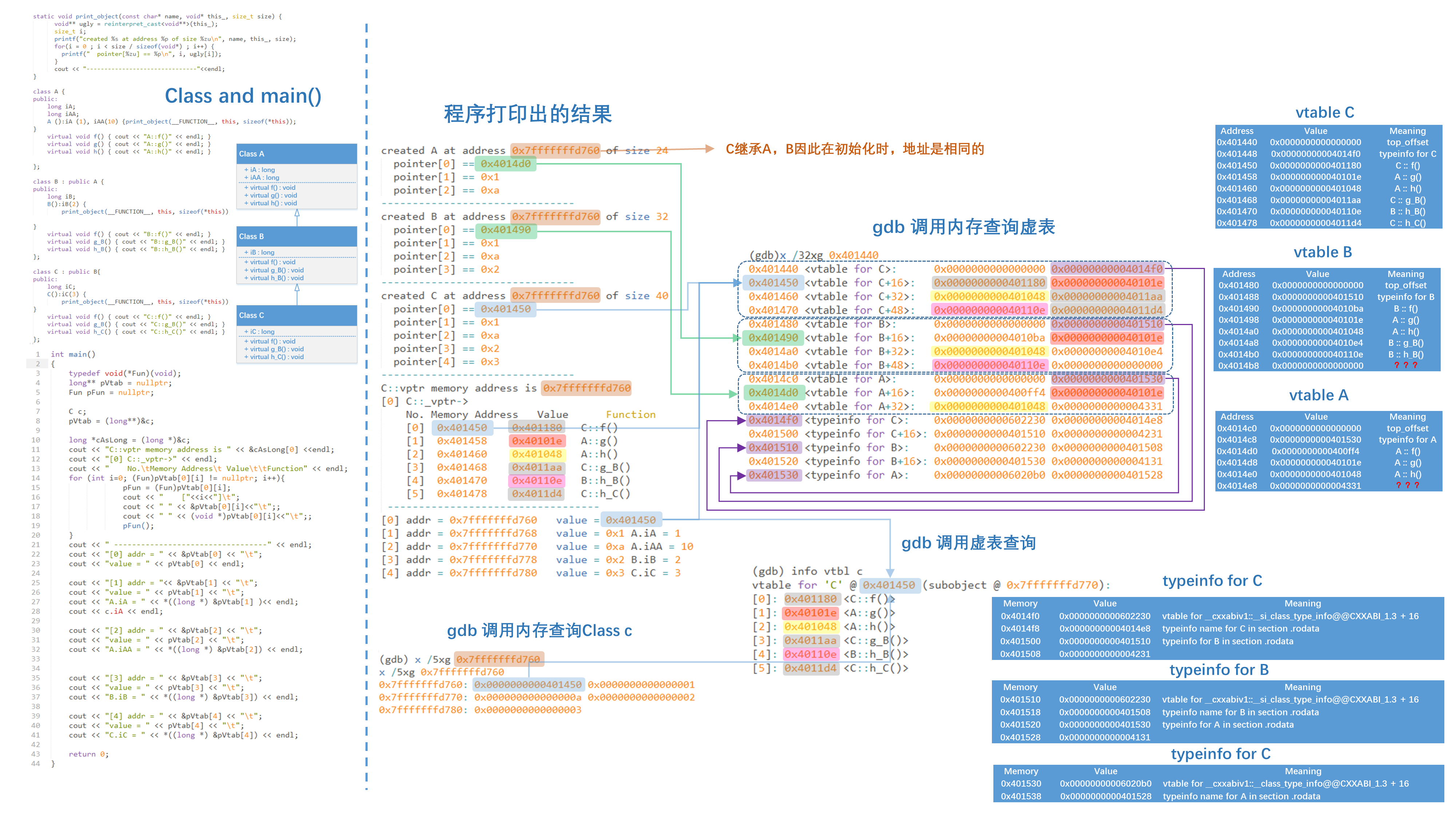
1. 传统继承类的设计
static void print_object(const char* name, void* this_, size_t size) { void** ugly = reinterpret_cast<void**>(this_); size_t i; printf("created %s at address %p of size %zu
", name, this_, size); for(i = 0 ; i < size / sizeof(void*) ; i++) { printf(" pointer[%zu] == %p
", i, ugly[i]); } cout << "-------------------------------"<<endl;} class A {public: long iA; long iAA; A ():iA (1), iAA(10) {print_object(__FUNCTION__, this, sizeof(*this));} virtual void f() { cout << "A::f()" << endl; } virtual void g() { cout << "A::g()" << endl; } virtual void h() { cout << "A::h()" << endl; }};class B : public A {public: long iB; B():iB(2) { print_object(__FUNCTION__, this, sizeof(*this));} virtual void f() { cout << "B::f()" << endl; } virtual void g_B() { cout << "B::g_B()" << endl; } virtual void h_B() { cout << "B::h_B()" << endl; }}; class C : public B{public: long iC; C():iC(3) { print_object(__FUNCTION__, this, sizeof(*this));} virtual void f() { cout << "C::f()" << endl; } virtual void g_B() { cout << "C::g_B()" << endl; } virtual void h_C() { cout << "C::h_C()" << endl; }};
- A、B、C依次继承
- 并在构造过程中通过
print_object输出构建信息
2. 构造Class C,并通过指针来一次访问内容或调用函数
int main(){ typedef void(*Fun)(void); long** pVtab = nullptr; Fun pFun = nullptr; C c; pVtab = (long**)&c; long *cAsLong = (long *)&c; cout << "C::vptr memory address is " << &cAsLong[0] <<endl; cout << "[0] C::_vptr->" << endl; cout << " No. Memory Address Value Function" << endl; for (int i=0; (Fun)pVtab[0][i] != nullptr; i++){ pFun = (Fun)pVtab[0][i]; cout << " ["<<i<<"] "; cout << " " << &pVtab[0][i]<<" ";; cout << " " << (void *)pVtab[0][i]<<" ";; pFun(); } cout << " ----------------------------------" << endl; cout << "[0] addr = " << &pVtab[0] << " "; cout << "value = " << pVtab[0] << endl; cout << "[1] addr = "<< &pVtab[1] << " "; cout << "value = " << pVtab[1] << " "; cout << "A.iA = " << *((long *) &pVtab[1] )<< endl; cout << c.iA << endl; cout << "[2] addr = " << &pVtab[2] << " "; cout << "value = " << pVtab[2] << " "; cout << "A.iAA = " << *((long *) &pVtab[2]) << endl; cout << "[3] addr = " << &pVtab[3] << " "; cout << "value = " << pVtab[3] << " "; cout << "B.iB = " << *((long *) &pVtab[3]) << endl; cout << "[4] addr = " << &pVtab[4] << " "; cout << "value = " << pVtab[4] << " "; cout << "C.iC = " << *((long *) &pVtab[4]) << endl; return 0;
pVtab用于显示虚表的位置,并用于后续的直接调用- 通过循环,一次输出虚表中各个成员的地址和对应的存储内容
- 最后,通过直接调用相应的存储内容来调用成员或调用函数。
3. gdb的使用方法
g++ -g -o test.cpp test
(gdb) r
(gdb) break line_number
(gdb) info vtbl c
(gdb) x /5xg 0xfffffffd70
(gdb) x /32xg 0x401440
4. 具体逻辑关系见下图
http://7xlos6.com1.z0.glb.clouddn.com/%E6%9D%82.png