在开始介绍 scrapy 的去重之前,先想想我们是怎么对 requests 对去重的。
requests 只是下载器,本身并没有提供去重功能。所以我们需要自己去做。
很典型的做法是事先定义一个去重队列,判断抓取的 url 是否在其中,如
crawled_urls = set() def check_url(url): if url not in crawled_urls: return True return False此时的集合是保存在内存中的,随着爬虫抓取内容变多,该集合会越来越大,有什么办法呢?
接着往下看,你会知道的
scrapy 的去重
scrapy 对 request 不做去重很简单,只需要在 request 对象中设置
dont_filter为 True,如yield Request('https://www.baidu.com/?w=python',dont_filter=True)看看源码是如何做的
_fingerprint_cache = weakref.WeakKeyDictionary() def request_fingerprint(request, include_headers=None): if include_headers: include_headers = tuple(to_bytes(h.lower()) for h in sorted(include_headers)) cache = _fingerprint_cache.setdefault(request, {}) if include_headers not in cache: fp = hashlib.sha1() fp.update(to_bytes(request.method)) fp.update(to_bytes(canonicalize_url(request.url))) fp.update(request.body or b'') if include_headers: for hdr in include_headers: if hdr in request.headers: fp.update(hdr) for v in request.headers.getlist(hdr): fp.update(v) cache[include_headers] = fp.hexdigest() return cache[include_headers]翻译
返回请求指纹 请求指纹是唯一标识请求指向的资源的哈希。 例如,请使用以下两个网址: http://www.example.com/query?id=111&cat=222 http://www.example.com/query?cat=222&id=111 即使这两个不同的 URL 都指向相同的资源并且是等价的(即,它们应该返回相同的响应) 另一个例子是用于存储会话 ID 的 cookie。 假设以下页面仅可供经过身份验证的用户访问: http://www.example.com/members/offers.html 许多网站使用 cookie 来存储会话 ID,这会随机添加字段到 HTTP 请求,因此在计算时应该被忽略指纹。 因此,计算时默认会忽略 request headers。 如果要包含特定 headers,请使用 include_headers 参数,它是要计算 Request headers 的列表其实就是说:scrapy 使用 sha1 算法,对每一个 request 对象加密,生成 40 位十六进制数
我们看源码,重点是以下三行
fp = hashlib.sha1() fp.update(to_bytes(request.method)) fp.update(to_bytes(canonicalize_url(request.url))) fp.update(request.body or b'')如果没有自定义 headers,只计算 method、url、和二进制 body,我们来计算下,代码
print(request_fingerprint(scrapy.Request('http://www.example.com/query?id=111&cat=222'))) print(request_fingerprint(scrapy.Request('http://www.example.com/query?cat=222&id=111'))) print(request_fingerprint(scrapy.Request('http://www.example.com/query')))输出
fad8cefa4d6198af8cb1dcf46add2941b4d32d78 fad8cefa4d6198af8cb1dcf46add2941b4d32d78 b64c43a23f5e8b99e19990ce07b75c295165a923可以看到第一条和第二条的密码是一样的,是因为调用了
canonicalize_url方法scrapy 的去重默认会保存到内存中,如果任务重启,会导致内存中所有去重队列消失
scrapy-redis 去重
scrapy-redis 重写了 scrapy 的调度器和去重队列,所以需要在 settings 中修改如下两列
# Enables scheduling storing requests queue in redis. SCHEDULER = "scrapy_redis.scheduler.Scheduler" # Ensure all spiders share same duplicates filter through redis. DUPEFILTER_CLASS = "scrapy_redis.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter"一般我们会在 redis 中看到这两个,分别是去重队列和种子链接
源码
def request_seen(self, request): """Returns True if request was already seen. Parameters ---------- request : scrapy.http.Request Returns ------- bool """ fp = self.request_fingerprint(request) # This returns the number of values added, zero if already exists. added = self.server.sadd(self.key, fp) return added == 0 def request_fingerprint(self, request): """Returns a fingerprint for a given request. Parameters ---------- request : scrapy.http.Request Returns ------- str """ return request_fingerprint(request)首先拿到 scrapy.http.Request 会先调用 self.request_fingerprint 去计算,也就是 scrapy 的 sha1 算法去加密,然后会向 redis 中添加该指纹。
该函数的作用是:计算该请求指纹,添加到 redis 的去重队列,如果已经存在该指纹,返回 True。
我们可以看到,只要有在 settings 中添加
DUPEFILTER_CLASS = "scrapy_redis.dupefilter.RFPDupeFilter",就会在 redis 中新加一列去重队列,说下这样做的优劣势:
- 优点:将内存中的去重队列序列化到 redis 中,就算爬虫重启或者关闭,也可以再次使用,你可以使用 SCHEDULER_PERSIST 来调整缓存
- 缺点:如果你需要去重的指纹过大,redis 占用空间过大。8GB=8589934592Bytes,平均一个去重指纹 40Bytes,约可以存储 214,748,000 个(2 亿)。所以在做关系网络爬虫中,序列化到 redis 中可能并不是很好,保存在内存中也不好,所以就产生了布隆过滤器。
自定义过滤
如果想自定义 Filter,可以通过继承,重写 request_seen
from scrapy.dupefilter import RFPDupeFilter class SeenURLFilter(RFPDupeFilter): """A dupe filter that considers the URL""" def __init__(self, path=None): self.urls_seen = set() RFPDupeFilter.__init__(self, path) def request_seen(self, request): if request.url in self.urls_seen: return True else: self.urls_seen.add(request.url) # 修改settings设置 DUPEFILTER_CLASS ='scraper.custom_filters.SeenURLFilter'
布隆过滤器
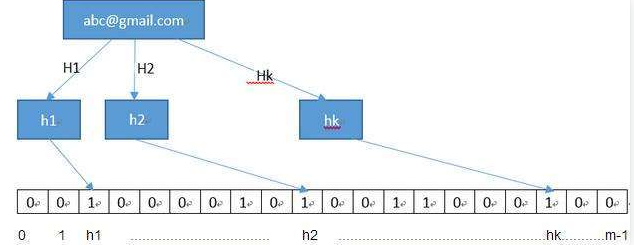
bloomfilter:是一个通过多哈希函数映射到一张表的数据结构,能够快速的判断一个元素在一个集合内是否存在,具有很好的空间和时间效率。(典型例子,爬虫 url 去重)
原理:
BloomFilter 会开辟一个m位的bitArray(位数组),开始所有数据全部置 0 。当一个元素过来时,能过多个哈希函数(h1,h2,h3....)计算不同的在哈希值,并通过哈希值找到对应的bitArray下标处,将里面的值 0 置为 1 。在验证的时候只需要验证这些比特位是否都是 1 即可,如果其中有一个为 0,那么元素一定不在集合里,如果全为 1,则很可能在集合里。(因为可能会有其它的元素也映射到相应的比特位上)
另外说明一下,当来查找对应的值时,同样通过哈希函数求值,再去寻找数组的下标,如果所有下标都为1时,元素存在。当然也存在错误率。(如:当数组全部为1时,那么查找什么都是存在的),但是这个错误率的大小,取决于数组的位数和哈希函数的个数。
python 中使用布隆过滤器
#python3.6 安装 #需要先安装bitarray pip3 install bitarray-0.8.1-cp36-cp36m-win_amd64.whl(pybloom_live依赖这个包,需要先安装) #下载地址:https://www.lfd.uci.edu/~gohlke/pythonlibs/ pip3 install pybloom_live示例一
#ScalableBloomFilter 可以自动扩容 from pybloom_live import ScalableBloomFilter bloom = ScalableBloomFilter(initial_capacity=100, error_rate=0.001, mode=ScalableBloomFilter.LARGE_SET_GROWTH) url = "www.cnblogs.com" url2 = "www.liuqingzheng.top" bloom.add(url) print(url in bloom) print(url2 in bloom)示例二
#BloomFilter 是定长的 from pybloom_live import BloomFilter bf = BloomFilter(capacity=1000) url='www.baidu.com' bf.add(url) print(url in bf) print("www.liuqingzheng.top" in bf)用了 布隆过滤器 后,就可以判断 url 是否爬过,从而可以实现增量式爬取
布隆过滤器的结果是存在内存中的,后期可以存进 redis 中