.00', '1');
-- ----------------------------
-- Table structure for department
-- ----------------------------
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `department`;
CREATE TABLE `department` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`deptName` varchar(30) DEFAULT NULL,
`address` varchar(40) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=6 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
-- ----------------------------
-- Records of department
-- ----------------------------
INSERT INTO `department` VALUES ('1', '研发部(RD)', '2层');
INSERT INTO `department` VALUES ('2', '人事部(HR)', '3层');
INSERT INTO `department` VALUES ('3', '市场部(MK)', '4层');
INSERT INTO `department` VALUES ('4', '后勤部(MIS)', '5层');
INSERT INTO `department` VALUES ('5', '财务部(FD)', '6层');
5.explain的执行id的分析
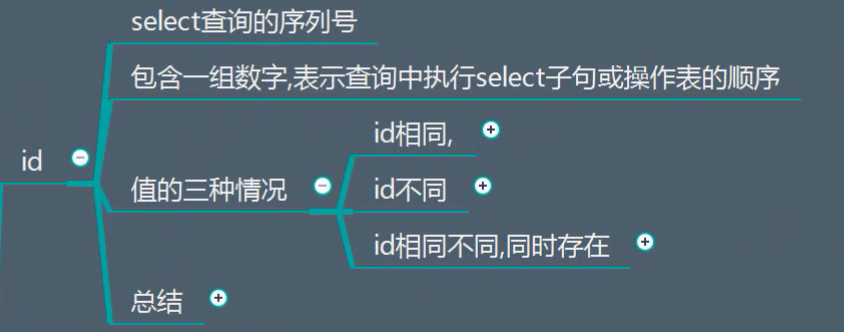
id相同:
explain select * from employee e, department d, customer c where e.dep_id = d.id and e.cus_id = c.id;
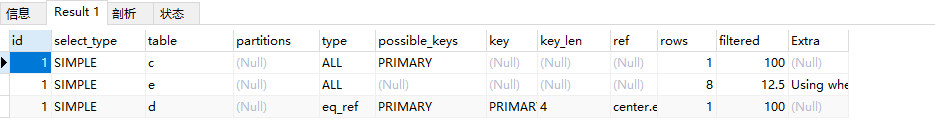
说明:执行的顺序是,c,e,d表。查询顺序从上往下
id不同:
explain select * from department d where id = ( select id from employee where id = (select id from customer where id = 1) )
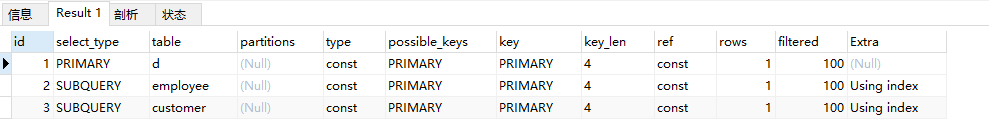
说明:先执行customer,然后执行employee,然后d。查询顺序从大到小。
id有相同,有不同
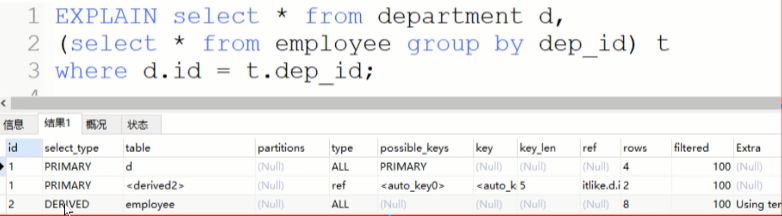
explain select * from department d, (select * from employee group by id) t where d.id = t.dep_id
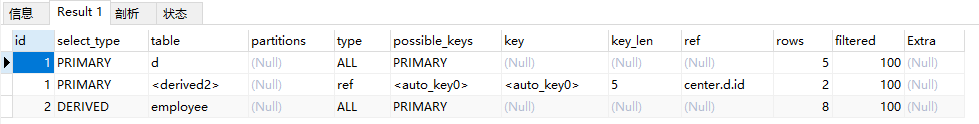
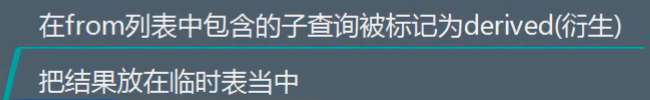
6.select_type

simple:

parimary:

derived:
7.table
这一行数据使用的是哪一张表,看6的最后一张图就可以了
8.partitions

9.type
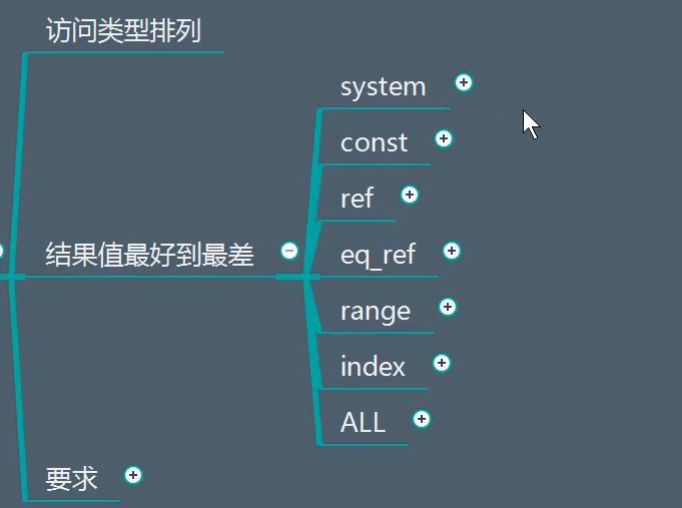
system:
表中有一行记录,一次性就找到了
const:
通过索引一次就找到了,用于primary或者unique索引,直接查询主键或者唯一索引
因为只匹配一行数据
explain select * from department where id =2

eq_ref:
唯一性索引扫描
对于魅影索引建,表中只有一条记录与之匹配
常见于主键或者伪意见索引扫描
explain select * from department d , employee e where e.id = d.id
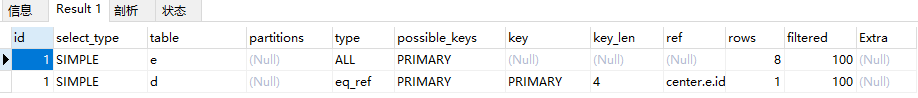
ref:
非唯一索引扫描,返回匹配某个单独值得所有行
本质上也是一种索引访问
返回所有匹配某个单独值得行
可能会找到多个符合条件的行
alter table employee add index idx_depId(dep_id); explain select d.id from department d , employee e where e.dep_id = d.id;
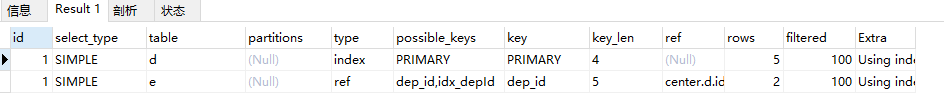
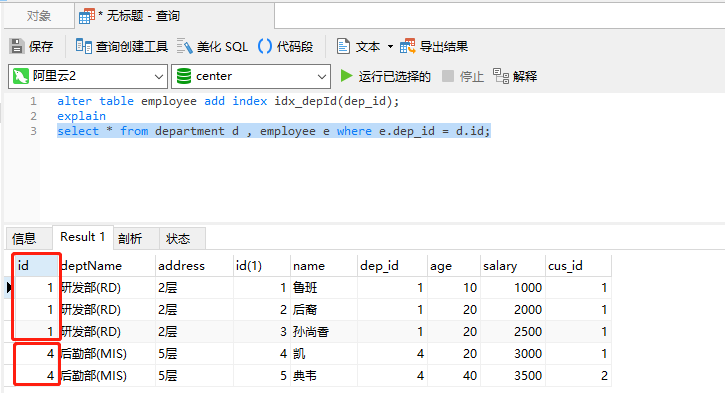
range:
explain select * from department d where id > 2

index:
只有索引列查询
explain select id from department d ;

10.possible_keys与key
可能使用的索引,实际使用的索引
explain select dep_id from employee e ;

explain select * from employee e, department d where e.dep_id = d.id ;
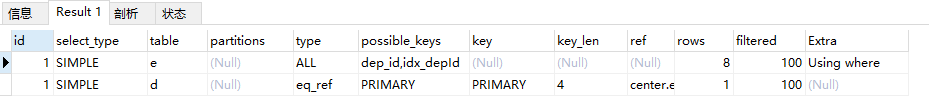
11.索引长度key_len
表示索引中使用的字节数,可通过该列计算查询中使用的索引长度
12.ref
索引是否被引用到,引用了哪些索引
EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employee e, department d WHERE e.dep_id = d.id;

EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM employee e, department d , customer c WHERE e.dep_id = d.id and e.cus_id = c.id and e.name = "鲁班"
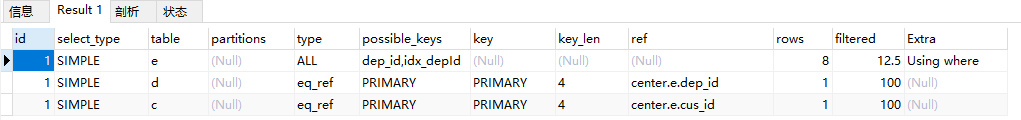
13.rows与filtered
rows:每个表被优化器查询过
filtered:满足查询条件的比例
14.Extra
额外信息
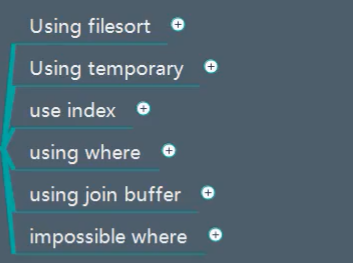
Using filesort:产生了文件排序
Using temporary:使用了临时表
useing join buffer:使用了连接缓存
impossible where:永远是一个false,说明条件是有问题的