题目可在vj上提交:https://vjudge.net/problem/SPOJ-COT2
题意翻译
- 给定 n 个结点的树,每个结点有一种颜色。
- m 次询问,每次询问给出 u,v,回答 u,v 之间的路径上的结点的不同颜色数。
- 1<=n<=4e4, 1<=m<=1e5
输入输出样例
输入 #1
8 2 105 2 9 3 8 5 7 7 1 2 1 3 1 4 3 5 3 6 3 7 4 8 2 5 7 8
输出 #1
4 4
题解:
树上莫队需要用到欧拉序
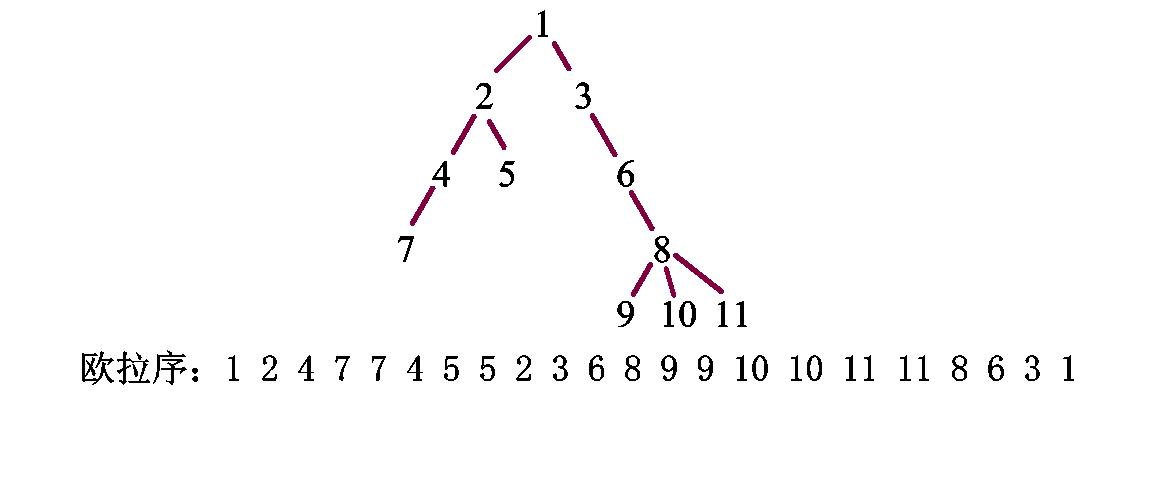
欧拉序就是第一次遇见x结点的时候把它放到数组里面,最后x子节点遍历完之后再把x放入数组
void dfs(int x) { ord[++len]=x; //第一次遇见的时候放入数组 first[x]=len; //first和second数组是记录某个数在欧拉序中第一次出现和第二次出现的位置 for(int i=head[x];i;i=e[i].next) { int to=e[i].to; if(to==fa[x][0]) continue; depth[to]=depth[x]+1; //记录节点深度,深度从1开始 fa[to][0]=x; for(int j=1;(1<<j)<=depth[to];++j) //这一部分是为了求lca做的处理 { fa[to][j]=fa[fa[to][j-1]][j-1]; } dfs(to); } ord[++len]=x; //子节点遍历完之后再放入数组 second[x]=len; }
比如你需要找1->7这条路径上的所有点,就可以通过欧拉序区间[first[1],first[7]]这个区间内的值就对应的1->7这个路径
但是有些路径不是,看下图:
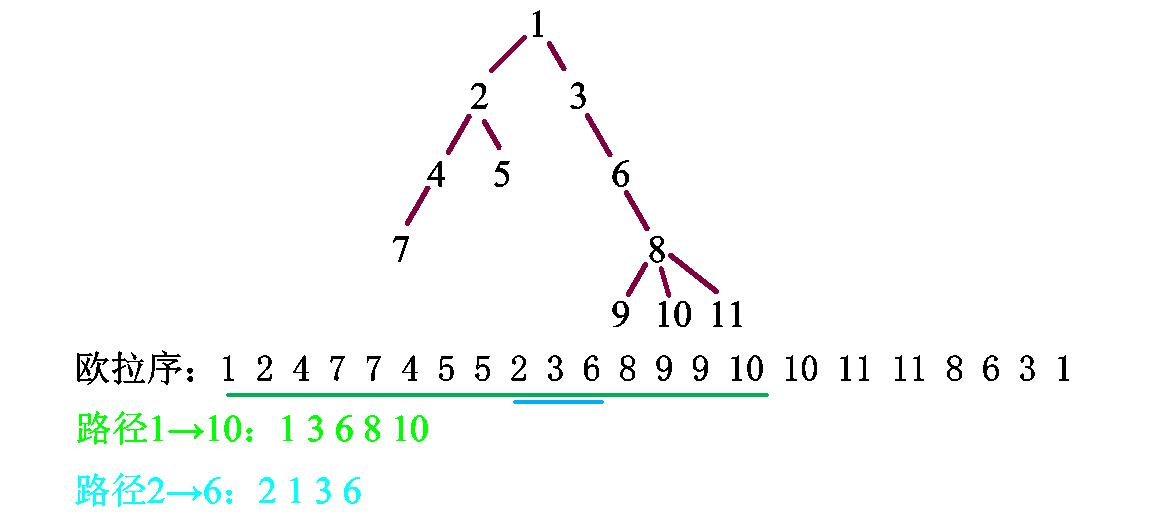
对于1->10你会发现,这个区间内包含了很多实际上用不到的数。
其实我们只需要把这个区间内出现两次的数删掉,剩下的就是1->10这个路径上遇到的点。
1 2 4 7 7 4 5 5 2 3 6 8 9 9 10这个序列删除4、7、5、2、9就变成了1,3,6,8,10正好就是原路经
至于为什么,你可以想一想欧拉序是怎么构成的,如果一个数出现了两次,那就证明这个数是1->10路径上的分支
但是对于路径2->6,我们使用上面的方法你会发现获得的序列不满足我们的实际需求,正确操作是找到欧拉序的区间[last[2],start[6]]
这一部分区间对应欧拉序为:2,3,6。少一个1,为什么少一个1?
因为1是它们的最近父节点,你找的2,6分别在1的两个分支上,所以欧拉序这个区间内肯定不包含1。那我们只需要加上2和6的最近父节点就可以了
这个找最近父节点可以使用lca,不会的可以看一下:lca讲解 && 例题 HDU - 4547
我们这里使用lca的第三种方式,使用倍增lca
这样分析之后,我们就发现树上莫队就和普通莫队差不多了
代码:
#include <map> #include <set> #include <list> #include <queue> #include <deque> #include <cmath> #include <stack> #include <vector> #include <bitset> #include <cstdio> #include <string> #include <cstdlib> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int maxn = 2e5+10; const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f; const double PI = 3.1415926; const long long N = 1000006; const double eps = 1e-10; typedef long long ll; #define mem(A, B) memset(A, B, sizeof(A)) #define lson rt<<1 , L, mid #define rson rt<<1|1 , mid + 1, R #define ls rt<<1 #define rs rt<<1|1 #define SIS std::ios::sync_with_stdiget_mod_new(z-x)o(false), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0) #define pll pair<long long, long long> #define lowbit(abcd) (abcd & (-abcd)) #define max(a, b) ((a > b) ? (a) : (b)) #define min(a, b) ((a < b) ? (a) : (b)) inline int read() { //读取整数 int res = 0; char c = getchar(); while(!isdigit(c)) c = getchar(); while(isdigit(c)) res = (res << 1) + (res << 3) + (c ^ 48), c = getchar(); return res; } int arr[maxn],cnt[maxn],first[maxn],second[maxn],ans[maxn],belong[maxn]; int cnte,inp[maxn],vis[maxn],sizes,new_size,len,now,n,m; //莫队相关 int ord[maxn],val[maxn],head[maxn],depth[maxn],fa[maxn][30]; //ord保存的是欧拉序 struct edge{ int to,next; }e[maxn]; struct Node{ int l,r,lca,id; }node[maxn]; bool cmp(Node a,Node b) { return (belong[a.l]^belong[b.l])?(belong[a.l]<belong[b.l]):((belong[a.l]&1)?a.r<b.r:a.r>b.r); } void add_edge(int x,int y) { e[++cnte]=(edge){y,head[x]}; head[x]=cnte; e[++cnte]=(edge){x,head[y]}; head[y]=cnte; } void dfs(int x) { ord[++len]=x; //第一次遇见的时候放入数组 first[x]=len; //first和second数组是记录某个数在欧拉序中第一次出现和第二次出现的位置 for(int i=head[x];i;i=e[i].next) { int to=e[i].to; if(to==fa[x][0]) continue; depth[to]=depth[x]+1; //记录节点深度,深度从1开始 fa[to][0]=x; for(int j=1;(1<<j)<=depth[to];++j) //这一部分是为了求lca做的处理 { fa[to][j]=fa[fa[to][j-1]][j-1]; } dfs(to); } ord[++len]=x; //子节点遍历完之后再放入数组 second[x]=len; } int get_lca(int u,int v) //使用倍增lca { if(depth[u] < depth[v]) swap(u, v); for(int i = 20; i + 1; --i) if(depth[u] - (1 << i) >= depth[v]) u = fa[u][i]; if(u == v) return u; for(int i = 20; i + 1; --i) if(fa[u][i] != fa[v][i]) u = fa[u][i], v = fa[v][i]; return fa[u][0]; } void work(int pos) //因为欧拉序中一个数出现两次就要删除,所以使用vis数组来标记下 { vis[pos] ? now-=!--cnt[val[pos]] : now += !cnt[val[pos]]++; vis[pos] ^= 1; } int main() { //scanf("%d%d",&n,&m); n=read(); m=read(); for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) { //scanf("%d",&val[i]); inp[i]=val[i]=read(); } sort(inp+1,inp+1+n); int tot=unique(inp+1,inp+1+n)-inp-1; //去重后有多少元素 for(int i=1;i<=n;++i) { //对去重后的数组进行二分 val[i]=lower_bound(inp+1,inp+1+tot,val[i])-inp; //printf("%d ",val[i]); } for(int i=1;i<n;++i) { int x,y; scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); add_edge(x,y); } depth[1]=1; dfs(1); sizes=sqrt(len); new_size=ceil((double)len/sizes); for(int i=1;i<=new_size;++i) { for(int j=(i-1)*sizes+1;j<=i*sizes;++j) { belong[j]=i; } } for(int i=1;i<=m;++i) { int x,y,z; x=read(); y=read(); //scanf("%d%d",&x,&y); z=get_lca(x,y); if(first[x]>first[y]) swap(x,y); if(x==z) //如果其中一个节点是它俩的最近父节点,那就采用第一种方法 { node[i].l=first[x]; node[i].r=first[y]; } else //否则就要最后加一个父节点 { node[i].l=second[x]; node[i].r=first[y]; node[i].lca=z; } node[i].id=i; } sort(node+1,node+1+m,cmp); int l=1,r=0; for(int i=1;i<=m;++i) { int start=node[i].l,last=node[i].r,lca=node[i].lca; while(l<start) work(ord[l++]); while(l>start) work(ord[--l]); while(r>last) work(ord[r--]); while(r<last) work(ord[++r]); if(lca) work(lca); ans[node[i].id]=now; if(lca) work(lca); } for(int i=1;i<=m;++i) printf("%d ",ans[i]); return 0; }