当一个Action完成它的任务后,通常需要返回一个实现IActionResult的对象,而最常见的就是View或者ViewResult,所谓的视图对象。那么视图与最终所看到的页面之间的联系又是怎样形成的,这便是本文想要探讨的问题。
在ResourceInvoker类之中,可以找到下列的代码。这些代码是对返回结果——IActionResult的进一步处理。
case State.ResultInside:
{
...
var task = InvokeResultAsync(_result);
if (task.Status != TaskStatus.RanToCompletion)
{
next = State.ResultEnd;
return task;
}
goto case State.ResultEnd;
}
protected async Task InvokeResultAsync(IActionResult result)
{
var actionContext = _actionContext;
_diagnosticSource.BeforeActionResult(actionContext, result);
_logger.BeforeExecutingActionResult(result);
try
{
await result.ExecuteResultAsync(actionContext);
}
finally
{
_diagnosticSource.AfterActionResult(actionContext, result);
_logger.AfterExecutingActionResult(result);
}
}
IActionResult接口的实现类ViewResult中会调用ViewResultExecutor类的方法。
public override async Task ExecuteResultAsync(ActionContext context)
{
...
var executor = context.HttpContext.RequestServices.GetRequiredService<IActionResultExecutor<ViewResult>>();
await executor.ExecuteAsync(context, this);
}
ViewResultExecutor类里则需要先通过RazorViewEngine类找到对应的视图。
public async Task ExecuteAsync(ActionContext context, ViewResult result)
{
...
var viewEngineResult = FindView(context, result);
viewEngineResult.EnsureSuccessful(originalLocations: null);
var view = viewEngineResult.View;
using (view as IDisposable)
{
await ExecuteAsync(
context,
view,
result.ViewData,
result.TempData,
result.ContentType,
result.StatusCode);
}
...
}
RazorViewEngine类返回的结果是RazorView对象。注意其内部已包含了IRazorPage对象。
public ViewEngineResult GetView(string executingFilePath, string viewPath, bool isMainPage)
{
...
var cacheResult = LocatePageFromPath(executingFilePath, viewPath, isMainPage);
return CreateViewEngineResult(cacheResult, viewPath);
}
public ViewEngineResult FindView(ActionContext context, string viewName, bool isMainPage)
{
...
var cacheResult = LocatePageFromViewLocations(context, viewName, isMainPage);
return CreateViewEngineResult(cacheResult, viewName);
}
private ViewEngineResult CreateViewEngineResult(ViewLocationCacheResult result, string viewName)
{
...
var page = result.ViewEntry.PageFactory();
var viewStarts = new IRazorPage[result.ViewStartEntries.Count];
for (var i = 0; i < viewStarts.Length; i++)
{
var viewStartItem = result.ViewStartEntries[i];
viewStarts[i] = viewStartItem.PageFactory();
}
var view = new RazorView(this, _pageActivator, viewStarts, page, _htmlEncoder, _diagnosticSource);
return ViewEngineResult.Found(viewName, view);
}
找到视图后,ViewResultExecutor再调用其父类ViewExecutor的ExecuteAsync方法。其内部将调用RazorView类的RenderAsync方法。
protected async Task ExecuteAsync(
ViewContext viewContext,
string contentType,
int? statusCode)
{
...
var response = viewContext.HttpContext.Response;
ResponseContentTypeHelper.ResolveContentTypeAndEncoding(
contentType,
response.ContentType,
DefaultContentType,
out var resolvedContentType,
out var resolvedContentTypeEncoding);
response.ContentType = resolvedContentType;
if (statusCode != null)
{
response.StatusCode = statusCode.Value;
}
using (var writer = WriterFactory.CreateWriter(response.Body, resolvedContentTypeEncoding))
{
var view = viewContext.View;
var oldWriter = viewContext.Writer;
try
{
viewContext.Writer = writer;
DiagnosticSource.BeforeView(view, viewContext);
await view.RenderAsync(viewContext);
DiagnosticSource.AfterView(view, viewContext);
}
finally
{
viewContext.Writer = oldWriter;
}
// Perf: Invoke FlushAsync to ensure any buffered content is asynchronously written to the underlying
// response asynchronously. In the absence of this line, the buffer gets synchronously written to the
// response as part of the Dispose which has a perf impact.
await writer.FlushAsync();
}
}
RazorView类中可以看到其核心的处理与IRazorPage的ExecuteAsync方法紧密相关。
public virtual async Task RenderAsync(ViewContext context)
{
...
_bufferScope = context.HttpContext.RequestServices.GetRequiredService<IViewBufferScope>();
var bodyWriter = await RenderPageAsync(RazorPage, context, invokeViewStarts: true);
await RenderLayoutAsync(context, bodyWriter);
}
private async Task<ViewBufferTextWriter> RenderPageAsync(
IRazorPage page,
ViewContext context,
bool invokeViewStarts)
{
var writer = context.Writer as ViewBufferTextWriter;
...
// The writer for the body is passed through the ViewContext, allowing things like HtmlHelpers
// and ViewComponents to reference it.
var oldWriter = context.Writer;
var oldFilePath = context.ExecutingFilePath;
context.Writer = writer;
context.ExecutingFilePath = page.Path;
try
{
if (invokeViewStarts)
{
// Execute view starts using the same context + writer as the page to render.
await RenderViewStartsAsync(context);
}
await RenderPageCoreAsync(page, context);
return writer;
}
finally
{
context.Writer = oldWriter;
context.ExecutingFilePath = oldFilePath;
}
}
private async Task RenderPageCoreAsync(IRazorPage page, ViewContext context)
{
page.ViewContext = context;
_pageActivator.Activate(page, context);
_diagnosticSource.BeforeViewPage(page, context);
try
{
await page.ExecuteAsync();
}
finally
{
_diagnosticSource.AfterViewPage(page, context);
}
}
但当查找IRazorPage接口的实现。从RazorPageBase到RazorPage,再到RazorPage<TModel>,这些都只是抽象类,且都没有对ExecuteAsync方法有具体实现。
源码里找不到进一步的实现类,线索到这里断开了。
这时可以建立一个MVC的应用程序,编译后找到它的bin目录,会看到其中包含一个*.View.dll文件。
使用反编译软件,比如dotPeek,查看里面的内容,会找到一些由cshtml文件生成的类。
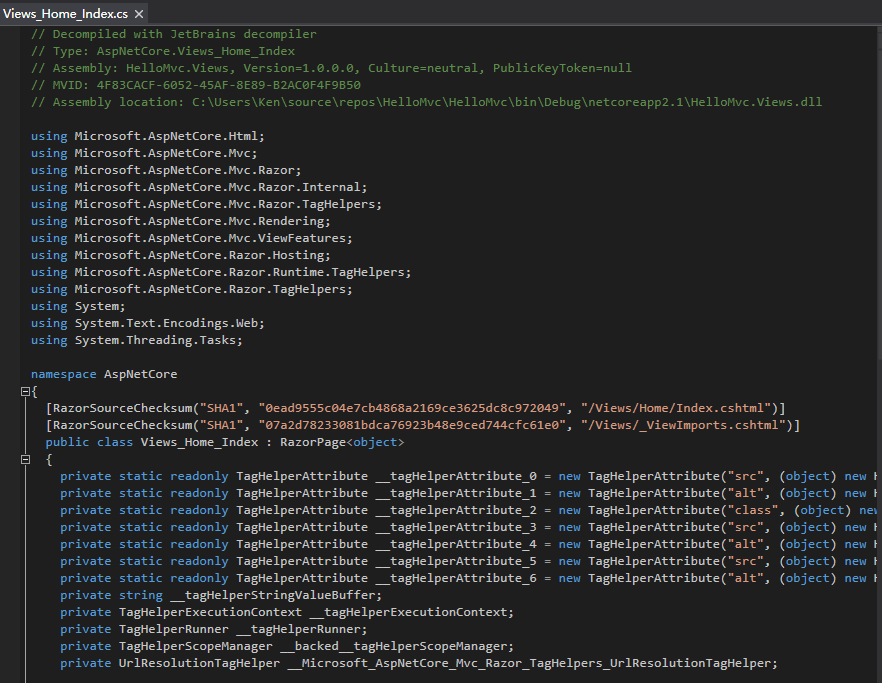
以其中Views_Home_Index为例,其实际上为RazorPage<TModel>的一个实现类。
它内部的ExecuteAsync方法正是生成页面内容的关键。
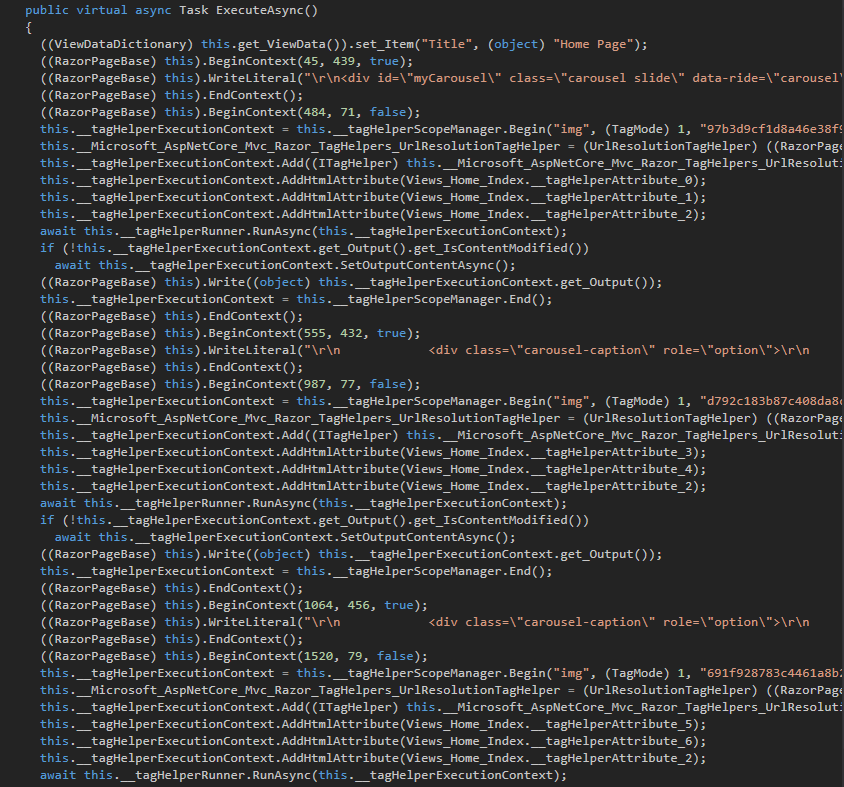
因为是VS模板自动生成的页面,上面的代码十分冗杂。为了更清晰地检查核心的代码,不妨减少下页面的复杂度。
把index.cshtml文件内容改成如下:
@{
ViewData["Title"] = "Home Page";
Layout = null;
}
<p>Hello World!</p>
再次编译后,可以看到ExecuteAsync方法的内容变成了下面的样子:
public virtual async Task ExecuteAsync()
{
((ViewDataDictionary) this.get_ViewData()).set_Item("Title", (object) "Home Page");
((RazorPageBase) this).set_Layout((string) null);
((RazorPageBase) this).BeginContext(65, 21, true);
((RazorPageBase) this).WriteLiteral("
<p>Hello World!</p>");
((RazorPageBase) this).EndContext();
}
不难看出,最终展现的页面内容便是通过RazorPageBase类的WriteLiteral方法生成的。