一、什么是组合模式
Composite模式也叫组合模式,是构造型的设 计模式之一。通过递归手段来构造树形的对象结 构,并可以通过一个对象来访问整个对象树。
二、组合模式的结构
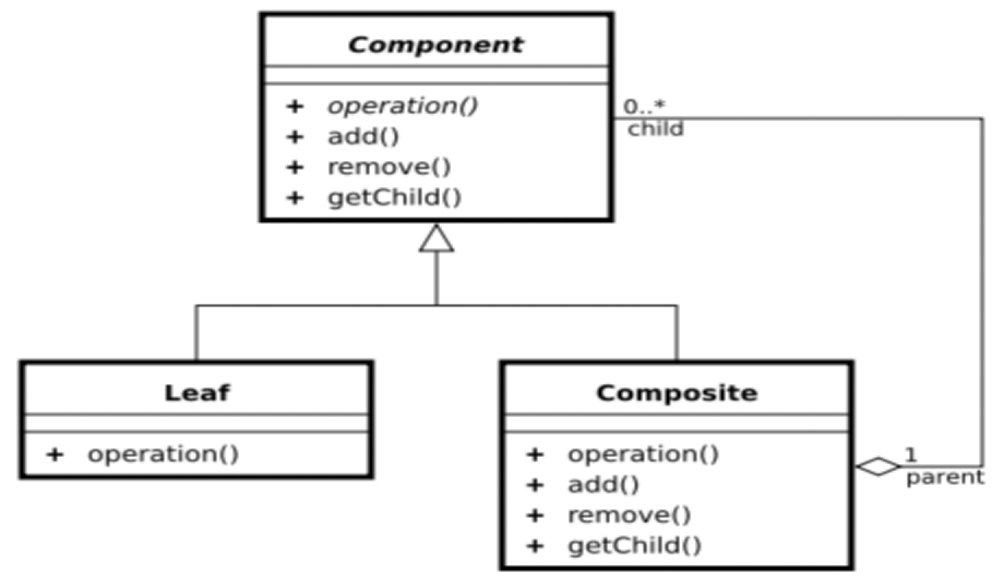
三、组合模式的角色和职责
Component (树形结构的节点抽象)
- 为所有的对象定义统一的接口(公共属性,行为等的定义)
- 提供管理子节点对象的接口方法
- [可选]提供管理父节点对象的接口方法
Leaf (树形结构的叶节点)
Component的实现子类
Composite(树形结构的枝节点)
Component的实现子类
文件和目录的父类
1 import java.util.List; 2 3 /* 4 * 文件节点抽象(是文件和目录的父类) 5 */ 6 public interface IFile { 7 8 //显示文件或者文件夹的名称 9 public void display(); 10 11 //添加 12 public boolean add(IFile file); 13 14 //移除 15 public boolean remove(IFile file); 16 17 //获得子节点 18 public List<IFile> getChild(); 19 }
文件
1 import java.util.List; 2 3 //文件 4 public class File implements IFile { 5 private String name; 6 7 public File(String name) { 8 this.name = name; 9 } 10 11 public void display() { 12 System.out.println(name); 13 } 14 15 public List<IFile> getChild() { 16 return null; 17 } 18 19 public boolean add(IFile file) { 20 return false; 21 } 22 23 public boolean remove(IFile file) { 24 return false; 25 } 26 }
文件夹
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.List; 3 4 //文件夹 5 public class Folder implements IFile{ 6 private String name; 7 private List<IFile> children; 8 9 public Folder(String name) { 10 this.name = name; 11 children = new ArrayList<IFile>(); 12 } 13 14 public void display() { 15 System.out.println(name); 16 } 17 18 public List<IFile> getChild() { 19 return children; 20 } 21 22 public boolean add(IFile file) { 23 return children.add(file); 24 } 25 26 public boolean remove(IFile file) { 27 return children.remove(file); 28 } 29 }
测试
1 import java.util.List; 2 3 public class MainClass { 4 public static void main(String[] args) { 5 //C盘 6 Folder rootFolder = new Folder("C:"); 7 //beifeng目录 8 Folder beifengFolder = new Folder("beifeng"); 9 //beifeng.txt文件 10 File beifengFile = new File("beifeng.txt"); 11 12 rootFolder.add(beifengFolder); 13 rootFolder.add(beifengFile); 14 15 //ibeifeng目录 16 Folder ibeifengFolder = new Folder("ibeifeng"); 17 File ibeifengFile = new File("ibeifeng.txt"); 18 beifengFolder.add(ibeifengFolder); 19 beifengFolder.add(ibeifengFile); 20 21 Folder iibeifengFolder = new Folder("iibeifeng"); 22 File iibeifengFile = new File("iibeifeng.txt"); 23 ibeifengFolder.add(iibeifengFolder); 24 ibeifengFolder.add(iibeifengFile); 25 26 displayTree(rootFolder,0); 27 28 } 29 30 public static void displayTree(IFile rootFolder, int deep) { 31 for(int i = 0; i < deep; i++) { 32 System.out.print("--"); 33 } 34 //显示自身的名称 35 rootFolder.display(); 36 //获得子树 37 List<IFile> children = rootFolder.getChild(); 38 //遍历子树 39 for(IFile file : children) { 40 if(file instanceof File) { 41 for(int i = 0; i <= deep; i++) { 42 System.out.print("--"); 43 } 44 file.display(); 45 } else { 46 displayTree(file,deep + 1); 47 } 48 } 49 } 50 }