前言
什么是mybatis二级缓存?
二级缓存是多个sqlsession共享的,其作用域是mapper的同一个namespace。
即,在不同的sqlsession中,相同的namespace下,相同的sql语句,并且sql模板中参数也相同的,会命中缓存。
第一次执行完毕会将数据库中查询的数据写到缓存,第二次会从缓存中获取数据将不再从数据库查询,从而提高查询效率。
Mybatis默认没有开启二级缓存,需要在全局配置(mybatis-config.xml)中开启二级缓存。
本文讲述的是使用Redis作为缓存,与springboot、mybatis进行集成的方法。
1、pom依赖
使用springboot redis集成包,方便redis的访问。redis客户端选用Jedis。
另外读写kv缓存会进行序列化,所以引入了一个序列化包。
<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-redis</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> <version>2.8.0</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>com.alibaba</groupId> <artifactId>fastjson</artifactId> <version>1.2.19</version> </dependency>
依赖搞定之后,下一步先调通Redis客户端。
2、Redis访问使用的Bean
增加Configuration,配置jedisConnectionFactory bean,留待后面使用。
一般来讲,也会生成了redisTemplate bean,但是在接下来的场景没有使用到。
@Configuration public class RedisConfig { @Value("${spring.redis.host}") private String host; // 篇幅受限,省略了 @Bean public JedisPoolConfig getRedisConfig(){ JedisPoolConfig config = new JedisPoolConfig(); config.setMaxIdle(maxIdle); config.setMaxTotal(maxTotal); config.setMaxWaitMillis(maxWaitMillis); config.setMinIdle(minIdle); return config; } @Bean(name = "jedisConnectionFactory") public JedisConnectionFactory getConnectionFactory(){ JedisConnectionFactory factory = new JedisConnectionFactory(); JedisPoolConfig config = getRedisConfig(); factory.setPoolConfig(config); factory.setHostName(host); factory.setPort(port); factory.setDatabase(database); factory.setPassword(password); factory.setTimeout(timeout); return factory; } @Bean(name = "redisTemplate") public RedisTemplate<?, ?> getRedisTemplate(){ RedisTemplate<?,?> template = new StringRedisTemplate(getConnectionFactory()); return template; } }
这里使用@Value读入了redis相关配置,有更简单的配置读取方式(@ConfigurationProperties(prefix=...)),可以尝试使用。
Redis相关配置如下
#redis
spring.redis.host=10.93.84.53
spring.redis.port=6379
spring.redis.password=bigdata123
spring.redis.database=15
spring.redis.timeout=0
spring.redis.pool.maxTotal=8
spring.redis.pool.maxWaitMillis=1000
spring.redis.pool.maxIdle=8
spring.redis.pool.minIdle=0
Redis客户端的配置含义,这里不再讲解了。pool相关的一般都和性能有关,需要根据并发量权衡句柄、内存等资源进行设置。
Redis客户端设置好了,我们开始配置Redis作为Mybatis的缓存。
3、Mybatis Cache
这一步是最为关键的一步。实现方式是实现Mybatis的一个接口org.apache.ibatis.cache.Cache。
这个接口设计了写缓存,读缓存,销毁缓存的方式,和访问控制读写锁。
我们实现实现Cache接口的类是MybatisRedisCache。
MybatisRedisCache.java
public class MybatisRedisCache implements Cache { private static JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory; private final String id; private final ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(); public MybatisRedisCache(final String id) { if (id == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cache instances require an ID"); } this.id = id; } @Override public void clear() { RedisConnection connection = null; try { connection = jedisConnectionFactory.getConnection(); connection.flushDb(); connection.flushAll(); } catch (JedisConnectionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (connection != null) { connection.close(); } } } @Override public String getId() { return this.id; } @Override public Object getObject(Object key) { Object result = null; RedisConnection connection = null; try { connection = jedisConnectionFactory.getConnection(); RedisSerializer<Object> serializer = new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer(); result = serializer.deserialize(connection.get(serializer.serialize(key))); } catch (JedisConnectionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (connection != null) { connection.close(); } } return result; } @Override public ReadWriteLock getReadWriteLock() { return this.readWriteLock; } @Override public int getSize() { int result = 0; RedisConnection connection = null; try { connection = jedisConnectionFactory.getConnection(); result = Integer.valueOf(connection.dbSize().toString()); } catch (JedisConnectionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (connection != null) { connection.close(); } } return result; } @Override public void putObject(Object key, Object value) { RedisConnection connection = null; try { connection = jedisConnectionFactory.getConnection(); RedisSerializer<Object> serializer = new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer(); connection.set(serializer.serialize(key), serializer.serialize(value)); } catch (JedisConnectionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (connection != null) { connection.close(); } } } @Override public Object removeObject(Object key) { RedisConnection connection = null; Object result = null; try { connection = jedisConnectionFactory.getConnection(); RedisSerializer<Object> serializer = new JdkSerializationRedisSerializer(); result = connection.expire(serializer.serialize(key), 0); } catch (JedisConnectionException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if (connection != null) { connection.close(); } } return result; } public static void setJedisConnectionFactory(JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory) { MybatisRedisCache.jedisConnectionFactory = jedisConnectionFactory; } }
注意:
可以看到,这个类并不是由Spring虚拟机管理的类,但是,其中有一个静态属性jedisConnectionFactory需要注入一个Spring bean,也就是在RedisConfig中生成的bean。
在一个普通类中使用Spring虚拟机管理的Bean,一般使用Springboot自省的SpringContextAware。
这里使用了另一种方式,静态注入的方式。这个方式是通过RedisCacheTransfer来实现的。
4、静态注入
RedisCacheTransfer.java
@Component public class RedisCacheTransfer { @Autowired public void setJedisConnectionFactory(JedisConnectionFactory jedisConnectionFactory) { MybatisRedisCache.setJedisConnectionFactory(jedisConnectionFactory); } }
可以看到RedisCacheTransfer是一个springboot bean,在容器创建之初进行初始化的时候,会注入jedisConnectionFactory bean给setJedisConnectionFactory方法的传参。
而setJedisConnectionFactory通过调用静态方法设置了类MybatisRedisCache的静态属性jedisConnectionFactory。
这样就把spring容器管理的jedisConnectionFactory注入到了静态域。
到这里,代码基本已经搞定,下面是一些配置。主要有(1)全局开关;(2)namespace作用域开关;(3)Model实例序列化。
5、Mybatis二级缓存的全局开关
前面提到过,默认二级缓存没有打开,需要设置为true。这是全局二级缓存的开关。
Mybatis的全局配置。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE configuration PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> <configuration> <!-- 全局参数 --> <settings> <!-- 使全局的映射器启用或禁用缓存。 --> <setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/> </settings> </configuration>
全局配置的加载在dataSource中可以是这样的。
bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:mybatis-mapper/*.xml"));
指定了mapper.xml的存放路径,在mybatis-mapper路径下,所有后缀是.xml的都会读入。
bean.setConfigLocation(new ClassPathResource("mybatis-config.xml"));
指定了mybatis-config.xml的存放路径,直接放在Resource目录下即可。
@Bean(name = "moonlightSqlSessionFactory") @Primary public SqlSessionFactory moonlightSqlSessionFactory(@Qualifier("moonlightData") DataSource dataSource) throws Exception { SqlSessionFactoryBean bean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean(); bean.setDataSource(dataSource); bean.setMapperLocations(new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver().getResources("classpath:mybatis-mapper/*.xml")); bean.setConfigLocation(new ClassPathResource("mybatis-config.xml")); return bean.getObject(); }
6、配置mapper作用域namespace
前面提到过,二级缓存的作用域是mapper的namespace,所以这个配置需要到mapper中去写。
<mapper namespace="com.kangaroo.studio.moonlight.dao.mapper.MoonlightMapper"> <cache type="com.kangaroo.studio.moonlight.dao.cache.MybatisRedisCache"/> <resultMap id="geoFenceList" type="com.kangaroo.studio.moonlight.dao.model.GeoFence"> <constructor> <idArg column="id" javaType="java.lang.Integer" jdbcType="INTEGER" /> <arg column="name" javaType="java.lang.String" jdbcType="VARCHAR" /> <arg column="type" javaType="java.lang.Integer" jdbcType="INTEGER" /> <arg column="group" javaType="java.lang.String" jdbcType="VARCHAR" /> <arg column="geo" javaType="java.lang.String" jdbcType="VARCHAR" /> <arg column="createTime" javaType="java.lang.String" jdbcType="VARCHAR" /> <arg column="updateTime" javaType="java.lang.String" jdbcType="VARCHAR" /> </constructor> </resultMap> <select id="queryGeoFence" parameterType="com.kangaroo.studio.moonlight.dao.model.GeoFenceQueryParam" resultMap="geoFenceList"> select <include refid="base_column"/> from geoFence where 1=1 <if test="type != null"> and type = #{type} </if> <if test="name != null"> and name like concat('%', #{name},'%') </if> <if test="group != null"> and `group` like concat('%', #{group},'%') </if> <if test="startTime != null"> and createTime >= #{startTime} </if> <if test="endTime != null"> and createTime <= #{endTime} </if> </select> </mapper>
注意:
namespace下的cache标签就是加载缓存的配置,缓存使用的正式我们刚才实现的MybatisRedisCache。
<cache type="com.kangaroo.studio.moonlight.dao.cache.MybatisRedisCache"/>
这里只实现了一个查询queryGeoFence,你可以在select标签中,开启或者关闭这个sql的缓存。使用属性值useCache=true/false。
7、Mapper和Model
读写缓存Model需要序列化:只需要类声明的时候实现Seriaziable接口就好了。
public class GeoFence implements Serializable { // setter和getter省略 } public class GeoFenceParam implements Serializable { // setter和getter省略 }
mapper就还是以前的写法,使用mapper.xml的方式这里只需要定义出抽象函数即可。
@Mapper public interface MoonlightMapper { List<GeoFence> queryGeoFence(GeoFenceQueryParam geoFenceQueryParam); }
到这里,所有的代码和配置都完成了,下面测试一下。
8、测试一下
Controller中实现一个这样的接口POST。
@RequestMapping(value = "/fence/query", method = RequestMethod.POST) @ResponseBody public ResponseEntity<Response> queryFence(@RequestBody GeoFenceQueryParam geoFenceQueryParam) { try { Integer pageNum = geoFenceQueryParam.getPageNum()!=null?geoFenceQueryParam.getPageNum():1; Integer pageSize = geoFenceQueryParam.getPageSize()!=null?geoFenceQueryParam.getPageSize():10; PageHelper.startPage(pageNum, pageSize); List<GeoFence> list = moonlightMapper.queryGeoFence(geoFenceQueryParam); return new ResponseEntity<>( new Response(ResultCode.SUCCESS, "查询geoFence成功", list), HttpStatus.OK); } catch (Exception e) { logger.error("查询geoFence失败", e); return new ResponseEntity<>( new Response(ResultCode.EXCEPTION, "查询geoFence失败", null), HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR); }
使用curl发送请求,注意
1)-H - Content-type:application/json方式
2)-d - 后面是json格式的参数包体
curl -H "Content-Type:application/json" -XPOST http://。。。/moonlight/fence/query -d '{
"name" : "test",
"group": "test",
"type": 1,
"startTime":"2017-12-06 00:00:00",
"endTime":"2017-12-06 16:00:00",
"pageNum": 1,
"pageSize": 8
}'
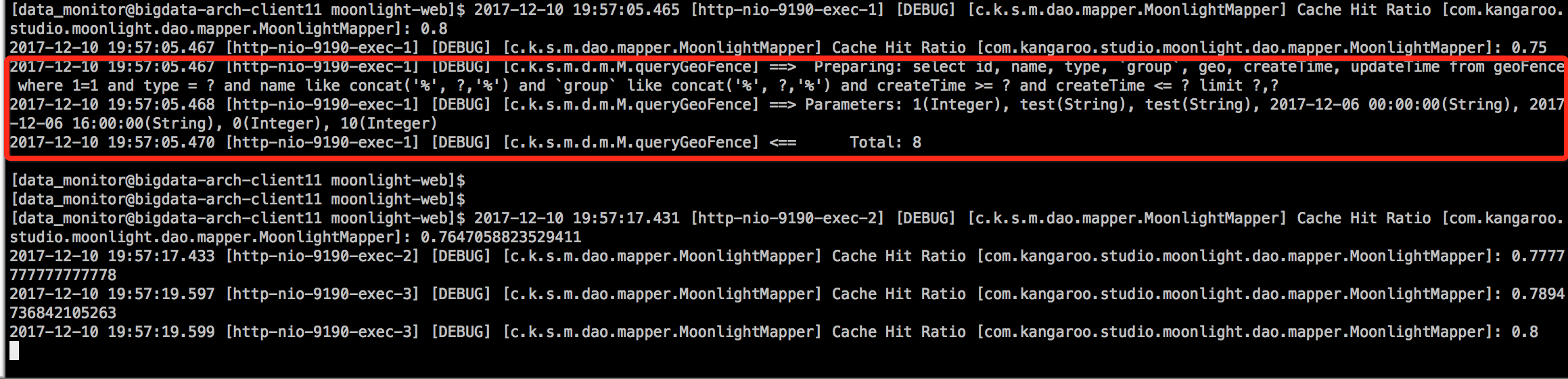
请求了三次,日志打印如下,
可以看到,只有第一次执行了sql模板查询,后面都是命中了缓存。
在我们的测试环境中由于数据量比较小,缓存对查询速度的优化并不明显。这里就不过多说明了。
最后上一篇打脸文。给你参考http://blog.csdn.net/isea533/article/details/44566257
完毕。