原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/fengkeyleaf/article/details/117692135
如果看过上一节的直线交点,那么这里求直线和圆的交点思路是非常相似的:
1、用直线到圆心的距离和半径相比,判断是否和圆有交点;
2、求出圆心在直线上面的投影点(projectPoint);
3、算出直线的单位向量e;
4、求出一侧交点(Intersection)到projectPoint的长度(sideLength);
5、求出sideLength和这侧端点到projectPoint距离的比例(ratio);
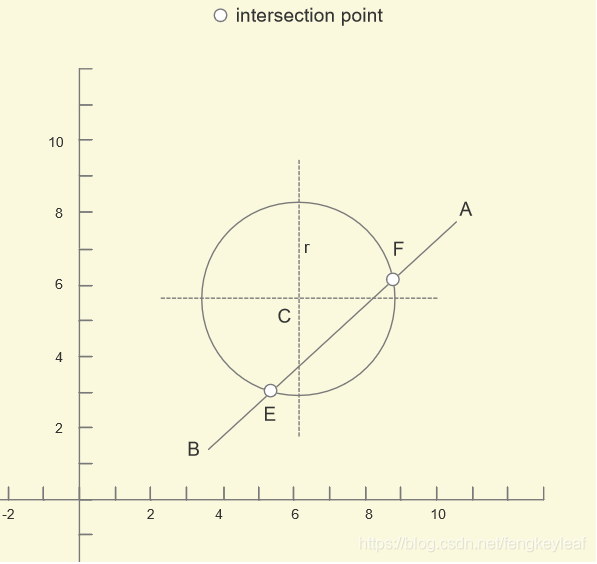
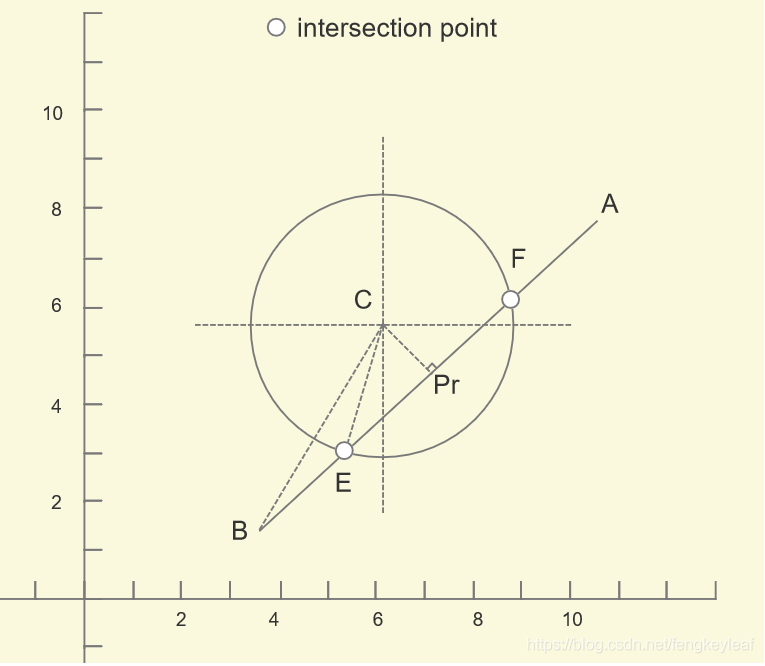
6、projectPoint +/- ratio * e = 两侧交点;同样,我们还是通过一个图例来讲解。我们给定圆,圆心为C,半径为r,和直线AB,以及它们两个交点E和F:
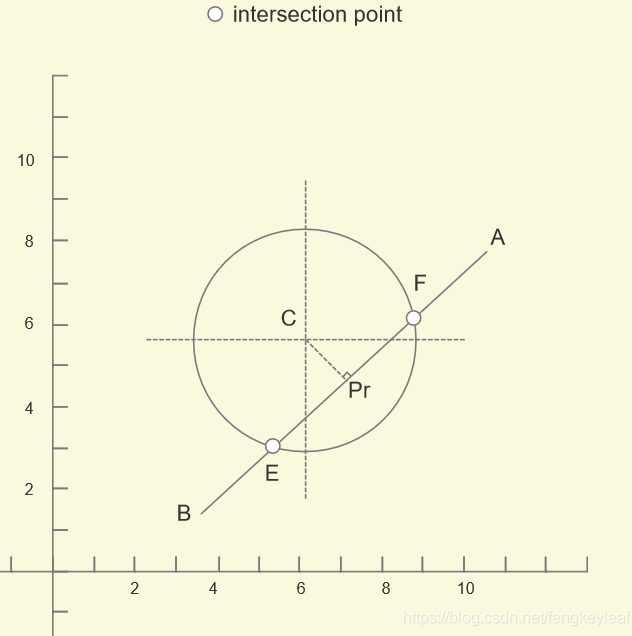
现在我们以求交点E为例来进行讲解。使用求直线交点的思路,如果我们首先会考虑从B出发,求得BE和某个向量的比例,即可通过B来计算交点E,但是这样不是很好找比例,所以我们换一种思路,先求C在直线AB上面的投影Pr:
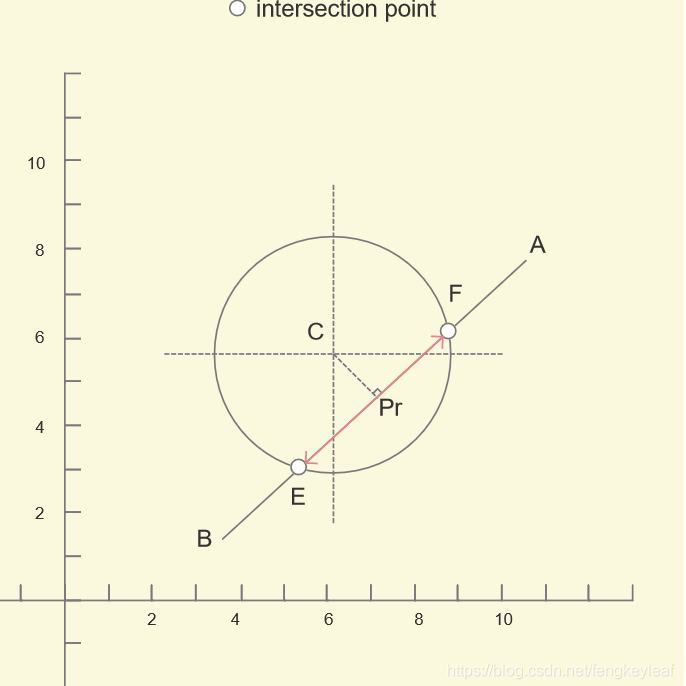
那么显然,我们可以得到一组向量的比例关系:BPr 和 EPr(加粗表示向量),因为圆和直线可能有两个交点,分别位于Pr的两边,所以我们选Pr作为起点求交点比较方便:
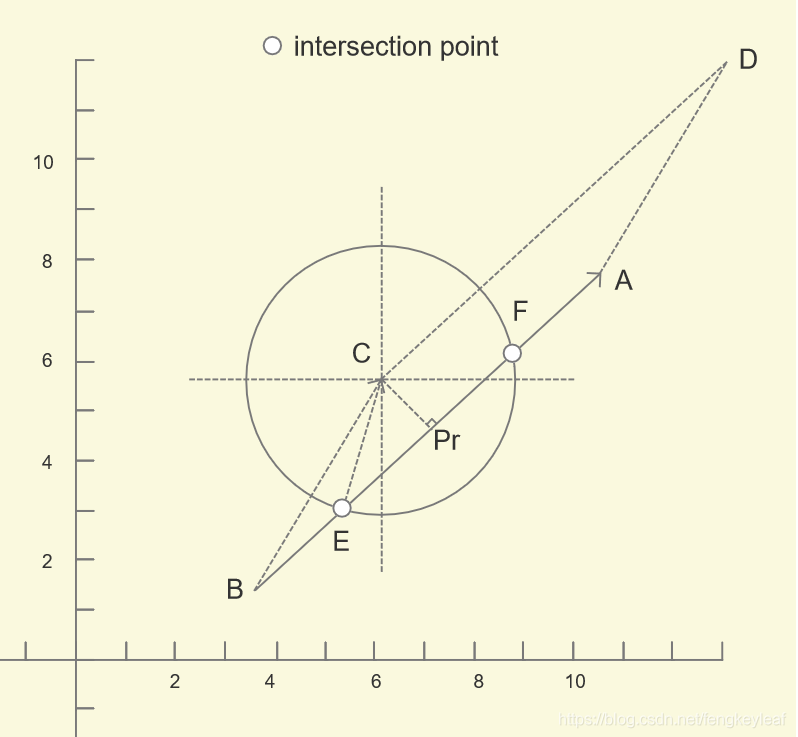
有了这个比例关系(ratio),我们只要知道BA的单位向量e,用 ratio * e,就可以得到EPr和PrF。因为根据垂径定理1,|EPr| = |PrF|。所以我们先假设求得了Pr,那么|EPr|和|BPr|怎么求呢?我们连接BC和EC看看:
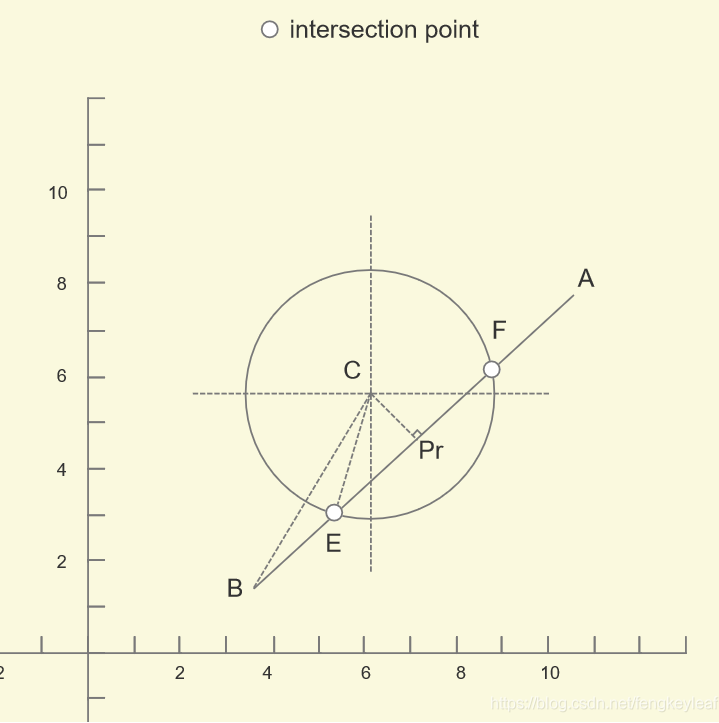
从图中可知,|EPr|不难求,直角三角形CEPr可用勾股定理求得;那么|BPr|呢?现在又需要向量的帮助了,大家还记得向量得点积么?两个向量a和b的点积表示a在b上面的投影,所以|BPr| = BC * BPr。那么到现在,还剩下两个问题就能解决交点了:1)如何求C在直线AB上面的投影;2)如何求C到直线AB的距离;
2.2 点在直线上面的投影
在文章开头,我们曾经提到下面的思路去求解交点:现在我们以求交点E为例来进行讲解。使用求直线交点的思路,如果我们首先会考虑从B出发,求得BE和某个向量的比例,即可通过B来计算交点E
虽然这个方法求交点不是很好,但是我们可以用它来求解点在直线上面的投影。还是上面圆的图例:
所以我们只需要求出BPr和BA的比例关系,即可以求解Pr,而且|BPr|可以BC和BA的点积来求得,因为两者点积是BC在BA上面的投影,通过这样,我们就能求得比例关系了,如下图所示:
2.3 点到直线的距离
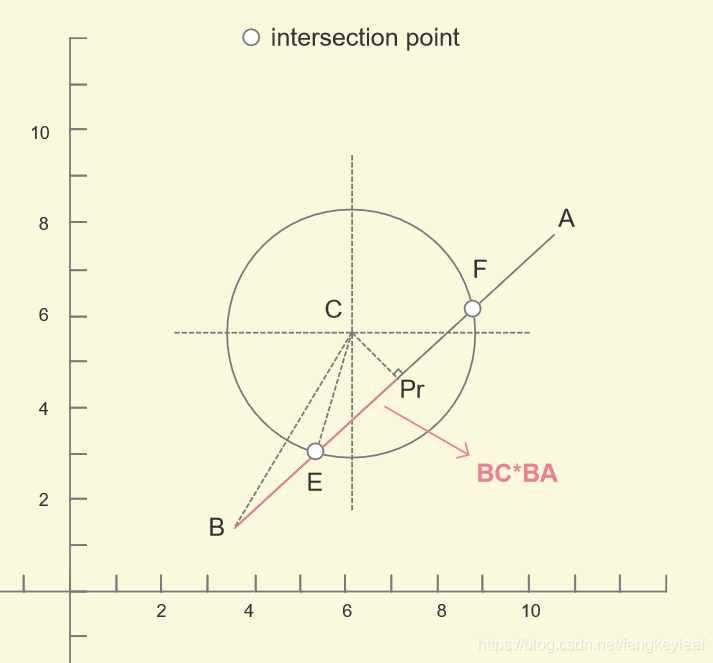
点到直线的距离,我们可以看成平行四边形的高,然后用叉积来求得,还是刚才的图例:
我们看到C到AB的距离(CPr)其实平行四边形BADC的高,所以我们可以利用BC和BA的叉积来求解。
代码来源于https://blog.csdn.net/qq_40998706/article/details/87521165:
这是一个题目:

#include<stdio.h> #include<iostream> #include<cmath> #include<assert.h> using namespace std; #define EPS (1e-10) #define equals(a, b) (fabs((a) - (b)) < EPS) class Point {//Point类,点 public: double x, y; Point(double x = 0, double y = 0): x(x), y(y) {} Point operator + (Point p) { return Point(x + p.x, y + p.y); } Point operator - (Point p) { return Point(x - p.x, y - p.y); } Point operator * (double a) { return Point(a * x, a * y); } Point operator / (double a) { return Point(x / a, y / a); } double abs() { return sqrt(norm()); } double norm() { return x * x + y * y; } bool operator < (const Point &p) const { return x != p.x ? x < p.x : y < p.y; } bool operator == (const Point &p) const { return fabs(x - p.x) < EPS && fabs(y - p.y) < EPS; } }; typedef Point Vector;//Vector类,向量 struct Segment{//Segment 线段 Point p1, p2; }; typedef Segment Line; class Circle {//Circle 圆 public: Point c; double r; Circle(Point c = Point(), double r = 0.0): c(c), r(r) {} }; double dot(Vector a, Vector b) {//内积 return a.x * b.x + a.y * b.y; } double cross(Vector a, Vector b) {//外积 return a.x*b.y - a.y*b.x; } Point project(Segment s, Point p) {//投影 对于给定的三个点p1、p2、p,从点p向通过 //p1、p2的直线引一条垂线,求垂足x的坐标。(点p在直线p1p2上的投影) Vector base = s.p2 - s.p1; double r = dot(p - s.p1, base) / base.norm(); return s.p1 + base * r; } double getDistanceLP(Line l, Point p) {//直线l和点p的距离 return abs(cross(l.p2 - l.p1, p - l.p1) / (l.p2 - l.p1).abs() ); } bool intersect(Circle c, Line l) { if(getDistanceLP(l, c.c) > c.r) { return false; } else { return true; } } Point getCrossPoint(Segment s1, Segment s2) { Vector base = s2.p2 - s2.p1; double d1 = abs(cross(base, s1.p1 - s2.p1)); double d2 = abs(cross(base, s1.p2 - s2.p1)); double t = d1 / (d1 + d2); return s1.p1 + (s1.p2 - s1.p1) * t; } pair<Point, Point> getCrossPoints(Circle c, Line l) { assert(intersect(c, l)); Vector pr = project(l, c.c); Vector e = (l.p2 - l.p1) / (l.p2 - l.p1).abs(); double base = sqrt(c.r * c.r - (pr - c.c).norm() ); return make_pair(pr + e * base, pr - e * base); } int main(){ Circle c; cin>>c.c.x>>c.c.y>>c.r; int q; cin>>q; Line l; pair<Point, Point> p; while(q--){ cin>>l.p1.x>>l.p1.y>>l.p2.x>>l.p2.y; p = getCrossPoints(c, l); if(p.first.x < p.second.x || (p.first.x == p.second.x && p.first.y <= p.second.y) ) { printf("%.6f %.6f %.6f %.6f ", p.first.x, p.first.y, p.second.x, p.second.y); } else { printf("%.6f %.6f %.6f %.6f ", p.second.x, p.second.y, p.first.x, p.first.y); } } }