Chapter 4 - Clustering Models
Segment 1 - K-means method
Clustering and Classification Algorithms
K-Means clustering: unsupervised clustering algorithm where you know how many clusters are appropriate
K-Means Use Cases
- Market Price and Cost Modeling
- Insurance Claim Fraud Detection
- Hedge Fund Classification
- Customer Segmentation
K-Means Clustering
Predictions are based on the number of centroids present(K) and nearest mean values, given an Euclidean distance measurement between observations.
When using K-means:
- Scale your variables
- Look at a scatterplot or the data table to estimate the appropriate number of centroids to use for the K parameter value
Setting up for clustering analysis
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sklearn
from sklearn.preprocessing import scale
import sklearn.metrics as sm
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix, classification_report
from sklearn.cluster import KMeans
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
from sklearn import datasets
%matplotlib inline
plt.figure(figsize=(7,4))
<Figure size 504x288 with 0 Axes>
<Figure size 504x288 with 0 Axes>
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = scale(iris.data)
y = pd.DataFrame(iris.target)
varibale_names = iris.feature_names
X[0:10]
array([[-0.90068117, 1.01900435, -1.34022653, -1.3154443 ],
[-1.14301691, -0.13197948, -1.34022653, -1.3154443 ],
[-1.38535265, 0.32841405, -1.39706395, -1.3154443 ],
[-1.50652052, 0.09821729, -1.2833891 , -1.3154443 ],
[-1.02184904, 1.24920112, -1.34022653, -1.3154443 ],
[-0.53717756, 1.93979142, -1.16971425, -1.05217993],
[-1.50652052, 0.78880759, -1.34022653, -1.18381211],
[-1.02184904, 0.78880759, -1.2833891 , -1.3154443 ],
[-1.74885626, -0.36217625, -1.34022653, -1.3154443 ],
[-1.14301691, 0.09821729, -1.2833891 , -1.44707648]])
Building and running your model
clustering = KMeans(n_clusters=3, random_state=5)
clustering.fit(X)
KMeans(n_clusters=3, random_state=5)
Plotting your model outputs
iris_df = pd.DataFrame(iris.data)
iris_df.columns = ['Sepal_Length','Sepal_Width','Petal_Length','Petal_Width']
y.columns = ['Targets']
color_theme = np.array(['darkgray','lightsalmon','powderblue'])
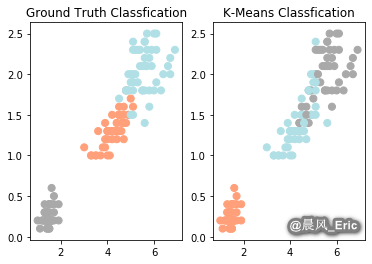
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.scatter(x=iris_df.Petal_Length, y=iris_df.Petal_Width, c=color_theme[iris.target],s=50)
plt.title('Ground Truth Classfication')
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.scatter(x=iris_df.Petal_Length, y=iris_df.Petal_Width, c=color_theme[clustering.labels_],s=50)
plt.title('K-Means Classfication')
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'K-Means Classfication')
relabel = np.choose(clustering.labels_, [2, 0, 1]).astype(np.int64)
plt.subplot(1,2,1)
plt.scatter(x=iris_df.Petal_Length, y=iris_df.Petal_Width, c=color_theme[iris.target],s=50)
plt.title('Ground Truth Classfication')
plt.subplot(1,2,2)
plt.scatter(x=iris_df.Petal_Length, y=iris_df.Petal_Width, c=color_theme[relabel],s=50)
plt.title('K-Means Classfication')
Text(0.5, 1.0, 'K-Means Classfication')
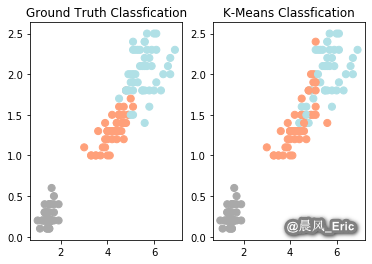
Evaluate your clustering results
print(classification_report(y, relabel))
precision recall f1-score support
0 1.00 1.00 1.00 50
1 0.74 0.78 0.76 50
2 0.77 0.72 0.74 50
accuracy 0.83 150
macro avg 0.83 0.83 0.83 150
weighted avg 0.83 0.83 0.83 150