摘要:状态机模式是一种行为模式,在《设计模式》这本书中对其有详细的描述,通过多态实现不同状态的调转行为的确是一种很好的方法,只可惜在嵌入式环境下,有时只能写纯C代码,并且还需要考虑代码的重入和多任务请求跳转等情形,因此实现起来着实需要一番考虑。本文主要为你实现一个简单的有限状态机,没有考虑代码的重入和多任务跳转,为以后复杂的状态机实现,打下基础。
本文来源:用C语言实现有限状态自动机FSM
一、状态机实现的要素
首先,分析一下一个普通的状态机究竟要实现哪些内容。
状态机存储从开始时刻到现在的变化,并根据当前输入,决定下一个状态。这意味着,状态机要存储状态、获得输入(我们把它叫做跳转条件)、做出响应。
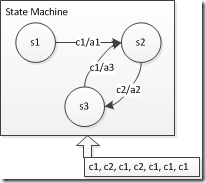
如上图所示,{s1, s2, s3}均为状态,箭头c1/a1表示在s1状态、输入为c1时,跳转到s2,并进行a1操作。
最下方为一组输入,状态机应做出如下反应:
| 当前状态 | 输入 | 下一个状态 | 动作 |
| s1 | c1 | s2 | a1 |
| s2 | c2 | s3 | a2 |
| s3 | c1 | s2 | a3 |
| s2 | c2 | s3 | a2 |
| s3 | c1 | s2 | a3 |
| s2 | c1 | s_trap | a_trap |
| s_trap | c1 | s_trap | a_trap |
当某个状态遇到不能识别的输入时,就默认进入陷阱状态,在陷阱状态中,不论遇到怎样的输入都不能跳出。
为了表达上面这个自动机,我们定义它们的状态和输入类型:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
typedef
int s
tate;
typedef
int c
ondition;
#define STATES 4
#define STATE1 0
#define STATE2 1
#define STATE3 2
#define STATETRAP 3
#define CONDITIONS 2
#define CONDITION1 0
#define CONDITION2 1
|
总结一下,我们需要定义的有状态、输入、行为(动作+下一个状态),其中,行为的个数是“状态数*输入数量”(其中有一些是重复的);其中动作一般来说可以用一个函数指针来实现。
二、具体设计
在嵌入式环境中,由于存储空间比较小,因此把它们全部定义成宏。此外,为了降低执行时间的不确定性,我们使用O(1)的跳转表来模拟状态的跳转。
首先定义跳转类型:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
typedef
void
(*actiontype)(state mystate, condition condition);
typedef
struct
{
s
tate next;
a
ctiontype action;
} trasition, * ptrasition;
|
然后按照上图中的跳转关系,把三个跳转加一个陷阱跳转先定义出来:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
// (s1, c1, s2, a1)
trasition t1 = {
STATE2,
action1
};
// (s2, c2, s3, a2)
trasition t2 = {
STATE3,
action2
};
// (s3, c1, s2, a3)
trasition t3 = {
STATE2,
action3
};
// (s, c, trap, a1)
trasition tt = {
STATETRAP,
actiontrap
};
|
其中的动作,由用户自己完成,在这里仅定义一条输出语句。
|
1
2
3
4
|
void
action1(State state, Condition condition)
{
printf
(
"Action 1 triggered.
"
);
}
|
|
1
|
最后定义跳转表:
|
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
pt
rasition transition_table[STATES][CONDITIONS] = {
/* c1, c2*/
/* s1 */
&t1, &tt,
/* s2 */
&tt, &t2,
/* s3 */
&t3, &tt,
/* st */
&tt, &tt,
};
|
即可表达上文中的跳转关系。
最后定义状态机,如果不考虑多任务请求,那么状态机仅需要存储当前状态便行了。例如:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
typedef
struct
{
State current;
} StateMachine, * pStateMachine;
State step(pStateMachine machine, Condition condition)
{
pTrasition t = transition_table[machine->current][condition];
(*(t->action))(machine->current, condition);
machine->current = t->next;
return
machine->current;
}
|
三、程序实现
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int state;
typedef int condition;
#define STATENUM 4
#define STATE1 0
#define STATE2 1
#define STATE3 2
#define STATETRAP 3
#define CONDITIONS 2
#define CONDITION1 0
#define CONDITION2 1
typedef void (* actiontype)(state mystate,condition mycondition);
typedef struct{
state next;
actiontype action;
}trasition, *ptrasition;
void action1(state mystate,condition myconditon);
void action2(state mystate,condition myconditon);
void action3(state mystate,condition myconditon);
void actiontrap(state mystate,condition myconditon);
trasition t1={
STATE2,action1
};
trasition t2={
STATE3,action2
};
trasition t3={
STATE2,action3
};
trasition tt={
STATETRAP,actiontrap
};
void action1(state mystate,condition myconditon){
printf("action1 one triggered
");
}
void action2(state mystate,condition myconditon){
printf("action2 one triggered
");
}
void action3(state mystate,condition myconditon){
printf("action3 one triggered
");
}
void actiontrap(state mystate,condition myconditon){
printf("actiontrap one triggered
");
}
ptrasition transition_table[STATENUM][CONDITIONS] = {
/* c1, c2*/
/* s1 */&t1, &tt,
/* s2 */&tt, &t2,
/* s3 */&t3, &tt,
/* st */&tt, &tt,
};
typedef struct
{
state current;
} StateMachine, * pStateMachine;
state step(pStateMachine machine, condition mycondition)
{
ptrasition t = transition_table[machine->current][mycondition];
(*(t->action))(machine->current, mycondition);
machine->current = t->next;
printf("the current state is %d
",t->next );
return machine->current;
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
StateMachine mymachine;
mymachine.current=STATE1;
int mycon;
char ch;
while(1){
scanf("%d",&mycon);
step(&mymachine,mycon);
}
return 0;
}
程序输入与输出结果示例: