稳定的算法用于对象排序
插入与归并等,稳定算法用于对象排序
插入排序
package com.m.algorithm;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Test {
/**
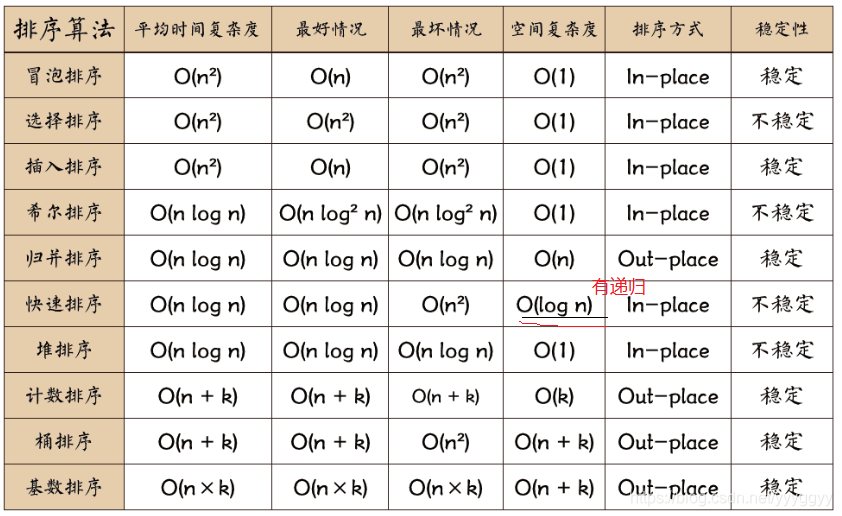
深入学习排序算法的思路
* 冒泡 选择
*
* 插入(二分) O(n^2) 归并(多路)
*
* 希尔 堆排 快排
*
* 计数 桶排 基数
*
*
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = { 64, 76, 36, 34, 6, 2, 74, 23 };
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
insertSort(arr);
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis()-start);
}
public static void insertSort(int[] arr1) {
// int[] arr1 = { 1, 3, 5, -2 };
for (int i = 0; i < arr1.length-1; i++) {
int end = i+1;
while(end>0 && arr1[end] < arr1[end-1]) {
int t = arr1[end];
arr1[end] = arr1[end-1];
arr1[end-1] = t;
end--;
}
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr1));
}
}
归并排序
package com.m.algorithm;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Random;
public class Test {
private List<Integer> arrayTemp;
public Test(List<Integer> arrayTemp) {
this.arrayTemp = arrayTemp;
}
public void mergeSort(List<Integer> arrayList,int left,int right) {
//1、
if(left < right) {
int mid = left + (right-left)/2;
//左分
mergeSort(arrayList, left, mid);
//右分
mergeSort(arrayList, mid+1, right);
//合并
merge(arrayList,left,mid,right);
}
}
public void merge(List<Integer> arrayList,int left,int mid,int right) {
int index = 0;
int i = left;
int j = mid+1;
while(i<=mid && j<=right) {
if(arrayList.get(i) < arrayList.get(j)) {
this.arrayTemp.set(index++, arrayList.get(i++));
}else {
this.arrayTemp.set(index++, arrayList.get(j++));
}
}
while(i<=mid) {
this.arrayTemp.set(index++, arrayList.get(i++));
}
while(j<=right) {
this.arrayTemp.set(index++, arrayList.get(j++));
}
index = 0;
while(left <= right) {
arrayList.set(left++, this.arrayTemp.get(index++));
}
}
}
插入与归并的JDK的应用
归并的应用-对象排序
Arrays.sort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> c)的JDK源码 ;
public static <T> void sort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> c) {
if (c == null) {
sort(a);
} else {
if (LegacyMergeSort.userRequested)
legacyMergeSort(a, c);
else
TimSort.sort(a, 0, a.length, c, null, 0, 0);
}
}
/** To be removed in a future release. */
private static <T> void legacyMergeSort(T[] a, Comparator<? super T> c) {
T[] aux = a.clone();
if (c==null)
mergeSort(aux, a, 0, a.length, 0);
else
mergeSort(aux, a, 0, a.length, 0, c);
}
TimSort.sort(a, 0, a.length, c, null, 0, 0)的源码
static <T> void sort(T[] a, int lo, int hi, Comparator<? super T> c,
T[] work, int workBase, int workLen) {
assert c != null && a != null && lo >= 0 && lo <= hi && hi <= a.length;
int nRemaining = hi - lo;
if (nRemaining < 2)
return; // Arrays of size 0 and 1 are always sorted
// If array is small, do a "mini-TimSort" with no merges
if (nRemaining < MIN_MERGE) {
int initRunLen = countRunAndMakeAscending(a, lo, hi, c);
binarySort(a, lo, hi, lo + initRunLen, c);
return;
}
/**
* March over the array once, left to right, finding natural runs,
* extending short natural runs to minRun elements, and merging runs
* to maintain stack invariant.
*/
TimSort<T> ts = new TimSort<>(a, c, work, workBase, workLen);
int minRun = minRunLength(nRemaining);
do {
// Identify next run
int runLen = countRunAndMakeAscending(a, lo, hi, c);
// If run is short, extend to min(minRun, nRemaining)
if (runLen < minRun) {
int force = nRemaining <= minRun ? nRemaining : minRun;
binarySort(a, lo, lo + force, lo + runLen, c);
runLen = force;
}
// Push run onto pending-run stack, and maybe merge
ts.pushRun(lo, runLen);
ts.mergeCollapse();
// Advance to find next run
lo += runLen;
nRemaining -= runLen;
} while (nRemaining != 0);
// Merge all remaining runs to complete sort
assert lo == hi;
ts.mergeForceCollapse();
assert ts.stackSize == 1;
}