一,首先我们对函数先进行分析
findHomography:
计算多个二维点对之间的最优单映射变换矩阵 H(3行x3列) (就是对图片的矫正),使用最小均方误差或者RANSAC方法
函数功能:找到两个平面之间的转换矩阵。

这里涉及到映射变换的知识,
下面介绍下什么是映射变换:
1,如下图所示:
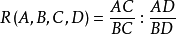
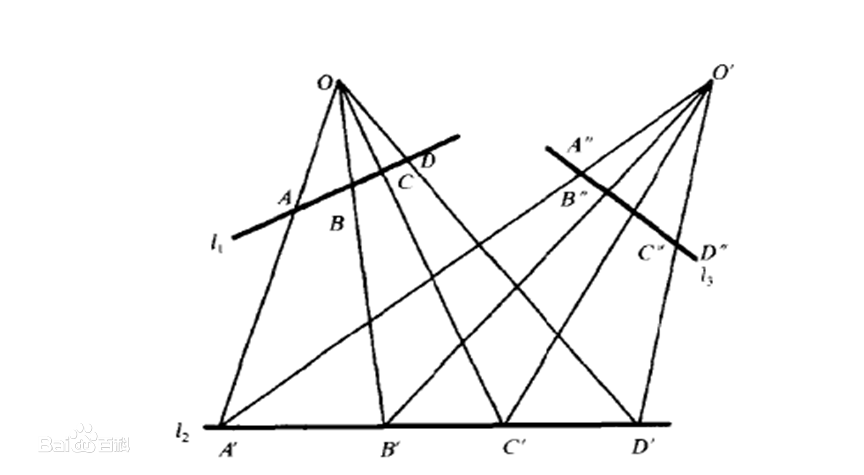
二维的图像是这样的
射影变换也叫做单应(Homography)


图1通过H矩阵变换变成图2,就是这个函数的公式
X′=HX
X′代表图2
其操作过程
- 在“大”图像(目标图像)上选择4个点和“小”图像(被合并图像)的四角做对应,然后根据这4对对应的点计算两幅图像的单应矩阵。
- 得到单应矩阵H后,利用函数warpPerspective将H应用到“小”图像上,得到图像M
- 将图像M合并到目标图像中选择的四个点的位置
Mat cv::findHomography ( InputArray srcPoints, InputArray dstPoints, int method = 0, double ransacReprojThreshold = 3, OutputArray mask = noArray(), const int maxIters = 2000, const double confidence = 0.995 )
参数详解:
srcPoints 源平面中点的坐标矩阵,可以是CV_32FC2类型,也可以是vector<Point2f>类型
dstPoints 目标平面中点的坐标矩阵,可以是CV_32FC2类型,也可以是vector<Point2f>类型
method 计算单应矩阵所使用的方法。不同的方法对应不同的参数,具体如下:
0 - 利用所有点的常规方法
RANSAC - RANSAC-基于RANSAC的鲁棒算法
LMEDS - 最小中值鲁棒算法
RHO - PROSAC-基于PROSAC的鲁棒算法
ransacReprojThreshold
将点对视为内点的最大允许重投影错误阈值(仅用于RANSAC和RHO方法)。如果
则点被认为是个外点(即错误匹配点对)。若srcPoints和dstPoints是以像素为单位的,则该参数通常设置在1到10的范围内。
mask
可选输出掩码矩阵,通常由鲁棒算法(RANSAC或LMEDS)设置。 请注意,输入掩码矩阵是不需要设置的。
maxIters RANSAC 算法的最大迭代次数,默认值为2000。
confidence 可信度值,取值范围为0到1.
首先定义两个vector保存对应的4对点
//图片映射矩阵把不同角度的图片矫正 void findHomographyText(){ // Read source image. Mat src = imread("F:\视觉\opencv\pic\1.png"); // Four corners of the book in source image vector<Point2f> pts_src; pts_src.push_back(Point2f(0, 0)); pts_src.push_back(Point2f(src.cols, 0)); pts_src.push_back(Point2f(src.cols, src.rows)); pts_src.push_back(Point2f(0, src.rows)); // Four corners of the book in destination image. vector<Point2f> pts_dst; pts_dst.push_back(Point2f(0, 0)); pts_dst.push_back(Point2f(src.cols/4, 0)); pts_dst.push_back(Point2f(src.cols/3, src.rows)); pts_dst.push_back(Point2f(0, src.rows/2)); // Calculate Homography Mat h = findHomography(pts_src, pts_dst); // Output image Mat im_out; // Warp source image to destination based on homography warpPerspective(src, im_out, h, src.size()); // Display images imshow("Source Image", src); imshow("Warped Source Image", im_out); waitKey(0); }
结果如下图所示对图像进行拉伸
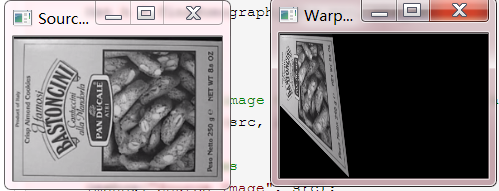
步骤如下
1,相求H
vector<Point2f> pts_src; pts_src.push_back(Point2f(0, 0)); pts_src.push_back(Point2f(src.cols, 0)); pts_src.push_back(Point2f(src.cols, src.rows)); pts_src.push_back(Point2f(0, src.rows)); // Four corners of the book in destination image. vector<Point2f> pts_dst; pts_dst.push_back(Point2f(0, 0)); pts_dst.push_back(Point2f(src.cols/4, 0)); pts_dst.push_back(Point2f(src.cols/3, src.rows)); pts_dst.push_back(Point2f(0, src.rows/2)); // Calculate Homography Mat h = findHomography(pts_src, pts_dst);
通过H求对应的图像(映射到输出图片上)
warpPerspective(src, im_out, h, src.size());
warpPerspective:通过H求取
im_out输出值介绍完两个主要的函数下面开始对图像进行识别和标记
2,SURF对图像的识别和标记
1,开发思路
(1)使用SIFT或者SURF进行角点检测,获取两个图像的的角点集合
(2)根据两个集合,使用特征点匹配,匹配类似的点 FlannBasedMatcher
(3)过滤特征点对。
(4)通过特征点对,求出H值
(5)画出特征区域
代码实现:
1,使用SIFT或者SURF进行角点检测,获取两个图像的的角点集合
src = imread("F:\视觉\opencv\pic\11.png");//读图片 src3 = imread("F:\视觉\opencv\pic\5.png");//读图片 int minHessian = 400; cvtColor(src, src, COLOR_BGR2GRAY); cvtColor(src3, src3, COLOR_BGR2GRAY); Ptr<SIFT> detector = SIFT::create(minHessian); vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_obj;//图片1特征点 vector<KeyPoint> keypoints_scene;//图片2特征点 Mat descriptor_obj, descriptor_scene; //找出特征点存到keypoints_obj与keypoints_scene点集中 detector->detectAndCompute(src, Mat(), keypoints_obj, descriptor_obj); detector->detectAndCompute(src3, Mat(), keypoints_scene, descriptor_scene); // matching 找到特征集合 FlannBasedMatcher matcher; vector<DMatch> matches; matcher.match(descriptor_obj, descriptor_scene, matches);
2,过滤相似度高的图像
// find good matched points double minDist = 1000; double maxDist = 0; for (int i = 0; i < descriptor_obj.rows; i++) { double dist = matches[i].distance; if (dist > maxDist) { maxDist = dist; } if (dist < minDist) { minDist = dist; } } printf("max distance : %f ", maxDist); printf("min distance : %f ", minDist); vector<DMatch> goodMatches; //过滤相同的点 for (int i = 0; i < descriptor_obj.rows; i++) { double dist = matches[i].distance;//相识度 printf("distance : %f ", dist); if (dist < max(3 * minDist, 0.2)) { goodMatches.push_back(matches[i]); } }
3,求出H
vector<Point2f> obj; vector<Point2f> objInScene; for (size_t t = 0; t < goodMatches.size(); t++) { //把DMatch转成坐标 Point2f obj.push_back(keypoints_obj[goodMatches[t].queryIdx].pt); objInScene.push_back(keypoints_scene[goodMatches[t].trainIdx].pt); } //用来求取“射影变换”的H转制矩阵函数 X'=H X ,并使用RANSAC消除一些出错的点 Mat H = findHomography(obj, objInScene, RANSAC);
4,使用H求出映射到大图的点
vector<Point2f> obj_corners(4); vector<Point2f> scene_corners(4); obj_corners[0] = Point(0, 0); obj_corners[1] = Point(src.cols, 0); obj_corners[2] = Point(src.cols, src.rows); obj_corners[3] = Point(0, src.rows); //透视变换(把斜的图片扶正) cout << H << endl; perspectiveTransform(obj_corners, scene_corners, H);
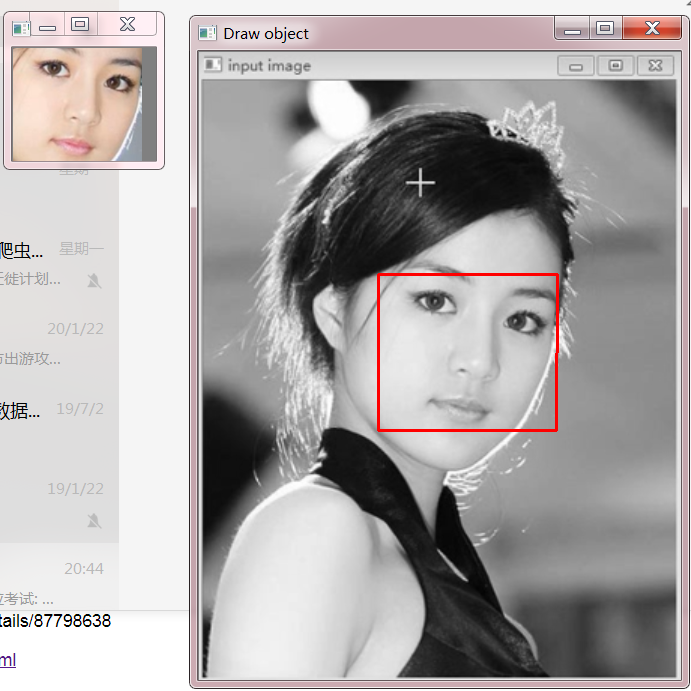
5,在原图上画线段
Mat dst;
cvtColor(src3, dst, COLOR_GRAY2BGR);
line(dst, scene_corners[0], scene_corners[1], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
line(dst, scene_corners[1], scene_corners[2], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
line(dst, scene_corners[2], scene_corners[3], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
line(dst, scene_corners[3], scene_corners[0], Scalar(0, 0, 255), 2, 8, 0);
imshow("Draw object", dst);
相似效果
谢谢,如果觉得可以请点个赞!转发请付链接。。。。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/fengyeer20120/article/details/87798638
https://www.cnblogs.com/wangguchangqing/p/4645805.html
// find good matched pointsdouble minDist = 1000;double maxDist = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < descriptor_obj.rows; i++) {double dist = matches[i].distance;if (dist > maxDist) {maxDist = dist;}if (dist < minDist) {minDist = dist;}}printf("max distance : %f
", maxDist);printf("min distance : %f
", minDist);
vector<DMatch> goodMatches;//过滤相同的点for (int i = 0; i < descriptor_obj.rows; i++) {double dist = matches[i].distance;//相识度printf("distance : %f
", dist);if (dist < max(3 * minDist, 0.2)) {goodMatches.push_back(matches[i]);}}