1.将列表转换为矩阵的方法:np.array()
import numpy as np array = np.array([[1, 2, 3],[2, 3, 4]])
2.numpy的属性:ndim, shape, size

ndim:空间维数, shape:几行几列, size:元素个数
3.numpy数组的reshape
numpy一维数组转高维数组通过reshape实现:

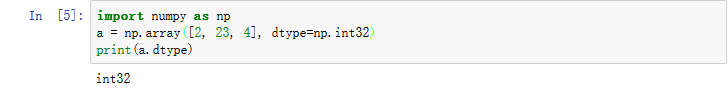
4.type(a)只是数组,要查a中的元素的类型用a.dtype。

5. 如果是多维数组,用逗号隔开index,但逗号前的内容不能省略。


6.高维数组可以用...省略内容:

7. 转置:.T 深拷贝:.copy() 视图:.view() 取整:np.floor()
8.改变数组形状:
(1).Splitting:(拆分)

(2)a.shape = 6, -1与a.shape = 6, 2的结果相同
.
(3).reshape()

9.数组中切片操作:

10.数组的拆分:split将会等分数组为指定的份数

11.数组的布尔运算

有all就应该有any,测试数组中是否全True和是否有True。
12.np.zeros(()),np.ones(()),np.eyes(())
np.empty(()):生成几乎接近于0的矩阵。
np.arange(10, 20, 2):生成有序的数列或矩阵,包括起始值10,终止值20,步长2。
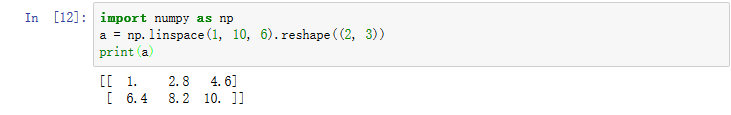
np.linspace(1, 10, 6).reshape((2, 3)):生成矩阵,包括起始值1,终止值10,其中6个数等距。
13.numpy中的乘法分两种:1.逐个相乘;2.矩阵中的乘法np.dot(a, b)或a.dot(b)

14.数组的生成
import numpy as np a = [[1,2], [3,4]], [[5,6], [7,8]] b = [1,2],[3,4],[5,6],[7,8] c = [[1,2,3,4], [5,6,7,8]] arr2 = np.array(a) arr3 = np.array(b) arr4 = np.array(c) print(arr2) print(arr2.shape) print("-"*10) print(arr3) print("-"*10) print(arr4)
[[[1 2] [3 4]] [[5 6] [7 8]]] (2, 2, 2) ---------- [[1 2] [3 4] [5 6] [7 8]] ---------- [[1 2 3 4] [5 6 7 8]]
15. 创建布尔数组
# np.full第一个参数是数组的形状,第二个参数是数组中填充的常数。 arr7 = np.full((3,3), True) print(arr7)
[[ True True True] [ True True True] [ True True True]]
16. 垂直叠加两个数组
# reshape参数设置为-1将自动决定cols的数量 a = np.arange(10).reshape(2,-1) b = np.repeat(1, 10).reshape(2,-1) print(a) print(b) # 垂直叠加两个数组 # 方法1 c = np.vstack([a, b]) print(c) # 方法2 c = np.concatenate([a, b], axis=0) print(c) # 方法3 c = np.r_[a, b] print(c)
[[0 1 2 3 4] [5 6 7 8 9]] [[1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1]] [[0 1 2 3 4] [5 6 7 8 9] [1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1]] [[0 1 2 3 4] [5 6 7 8 9] [1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1]] [[0 1 2 3 4] [5 6 7 8 9] [1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1]]
17. 水平叠加两个数组
a = np.arange(10).reshape(2,-1) b = np.repeat(1, 10).reshape(2,-1) print(a) print(b) # 垂直叠加两个数组 # 方法1 c = np.hstack([a, b]) print(c) # 方法2 c = np.concatenate([a, b], axis=1) print(c) # 方法3 c = np.c_[a, b] print(c)
[[0 1 2 3 4] [5 6 7 8 9]] [[1 1 1 1 1] [1 1 1 1 1]] [[0 1 2 3 4 1 1 1 1 1] [5 6 7 8 9 1 1 1 1 1]] [[0 1 2 3 4 1 1 1 1 1] [5 6 7 8 9 1 1 1 1 1]] [[0 1 2 3 4 1 1 1 1 1] [5 6 7 8 9 1 1 1 1 1]]
18. np.intersect1d():获取两个数组的公共项
a = np.array([1,2,3,2,3,4,3,4,5,6]) b = np.array([7,2,10,2,7,4,9,4,9,8]) c = np.intersect1d(a, b) # intersect相交,交叉 print(c)
[2 4]
19. np.setdiff1d():从一个数组中删除存在于另一个数组的项
a = np.array([1,2,3,4,5]) b = np.array([5,6,7,8,9]) c = np.setdiff1d(a, b) # setdiff求两个集合的差集 print(c)
[1 2 3 4]
20. 得到两个数组元素匹配的位置
import numpy as np a = np.array([1,2,3,2,3,4,3,4,5,6]) b = np.array([7,2,10,2,7,4,9,4,9,8]) c = np.where(a==b) print(c)
(array([1, 3, 5, 7], dtype=int64),)
21. np.where()提取给定范围的所有数字
# 方法1 a = np.array([2,6,1,9,10,3,27]) index = np.where((a>5) & (a<=10)) print(a[index]) # 方法2 print(a[(a>=5) & (a<=10)])
[ 6 9 10] [ 6 9 10]
22. 交换二维数组中的两列
arr = np.arange(9).reshape(3,3) print(arr) arr1 = arr[:, [1,0,2]] print(arr1)
[[0 1 2] [3 4 5] [6 7 8]] [[1 0 2] [4 3 5] [7 6 8]]
23. python中[-1]、[:-1]、[::-1]、[2::-1]的使用
import numpy as np a=[1,2,3,4,5] print(a) print(a[-1]) #取最后一个元素 print(a[:-1]) # 除了最后一个取全部 print(a[::-1]) # 取从后向前(相反)的元素 print(a[2::-1]) # 取从下标为2的元素翻转读取
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5] 5 [1, 2, 3, 4] [5, 4, 3, 2, 1] [3, 2, 1]
24. 翻转二维数组的行
arr = np.arange(16).reshape(4,4) print(arr) arr1 = arr[::-1] # 取从后向前(相反)的元素 print(arr1)
[[ 0 1 2 3] [ 4 5 6 7] [ 8 9 10 11] [12 13 14 15]] [[12 13 14 15] [ 8 9 10 11] [ 4 5 6 7] [ 0 1 2 3]]
25. 翻转二维数组的列
arr = np.arange(16).reshape(4,4) print(arr) arr1 = arr[:, ::-1] print(arr1)
[[ 0 1 2 3] [ 4 5 6 7] [ 8 9 10 11] [12 13 14 15]] [[ 3 2 1 0] [ 7 6 5 4] [11 10 9 8] [15 14 13 12]]
26. 创建[5,10)之间随机的二维数组
# 方法1 rand_arr = np.random.randint(low=5, high=10, size=(5,3)) + np.random.random((5,3)) # 生成5行 3列的浮点数,浮点数是从0-1中随机选择的 print(rand_arr) # 方法2 rand_arr = np.random.uniform(5,10,size=(5,3)) print(rand_arr)
[[ 6.1884914 9.88947032 5.31471845] [ 9.1859768 6.23840208 7.91602235] [ 9.27039021 5.71907495 7.71486389] [ 7.46502435 7.72722806 5.64604085] [ 6.7771569 7.87865787 6.09320748]] [[ 9.48594409 8.31390899 9.39036005] [ 5.11131931 7.81656875 9.14889476] [ 8.49732953 6.9615949 6.81419116] [ 9.0902507 7.4133782 9.62354346] [ 5.68558493 7.47428098 7.495766 ]]
27. 通过e式科学记数法打印numpy数组
import numpy as np np.set_printoptions(suppress=False) np.random.seed(10) # 生成同一个随机数 rand_arr = np.random.random([3,3])/1e3 print(rand_arr)
[[ 7.71320643e-04 2.07519494e-05 6.33648235e-04] [ 7.48803883e-04 4.98507012e-04 2.24796646e-04] [ 1.98062865e-04 7.60530712e-04 1.69110837e-04]]
np.set_printoptions(suppress=True) np.random.seed(10) rand_arr = np.random.random([3,3])/1e3 print(rand_arr)
[[ 0.00077132 0.00002075 0.00063365] [ 0.0007488 0.00049851 0.0002248 ] [ 0.00019806 0.00076053 0.00016911]]
28. 限制numpy数组中打印的项目数
np.set_printoptions(threshold=6) # 限制为最多6个元素。 print(arr) np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.nan) # 完整的数组元素而不被截断 print(arr)
[ 0 1 2 ..., 12 13 14] [ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14]