序言
平时在布局中较多使用px和%设置大小或者尺寸,但是在有些场景仅使用这两个显然不行,虽然平时使用时仅仅调理出差强人意的效果,没有细细把控各个属性的具体内涵。CSS中的尺寸(长度)单位有px、em、rem、%、vw、vh、vm,其中rem、vw、vh、vm(兼容性太差,不讲)为CSS3新增内容。CSS3已完全向后兼容,所以你就不必改变现有的设计。浏览器将永远支持CSS2。另外我们需要了解浏览器的默认字体高都是16px(也有说14px),下面会用到,由于1em默认等于浏览器默认值14或16px,那么咱们可以用如下代码测试。
<div style=" 256px; height: 100px; background: pink;">我宽是16 * 16px</div> <div style=" 16em; height: 100px; background: red;">我宽是16 * 1em</div> <div style=" 224px; height: 100px; background: green;">我宽是16 * 14px</div>
执行结果
从结果可以看出你当前浏览器默认的字体大小是多少px。我们后面默认浏览器的默认字体大小为16px(上方结果是当前浏览器渲染的结果,可能16px不是你当前浏览器的默认值)。
关于px在浏览器中真的就代表一个物理像素么,可以参考这篇文章:传送门
正文
1、px
单位名称为像素,相对长度单位,像素(px)是相对于显示器屏幕分辨率而言的,是我们网页设计常用的单位,也是基本单位。通过px可以设置固定的布局或者元素大小,缺点是没有弹性。相对长度单 位,像素(Pixels)
1in = 2.54cm = 25.4 mm = 101.6q = 72pt = 6pc = 96px
CSS长度单位px-CSS大小px详解,演示代码如下
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="zh-cn"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8" /> <title>CSS长度单位px-CSS大小px详解</title> <meta name="author" content="Joy Du(飘零雾雨), dooyoe@gmail.com, www.doyoe.com" /> <style> h1{margin:10px 0;font-size:16px;} ul{margin:0;padding:0;list-style:none;} li{margin-top:8px;background:#ccc;} .in{width:1in;} .pt{width:72pt;} .pc{width:6pc;} .px{width:96px;} .cm{width:2.54cm;} .mm{width:25.4mm;} </style> </head> <body> <h1>单位转换对比:</h1> <ul> <li class="in">1in</li> <li class="pt">72pt</li> <li class="pc">6pc</li> <li class="px">96px</li> <li class="cm">2.54cm</li> <li class="mm">25.4mm</li> </ul> <p>1in = 2.54cm = 25.4 mm = 72pt = 6pc = 96px</p> </body> </html>
运行结果:
单位转换对比:
- 1in
- 72pt
- 6pc
- 96px
- 2.54cm
- 25.4mm
1in = 2.54cm = 25.4 mm = 72pt = 6pc = 96px
2、pt
点(Points)。绝对长度单位。页面开发一般不用,具体的换算关系可以查看同px中列出的公式。下方演示的是1pt大小的文字和div
我的font-size为1PT
我的font-size为10PT
我的font-size为72PT
3、em
Em 相对长度单位,这里em与html <em>标签的"EM"拼写完全相同,而这里em作为单独文本单位。参考物是父元素的font-size,具有继承的特点。如果自身定义了font-size按自身来计算(浏览器默认字体是16px),整个页面内1em不是一个固定的值。
特点
- 1. em的值并不是固定的;
- 2. em会继承父级元素的字体大小。
演示代码如下:
<h2>测试em属性的特点</h2> <div> <p style="color: red">验证默认</p> <div style="font-size: 1em">父未定义font-size 此为1em字体</div> <div style="font-size: 2em">父未定义font-size 此为2em字体</div> <p style="color: red">验证比例</p> <div style="font-size: 1em"> <div style="font-size: 1em">当前元素父定义了font-size=1em 此为1em字体</div> <div style="font-size: 2em">当前元素父定义了font-size=1em 此为2em字体</div> </div> <br> <div style="font-size: 2em"> <div style="font-size: 1em">当前元素父定义了font-size=2em 此为1em字体</div> <div style="font-size: 2em">当前元素父定义了font-size=2em 此为2em字体</div> </div> <p style="color: red">验证继承</p> <div style="font-size: 2em"> <div> <div style="font-size: 1em">父未定义font-size 此为1em字体</div> <div style="font-size: 2em">父未定义font-size 此为2em字体</div> </div> </div> </div>
执行效果如下:
测试em属性的特点
验证默认
验证比例
验证继承
高级操作:任意浏览器的默认字体高度16px(16像素)。所有未经调整的浏览器都符合: 1em=16px。那么12px=0.75em,10px=0.625em。为了简化font-size的换算,需要在css中的body选择器中声明font-size=62.5%,这就使em值变为 16px*62.5%=10px, 这样12px=1.2em, 10px=1em, 也就是说只需要将你的原来的px数值除以10,然后换上em作为单位就行了。由于em的值具有传递性和继承性,所以在使用的时候务必要留意层次结构。
4、rem
rem是CSS3新增的一个相对单位(root em,根em),这个单位引起了广泛关注。这个单位与em有什么区别呢?区别在于使用rem为元素设定字体大小时,仍然是相对大小,但相对的只是HTML根元素。这个单位可谓集相对大小和绝对大小的优点于一身,通过它既可以做到只修改根元素就成比例地调整所有字体大小,又可以避免字体大小逐层复合的连锁反应。目前,除了IE8及更早版本外,所有浏览器均已支持rem。对于不支持它的浏览器,应对方法也很简单,就是多写一个绝对单位的声明。这些浏览器会忽略用rem设定的字体大小。如:
p {font-size:14px; font-size:.875rem;}
兼容性:
目前,IE9+,Firefox、Chrome、Safari、Opera 的主流版本都支持了rem。
就算对不支持的浏览器,应对方法也很简单,就是多写一个绝对单位的声明。这些浏览器会忽略用rem设定的字体大小。
使用%单位方便使用
css中的body中先全局声明font-size=62.5%,这里的%的算法和rem一样。
因为100%=16px,1px=6.25%,所以10px=62.5%,
这是的1rem=10px,所以12px=1.2rem。px与rem的转换通过10就可以得来,很方便了吧!
使用方法
注意,rem是只相对于根元素htm的font-size,即只需要设置根元素的font-size,其它元素使用rem单位设置成相应的百分比即可;
例子:
/*16px * 312.5% = 50px;*/ html{font-size: 312.5%;} /*50px * 0.5 = 25px;*/ body{ font-size: 0.5rem; font-size�:25px; }
一般情况下,是这样子使用的
html{font-size:62.5%;} body{font-size:12px;font-size:1.2rem ;} p{font-size:14px;font-size:1.4rem;}
rem部分参考博文:传送门
5、%
百分号使用较频繁的就是width、 height设置标签的宽高了,此时50%相当于父元素宽度的50%,height: 50%相当于父元素高度的50%。当父元素是body时,设置height:50%无效,而宽度widht:50%有效,body高度不确定,网上说高度是0导致的。
代码案例
HTML
<div class="father"> <div class="son1"> <div class="son2"></div> </div> </div>
CSS
.father{ width: 50%; height: 50%; /*设置高度无效*/ background-color: #0f0; } .son1{ width: 50%; height: 500px; background-color: yellow; } .son2{ width: 50%;/*相当于父元素的宽*/ height: 50%;/*相当于父元素的高*/ background-color: blue; } .father,.son1,.son2{ margin: 0px auto; }
执行结果
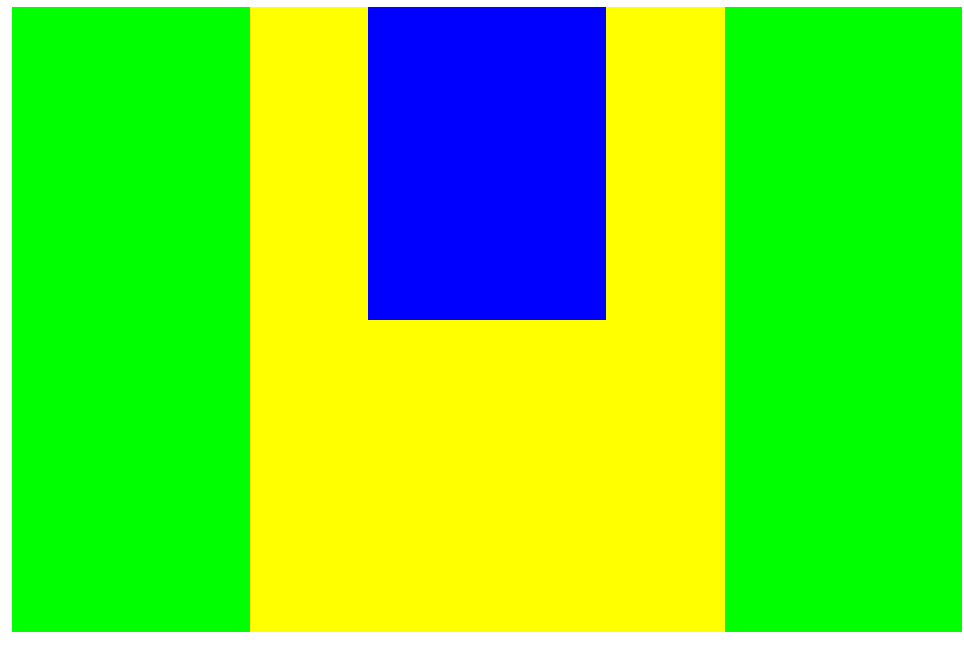
margin-top margin-right margin-bottom margin-left:40%中设置百分号都相当于父元素的宽度进行计算大小;同理同样处于盒子模型中的padding设置百分号时也是相对于父元素的宽度;w3c指出% 规定基于父元素的宽度的百分比的外边距。
html代码:
<div class="father"> <div class="son1"> <div class="son2"></div> </div> </div>
css代码:
.father{ width: 50%; height: 50%; /*设置高度无效*/ background-color: #0f0; } .son1{ width: 50%; height: 500px; background-color: yellow; border-top: 2px solid red; } .son2{ width: 50%;/*相当于父元素的宽*/ height: 50%;/*相当于父元素的高*/ background-color: blue; margin: 40% 40%;/*相当于父元素的宽度*/ /* padding-bottom: 20%;相当于父元素的宽度 } .father,.son1,.son2{ /* margin: 0px auto; */ }

border-raduis设置边界四个边界的弧度,共有8个参数来设值四个边界角的弧度,border-raduis也常用%中设置;此时如border-raduis:50% 50% 50% 50%含义border-top-left: 弧度垂直半径为该标签高度的50%,弧度水平半径为该标签宽度的50%,border-top-right、border-bottom-right、border-bottom-left同理;故由此知border-raduis中的%号是相当于当前元素的宽高来设置垂直和水平半径的。利用border-raduis这一属性,可设置出不同的形状。如半圆、椭圆、胶囊、环等、圆。
html代码:
<div class="circle"> </div> <div class="jiaonang"></div> <div class="ring"></div> <div class="halfcircle"></div>
css代码:
/* border %分号相对于自身的宽做水平半径 相当于自身的高做垂直半径 */ /* border 共有8个值 border的角弧线由垂直半径和水平半径决定,仅有一个值时垂直半径和水平半径相同*/ .circle{ width: 300px; height: 100px; background-color: red; border-radius:50%; /* border-top-left-radius: 50%; border-bottom-right-radius: 50%; border-top-right-radius: 50%; border-bottom-left-radius: 50%; */ } /* 高的一半 */ .jiaonang{ width: 200px; height:100px; background-color: #00f; border-radius: 50px; } .ring{ width: 100px; height: 100px; /* background-color: #0ff; */ border-radius: 50%; border: 30px solid #0ff; } /* 整个高 */ .halfcircle{ width: 100px; height: 50px; background-color: rgb(178, 224, 224); border-radius: 50px 50px 0px 0px ; }
运行结果:

positon:absolute定位脱离了标准的文档流(普通流),是相对最近的一个具有定位的祖先元素进行定位,所以此时设置top、bottom:50%是相对于其定位元素的高度进行计算的,left、right相对于定位元素的宽度计算的;非父元素的宽度或高度进行计算的。而positon:relative是相对于自己进行定位,故此时top、bottom:50%是相对于其父元素的高度进行计算的,left、right相对于父元素的宽度计算的
html代码:
<div class="abso"> <div class="absoSon"> <div class="absoSon2"></div> </div> </div> <div class="rela"> <div class="relaSon"></div> </div>
css代码:
.abso{ background-color: #c0c0c0; position: relative; width: 400px; height: 200px; } .absoSon{ width: 50%;/*width:200px height:100px*/ height: 50%; background-color: yellow; } .absoSon2{ width: 50%;/*未设置绝对定位前width 和height%都相当于父元素的宽高进行计算*/ height: 50%;/* 200px height: 100px*/ background-color: skyblue; position: absolute; /*设置绝对定位后相对于距离其最近的具有定位的祖先元素进行定位,此时所有的%规则都应相对于定位的祖先元素设置,*/ top: 50%;/*如width height%相对于定位元素的宽高进行设置 top bottom%相当于定位元素的高进行计算 left right%相当于定位元素的宽进行计算*/ left: 50%; /* margin-left: -50%;即200px 相对定位元素的宽度进行设置 */ /* margin-top: -50%; 200px */ } .rela{ border: 3px red solid; background-color: #c0c0c0; width: 400px; height: 200px; } .relaSon{ background-color: yellow; width: 50%; height: 50%; position: relative; top: 50%;/*top bottom 相当于父元素的高进行计算*/ left:50%;/*left right相当于父元素的宽进行计算*/ }
运行结果:

总结使用百分号%:
- width、height、relative:width相对于父元素的宽;height相对于父元素的高进行计算。relative:top、bottom相对父元素的高;left 、right相对于父元素的宽进行计算。
- border-raudis:相对自身标签的宽高设置每个边角的垂直和水平半径。
- margin: left、right、top、bottom相当于父元素的宽度进行
- absolute:top、bottom相对定位元素的高;left 、right相对于定位元素的宽进行计算。同时位于absolute中的其他属性如width heiht margin等都相当于定位元素进行计算。
- line-hight设置内联元素垂直居中时,%相对于文本的行高进行计算,非父元素。
%部分参考博文:传送门
6、vw与vh
视口单位(Viewport units)
什么是视口?
在PC端,视口指的是在PC端,指的是浏览器的可视区域;
而在移动端,它涉及3个视口:Layout Viewport(布局视口),Visual Viewport(视觉视口),Ideal Viewport(理想视口)。
视口单位中的“视口”,PC端指的是浏览器的可视区域;移动端指的就是Viewport中的Layout Viewport。
根据CSS3规范,视口单位主要包括以下4个:
1.vw:1vw等于视口宽度的1%。
2.vh:1vh等于视口高度的1%。
3.vmin:选取vw和vh中最小的那个。
4.vmax:选取vw和vh中最大的那个。
vh and vw:相对于视口的高度和宽度,而不是父元素的(CSS百分比是相对于包含它的最近的父元素的高度和宽度)。1vh 等于1/100的视口高度,1vw 等于1/100的视口宽度。
比如:浏览器高度950px,宽度为1920px, 1 vh = 950px/100 = 9.5 px,1vw = 1920px/100 =19.2 px。
vmax相对于视口的宽度或高度中较大的那个。其中最大的那个被均分为100单位的vmax。
vmin相对于视口的宽度或高度中较小的那个。其中最小的那个被均分为100单位的vmin。

vh/vw与%区别

请看下面简单的栗子:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge"> <title>VW&VH</title> </head> <style> * { padding: 0; margin: 0 } .left { float: left; width: 50vw; height: 20vh; background-color: blue; text-align: center; line-height: 20vh; font-size: 3rem } .right { float: right; width: 50vw; height: 20vh; background-color: green; text-align: center; line-height: 20vh; font-size: 3rem } </style> <body> <div class="left">left</div> <div class="right">right</div> </body> </html>
兼容性问题(在移动端 iOS 8 以上以及 Android 4.4 以上获得支持,并且在微信 x5 内核中也得到完美的全面支持)


vw和vh参考博文:传送门