At the children's day, the child came to Picks's house, and messed his house up. Picks was angry at him. A lot of important things were lost, in particular the favorite sequence of Picks.
Fortunately, Picks remembers how to repair the sequence. Initially he should create an integer array a[1], a[2], ..., a[n]. Then he should perform a sequence of m operations. An operation can be one of the following:
- Print operation l, r. Picks should write down the value of
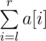 .
. - Modulo operation l, r, x. Picks should perform assignment a[i] = a[i] mod x for each i (l ≤ i ≤ r).
- Set operation k, x. Picks should set the value of a[k] to x (in other words perform an assignment a[k] = x).
Can you help Picks to perform the whole sequence of operations?
The first line of input contains two integer: n, m (1 ≤ n, m ≤ 105). The second line contains n integers, separated by space: a[1], a[2], ..., a[n] (1 ≤ a[i] ≤ 109) — initial value of array elements.
Each of the next m lines begins with a number type 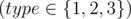 .
.
- If type = 1, there will be two integers more in the line: l, r (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n), which correspond the operation 1.
- If type = 2, there will be three integers more in the line: l, r, x (1 ≤ l ≤ r ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 2.
- If type = 3, there will be two integers more in the line: k, x (1 ≤ k ≤ n; 1 ≤ x ≤ 109), which correspond the operation 3.
For each operation 1, please print a line containing the answer. Notice that the answer may exceed the 32-bit integer.
5 5
1 2 3 4 5
2 3 5 4
3 3 5
1 2 5
2 1 3 3
1 1 3
8
5
10 10
6 9 6 7 6 1 10 10 9 5
1 3 9
2 7 10 9
2 5 10 8
1 4 7
3 3 7
2 7 9 9
1 2 4
1 6 6
1 5 9
3 1 10
49
15
23
1
9
Consider the first testcase:
- At first, a = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}.
- After operation 1, a = {1, 2, 3, 0, 1}.
- After operation 2, a = {1, 2, 5, 0, 1}.
- At operation 3, 2 + 5 + 0 + 1 = 8.
- After operation 4, a = {1, 2, 2, 0, 1}.
- At operation 5, 1 + 2 + 2 = 5.
思路:
暴力取模,减下枝就好了,
对某个区间取模,如果要取模的值大于当前区间的最大值就没必要取模了,可以直接跳过
因为每次他小于区间最大值那么一定会有一部分大于剩余区间的最大值,这部分剩余区间就可以跳过了,一步一步跑到叶子结点就全部更新完毕了
由线段树的遍历方式可知这种方法复杂度是logn的,可以过这道题
实现代码:
#include<bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; #define ll unsigned long long #define lson l,m,rt<<1 #define rson m+1,r,rt<<1|1 #define mid ll m = (l + r) >> 1 const ll M = 1e5+10maxx[rt] = c;; ll sum[M<<2]; ll maxx[M<<2]; void pushup(ll rt){ sum[rt] = sum[rt<<1] + sum[rt<<1|1]; maxx[rt] = max(maxx[rt<<1] , maxx[rt<<1|1]); } void build(ll l,ll r,ll rt){ if(l == r){ cin>>sum[rt]; maxx[rt] = sum[rt]; return ; } mid; build(lson); build(rson); pushup(rt); } void update1(ll L,ll R,ll c,ll l,ll r,ll rt){ //cout<<"maxx: "<<maxx[rt]<<endl; if(maxx[rt] < c) return ; if(l == r){ //cout<<"rt: "<<rt<<" "; sum[rt]%=c; maxx[rt]%=c; //cout<<"sum[rt]: "<<sum[rt]<<endl; return ; } mid; if(L <= m) update1(L,R,c,lson); if(R > m) update1(L,R,c,rson); pushup(rt); } void update2(ll p,ll c,ll l,ll r,ll rt){ if(l == r){ sum[rt] = c; maxx[rt] = c; return ; } mid; if(p <= m) update2(p,c,lson); if(p > m) update2(p,c,rson); pushup(rt); } ll query(ll L,ll R,ll l,ll r,ll rt){ if(L <= l&&R >= r){ return sum[rt]; } mid; ll ret = 0; if(L <= m) ret += query(L,R,lson); if(R > m) ret += query(L,R,rson); return ret; } int main() { ll n,q,l,r,d,x; ios::sync_with_stdio(0); cin.tie(0); cout.tie(0); cin>>n>>q; build(1,n,1); while(q--){ cin>>x; if(x==1){ cin>>l>>r; cout<<query(l,r,1,n,1)<<endl; } else if(x == 2){ cin>>l>>r>>d; update1(l,r,d,1,n,1); } else{ cin>>l>>r; update2(l,r,1,n,1); } //for(ll i = 0;i < n*4;i++) // cout<<sum[i]<<" "; //cout<<endl; } return 0; }