1.1 Linux命令行概述
1.2 在Linux命令行下查看命令帮助
1.3 Linux关机、重启、注销命令
1.4 老男孩的运维思想
1.1 Linux命令行概述
1.1.1 Linux命令行的作用与意义
Linux是一个主要通过命令来进行管理的操作系统。
1.1.2 Linux命令行介绍
1)通过SSH工具远程连接阿里云ECS服务器,如Xshell;

2)使用阿里云Web控制台-远程连接ECS服务器
3)CentOS Linux命令行退出命令操作的界面
1.1.3 Linux命令行常用快捷键
常见的Linux远程连接工具:SecureCRT、Xshell客户端软件;
1)最有用的快捷键;
- tab 命令自动补全快捷键;
2)移动光标快捷键;
- Ctrl +a
- Ctrl + e
- Ctrl + f
- Ctrl + b
3)剪切、粘贴、清除快捷键;
- Ctrl + Insert
- Shift + Insert
- Ctrl + k
- Ctrl + u
- Ctrl + w
- Ctrl + y
- Ctrl + e
- Ctrl + h
4)重复执行命令快捷键
- Ctrl + d
- Ctrl + r
- Ctrl + g
5)控制快捷键
- Ctrl + l
- Ctrl + s
- Ctrl + q
- Ctrl + z
6)!开头的快捷键
- !!
- !pw
- !pw:p
- !num(指数字)
- !$
7)Esc相关
- Esc + .
- Esc + b
- Esc + f
1.2 在Linux命令行下查看命令帮助
1.2.1 使用man获取命令帮助信息
1)man命令的基本用法
man命令是LInux系统中最核心的命令之一,可通过其查看其它Linux命令的使用、用法信息。还可查看软件服务配置文件、系统调用、库函数等帮助信息;
2) 语法格式
man 参数选项 命令/文件
3)选项说明
- User Commands 用户命令相关
- System calls 系统函数调用
- C Library Function C的库函数相关
- Device and Special Files 设备和特殊文件相关
- File Formats and Conventions 文件格式和规划
- Games et.AI 游戏及其他
- Miscellanea 宏、包及其他杂项
- System Administration tools and Deamons 系统管理员命令和进程
4)实战举例
man man
man cp
man ls

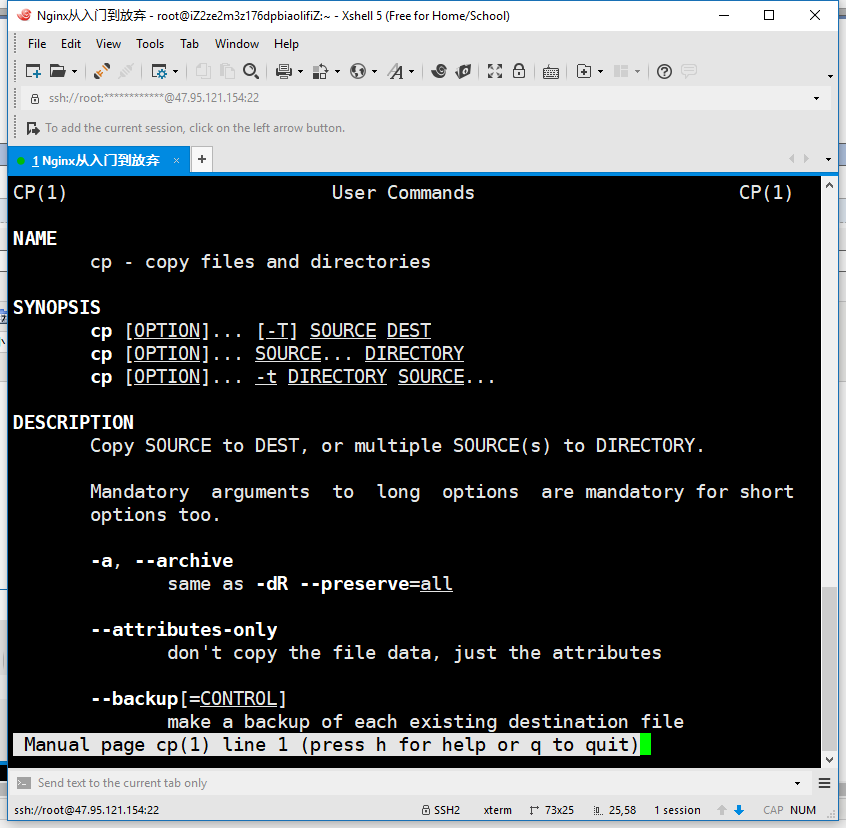

5) man帮助页的快捷键
- Page Down
- Page Up
- Home
- End
- /cuixiaozhao
- ?cuixiaozhao
- n,N
- q
1.2.2 使用--help参数获取命令帮助信息
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# cat --help Usage: cat [OPTION]... [FILE]... Concatenate FILE(s), or standard input, to standard output. -A, --show-all equivalent to -vET
-b, --number-nonblank number nonempty output lines, overrides -n
-e equivalent to -vE
-E, --show-ends display $ at end of each line
-n, --number number all output lines
-s, --squeeze-blank suppress repeated empty output lines
-t equivalent to -vT
-T, --show-tabs display TAB characters as ^I
-u (ignored)
-v, --show-nonprinting use ^ and M- notation, except for LFD and TAB
--help display this help and exit
--version output version information and exitWith no FILE,
or when FILE is -, read standard input.Examples:
- g Output f's contents, then standard input, then g's contents.
cat f
cat Copy standard input to standard output.GNU coreutils online help:
<http://www.gnu.org/software/coreutils/>
For complete documentation, run: info coreutils 'cat invocation'
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# more --help
more: unknown option -help
Usage: more [options] file...Options:
-d display help instead of ring bell
-f count logical, rather than screen lines
-l suppress pause after form feed
-p do not scroll, clean screen and display text
-c do not scroll, display text and clean line ends
-u suppress underlining
-s squeeze multiple blank lines into one
-NUM specify the number of lines per screenful
+NUM display file beginning from line number NUM
+/STRING display file beginning from search string match
-V output version information and exit
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]#
小结:
- 命令 --help 获取的是常用帮助信息;
- man 命令 获取的更多更复杂的帮助信息;
1.2.3 使用help命令获取bash内置命令帮助
BASH_BUILTINS(1) General Commands Manual BASH_BUILTINS(1)NAME
break, builtin, caller, cd, command, compgen, complete, compopt, continue, declare, dirs, disown, echo, enable, eval, exec, exit, export, false, fc, fg, getopts, hash, help, history, jobs, kill, let, local, logout, mapfile,
bash, :, ., [, alias, bg, bind,
popd, printf, pushd, pwd, read, readonly, return, set, shift, shopt, source, suspend, test, times, trap, true, type, typeset, ulimit, umask, unalias, unset, wait - bash built-in commands, see bash(1)BASH BUILTIN COMMANDS
in this section as accepting options preceded by - accepts -- to signify the end of the options. The :, true, false, and test builtins do not accept options and do not treat -- specially. The exit,
Unless otherwise noted, each builtin command documented
logout, break, continue, let, and shift builtins accept and process arguments beginning with - without requiring --. Other builtins that accept arguments but are not specified as accepting options interpret arguments beginning with - as invalid options
and require -- to prevent this interpretation.
: [arguments]
No effect; the command does nothing beyond expanding arguments and performing any specified redirections. A zero exit code is returned.
举例如下:
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# help cd cd: cd [-L|[-P [-e]]] [dir] Change the shell working directory.Exit Status: Returns 0 if the directory is changed, and if $PWD is set successfully when -P is used; non-zero otherwise. [root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# help history history: history [-c] [-d offset] [n] or history -anrw [filename] or history -ps arg [arg...] Display or manipulate the history list.Change the current directory to DIR. The default DIR </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span><span style="color: #000000;"> the value of the HOME shell variable. The variable CDPATH defines the search path </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">for</span><span style="color: #000000;"> the directory containing DIR. Alternative directory names </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">in</span><span style="color: #000000;"> CDPATH are separated by a colon (:). A null directory name </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span><span style="color: #000000;"> the same as the current directory. If DIR begins with a slash (</span>/), then CDPATH <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span><span style="color: #000000;"> used. If the directory </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span> found, <span style="color: #0000ff;">and</span> the shell option `cdable_vars<span style="color: #800000;">'</span><span style="color: #800000;"> is set,</span> the word <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span><span style="color: #000000;"> assumed to be a variable name. If that variable has a value, its value </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> used <span style="color: #0000ff;">for</span><span style="color: #000000;"> DIR. Options: </span>-<span style="color: #000000;">L force symbolic links to be followed </span>-<span style="color: #000000;">P use the physical directory structure without following symbolic links </span>-e <span style="color: #0000ff;">if</span> the -P option <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> supplied, <span style="color: #0000ff;">and</span><span style="color: #000000;"> the current working directory cannot be determined successfully, exit with a non</span>-<span style="color: #000000;">zero status The default </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> to follow symbolic links, as <span style="color: #0000ff;">if</span> `-L<span style="color: #800000;">'</span><span style="color: #800000;"> were specified.</span>Options: -c clear the history list by deleting all of the entries -d offset delete the history entry at offset OFFSET.Display the history list with line numbers, prefixing each modified entry with a `</span>*<span style="color: #800000;">'</span><span style="color: #800000;">. An argument of N lists only the last N entries.</span></span>-a append history lines <span style="color: #0000ff;">from</span><span style="color: #000000;"> this session to the history file </span>-n read all history lines <span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span> already read <span style="color: #0000ff;">from</span><span style="color: #000000;"> the history file </span>-r read the history file <span style="color: #0000ff;">and</span><span style="color: #000000;"> append the contents to the history list </span>-<span style="color: #000000;">w write the current history to the history file </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">and</span><span style="color: #000000;"> append them to the history list </span>-p perform history expansion on each ARG <span style="color: #0000ff;">and</span><span style="color: #000000;"> display the result without storing it </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">in</span><span style="color: #000000;"> the history list </span>-<span style="color: #000000;">s append the ARGs to the history list as a single entry If FILENAME </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> given, it <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span><span style="color: #000000;"> used as the history file. Otherwise, </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">if</span> $HISTFILE has a value, that <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> used, <span style="color: #0000ff;">else</span> ~/<span style="color: #000000;">.bash_history. If the $HISTTIMEFORMAT variable </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> set <span style="color: #0000ff;">and</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span> null, its value <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span><span style="color: #000000;"> used as a format string </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">for</span> strftime(3) to <span style="color: #0000ff;">print</span><span style="color: #000000;"> the time stamp associated with each displayed history entry. No time stamps are printed otherwise. Exit Status: Returns success unless an invalid option </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> given <span style="color: #0000ff;">or</span><span style="color: #000000;"> an error occurs.[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ
~]#
1.2.4 使用info获取帮助信息
- info ls
- info cd
- info man
1.2.5 通过互联网寻求帮助信息
搜索引擎的使用优先顺序(建议)
www.google.com ->www.bing.com ->www.baidu.com
1.3 Linux关机、重启、注销命令
1.3.1 重启或关机命令:shutdown
shutdown总体来讲,是一个用来安全关闭或重启Linux系统的命令。
与shutdown功能类似的有init halt poweroff reboot
SHUTDOWN(8) shutdown SHUTDOWN(8)NAME
- Halt, power-off or reboot the machine
shutdownSYNOPSIS
shutdown [OPTIONS...] [TIME] [WALL...]DESCRIPTION
-off or reboot the machine.
shutdown may be used to halt, powerThe first argument may be a time string (which </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> usually <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">now</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span>). Optionally, this may be followed by a wall message to be sent to all logged-<span style="color: #0000ff;">in</span><span style="color: #000000;"> users before going down. The time string may either be </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">in</span> the format <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">hh:mm</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">for</span> hour/minutes specifying the time to execute the shutdown at, specified <span style="color: #0000ff;">in</span> 24h clock format. Alternatively it may be <span style="color: #0000ff;">in</span> the syntax <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">+m</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span> referring to the specified number of minutes m <span style="color: #0000ff;">from</span> now. <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">now</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> an alias <span style="color: #0000ff;">for</span> <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">+0</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span>, i.e. <span style="color: #0000ff;">for</span> triggering an immediate shutdown. If no time argument <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> specified, <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">+1</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span><span style="color: #000000;"> implied. Note that to specify a wall message you must specify a time argument, too. If the time argument </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> used, 5 minutes before the system goes down the /run/nologin file <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> created to ensure that further logins shall <span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span><span style="color: #000000;"> be allowed.OPTIONS
The following options are understood:</span>--<span style="color: #000000;">help Print a short help text </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">and</span><span style="color: #000000;"> exit. </span>-H, --<span style="color: #000000;">halt Halt the machine. </span>-P, --<span style="color: #000000;">poweroff Power</span>-<span style="color: #000000;">off the machine (the default). </span>-r, --<span style="color: #000000;">reboot Reboot the machine. </span>-<span style="color: #000000;">h Equivalent to </span>--poweroff, unless --halt <span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span><span style="color: #000000;"> specified. </span>-<span style="color: #000000;">k Do </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span> halt, power-<span style="color: #000000;">off, reboot, just write wall message. </span>--no-<span style="color: #000000;">wall Do </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span> send wall message before halt, power-<span style="color: #000000;">off, reboot. </span>-<span style="color: #000000;">c Cancel a pending shutdown. This may be used cancel the effect of an invocation of shutdown with a time argument that </span><span style="color: #0000ff;">is</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">not</span> <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">+0</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span> <span style="color: #0000ff;">or</span> <span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #800000;">now</span><span style="color: #800000;">"</span><span style="color: #000000;">.EXIT STATUS
is returned, a non-zero failure code otherwise.
On success, 0SEE ALSO
1), systemctl(1), halt(8), wall(1)
systemd(Manual page shutdown(
8) line 1 (press h for help or q to quit)
shutdown实战举例
- shutdown -h +1 #一分钟后关闭Linux操作系统
- shutdown -c #取消shutdown操作
- shutdown -r 11:11 #11:11重启Linux系统
- shutdown -h now#now即现在,立刻关闭操作系统
1.3.2 关机与重启命令:halt/poweroff/reboot
从Redhat或CentOS6开始,这三者对应的man帮助信息都是同一个,而halt和poweroff命令是reboot命令的链接文件;
- reboot 选项
- halt 选项
- poweroff 选项
通常情况下,该3命令都不带任何参数
[root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# ls /sbin/poweroff /sbin/poweroff [root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# ls /sbin/halt /sbin/halt [root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# ls /sbin/reboot /sbin/reboot [root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# ls -l /sbin/poweroff lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 16 Oct 15 2017 /sbin/poweroff -> ../bin/systemctl [root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# ls -l /sbin/halt lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 16 Oct 15 2017 /sbin/halt -> ../bin/systemctl [root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]# ls -l /sbin/reboot lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 16 Oct 15 2017 /sbin/reboot -> ../bin/systemctl [root@iZ2ze2m3z176dpbiaolifiZ ~]#
1.3.3 关机、重启和注销的命令列表
1)关机命令
- shutdown -h now
- shutdown -h +1
- halt
- init 0
- poweroff
2)重启命令
- reboot
- shutdown -r now
- shutdown -r +1
- init 6
3)注销命令
- logout
- exit
- Ctrl + d(本质就是logout)
1.4 老男孩的运维思想
基础不牢,地动山摇!很多高大上的技术都是由细小的基础知识累积而成的!
Linux命令正是组成Linux系统最核心的、重要的基础之一。牢牢掌握基础命令,方能在日后使用Linux时随心所欲。
