1 int temp = 0;
2 if(scores[j]<scores[j+1]) {
3 temp = scores[j];
4 scores[j] = scores[j+1];
5 scores[j+1] = temp;
6 }
7 }
8 }//查看降序排列之后的数组
9 for(int score : scores) {
10 System.out.print(score+" ");
11 }
12 System.out.println();
13 Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
14 System.out.println("请输入学员的成绩:");
15 int addScore = sc.nextInt();
16 //用输入的成绩跟数组中每一个元素比较,当输入的成绩大于某个值时,
17 //这个值的位置,就是输入的成绩应该在的位置,也就是找到输入成绩应该的下标
18 int index = -1;
19 for(int i=0;i<scores.length;i++) {
20 if(addScore>scores[i]) {
21 index = i;//找到输入的成绩应该所在的下标
22 break;
23 }
24 }
25 //从倒数第二个值开始,每一个往后赋值,直到找到的下标
26 for(int i = scores.length-2;i>=index;i--) {
27 scores[i+1] = scores[i];
28 }
29 //给找到的下标赋值为刚刚添加的成绩
30 scores[index] = addScore;
31 System.out.println("插入一个学员的成绩后:");
32 for(int score : scores) {
33 System.out.print(score+" ");
34 }
35 System.out.println();
36 }
37 }
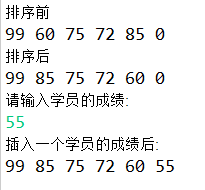
代码运行结果如下: