本篇研究下SpringMVC是怎么处理一条请求的
一 doDispatch 源码分析
protected void doDispatch(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws Exception { HttpServletRequest processedRequest = request; HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler = null; boolean multipartRequestParsed = false; WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); try { ModelAndView mv = null; Exception dispatchException = null; try { processedRequest = checkMultipart(request); multipartRequestParsed = (processedRequest != request); // Determine handler for the current request. mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);//1 获取HandlerExecutionChain if (mappedHandler == null || mappedHandler.getHandler() == null) { noHandlerFound(processedRequest, response); return; } // Determine handler adapter for the current request. HandlerAdapter ha = getHandlerAdapter(mappedHandler.getHandler());//2 获取HandlerAdapter // Process last-modified header, if supported by the handler. String method = request.getMethod(); boolean isGet = "GET".equals(method); if (isGet || "HEAD".equals(method)) { long lastModified = ha.getLastModified(request, mappedHandler.getHandler()); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Last-Modified value for [" + getRequestUri(request) + "] is: " + lastModified); } if (new ServletWebRequest(request, response).checkNotModified(lastModified) && isGet) { return; } } if (!mappedHandler.applyPreHandle(processedRequest, response)) { return; } // Actually invoke the handler. mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());//3 实际去执行 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return; } applyDefaultViewName(processedRequest, mv); mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv);//拦截器在这里执行 }
主要分为三部分
1 获取HandlerExecutionChain
2 获取HandlerAdapter
3 实际去执行
二 DispatcherServlet.getHandler
protected HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { for (HandlerMapping hm : this.handlerMappings) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace( "Testing handler map [" + hm + "] in DispatcherServlet with name '" + getServletName() + "'"); } HandlerExecutionChain handler = hm.getHandler(request); if (handler != null) { return handler; } } return null; }
AbstractHandlerMapping.getHandler
public final HandlerExecutionChain getHandler(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { Object handler = getHandlerInternal(request);//主要的逻辑就是获取 HandlerMethod if (handler == null) { handler = getDefaultHandler(); } if (handler == null) { return null; } // Bean name or resolved handler? if (handler instanceof String) { String handlerName = (String) handler; handler = getApplicationContext().getBean(handlerName); } HandlerExecutionChain executionChain = getHandlerExecutionChain(handler, request);//HandlerExecutionChain 就是HandlerMethod加上一些interceptor if (CorsUtils.isCorsRequest(request)) { CorsConfiguration globalConfig = this.corsConfigSource.getCorsConfiguration(request); CorsConfiguration handlerConfig = getCorsConfiguration(handler, request); CorsConfiguration config = (globalConfig != null ? globalConfig.combine(handlerConfig) : handlerConfig); executionChain = getCorsHandlerExecutionChain(request, executionChain, config); } return executionChain; }
protected HandlerMethod getHandlerInternal(HttpServletRequest request) throws Exception { String lookupPath = getUrlPathHelper().getLookupPathForRequest(request); if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Looking up handler method for path " + lookupPath); } this.mappingRegistry.acquireReadLock(); try { HandlerMethod handlerMethod = lookupHandlerMethod(lookupPath, request);//该方法逻辑不复杂,但是实现很复杂,原因就是url可能含有通配符,
所以该方法用了大量的代码解决如何寻找最匹配的url的问题
最终找到HandlerMethod if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { if (handlerMethod != null) { logger.debug("Returning handler method [" + handlerMethod + "]"); } else { logger.debug("Did not find handler method for [" + lookupPath + "]"); } } return (handlerMethod != null ? handlerMethod.createWithResolvedBean() : null); } finally { this.mappingRegistry.releaseReadLock(); } }
这样就找到了 HandlerExecutionChain
三 DispatcherServlet.getHandlerAdapter
拿到HandlerAdapter就会去执行,这里我们先看是怎么拿到的HandlerAdapter,具体逻辑我会再开一篇介绍
protected HandlerAdapter getHandlerAdapter(Object handler) throws ServletException { for (HandlerAdapter ha : this.handlerAdapters) { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("Testing handler adapter [" + ha + "]"); } if (ha.supports(handler)) {//这里的handler是一个HandlerMethod,就是要调用的方法 return ha; } } throw new ServletException("No adapter for handler [" + handler + "]: The DispatcherServlet configuration needs to include a HandlerAdapter that supports this handler"); }
这里的 handlerAdapters 有三种,都是系统默认初始化放进去的,处理HandlerMethod的第一种RequestMappingHandlerAdapter就负责处理
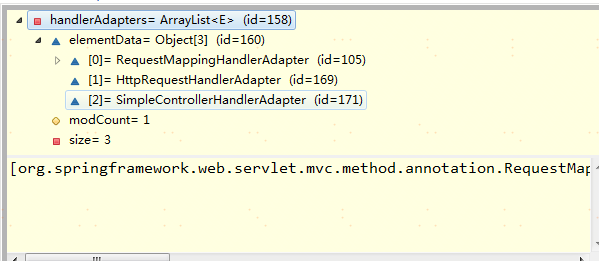
然后就是执行了
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
四 总结
总结一下就是,请求进来->根据url先找到MethodHandler->构造出RequestExecutionChain ->获取RequestMappingHandlerAdapter->执行方法->结果处理
在这个流程里,有两个环节没有细讲
1 RequestMappingHandlerAdapter是神马东西
2 结果处理比如@ResponseBody是怎样的原理
这两个我都会单独讲解