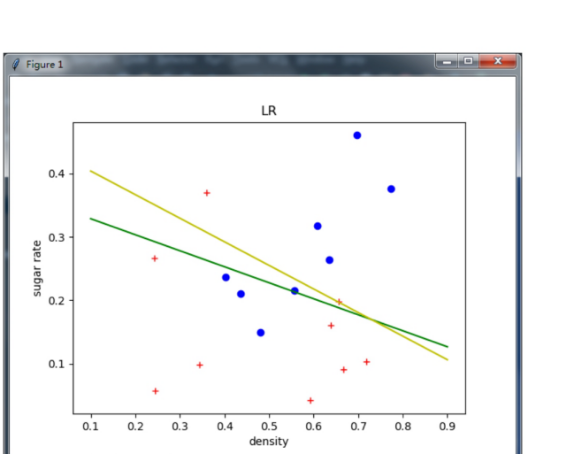
1 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt 2 import numpy as np 3 import xlrd 4 5 def sigmoid(x): 6 """ 7 Sigmoid function. 8 Input: 9 x:np.array 10 Return: 11 y: the same shape with x 12 """ 13 y =1.0 / ( 1 + np.exp(-x)) 14 return y 15 16 def newton(X, y): 17 """ 18 Input: 19 X: np.array with shape [N, 3]. Input. 20 y: np.array with shape [N, 1]. Label. 21 Return: 22 beta: np.array with shape [1, 3]. Optimal params with newton method 23 """ 24 N = X.shape[0] 25 #initialization 26 beta = np.ones((1, 3)) 27 #shape [N, 1] 28 z = X.dot(beta.T) 29 #log-likehood 30 old_l = 0 31 new_l = np.sum(-y*z + np.log( 1+np.exp(z) ) ) 32 iters = 0 33 while( np.abs(old_l-new_l) > 1e-5): 34 #shape [N, 1] 35 p1 = np.exp(z) / (1 + np.exp(z)) 36 #shape [N, N] 37 p = np.diag((p1 * (1-p1)).reshape(N)) 38 #shape [1, 3] 39 first_order = -np.sum(X * (y - p1), 0, keepdims=True) 40 #shape [3, 3] 41 second_order = X.T .dot(p).dot(X) 42 43 #update 44 beta -= first_order.dot(np.linalg.inv(second_order)) 45 z = X.dot(beta.T) 46 old_l = new_l 47 new_l = np.sum(-y*z + np.log( 1+np.exp(z) ) ) 48 49 iters += 1 50 print "iters: ", iters 51 print new_l 52 return beta 53 54 def gradDescent(X, y): 55 """ 56 Input: 57 X: np.array with shape [N, 3]. Input. 58 y: np.array with shape [N, 1]. Label. 59 Return: 60 beta: np.array with shape [1, 3]. Optimal params with gradient descent method 61 """ 62 63 N = X.shape[0] 64 lr = 0.05 65 #initialization 66 beta = np.ones((1, 3)) * 0.1 67 #shape [N, 1] 68 z = X.dot(beta.T) 69 70 for i in range(150): 71 #shape [N, 1] 72 p1 = np.exp(z) / (1 + np.exp(z)) 73 #shape [N, N] 74 p = np.diag((p1 * (1-p1)).reshape(N)) 75 #shape [1, 3] 76 first_order = -np.sum(X * (y - p1), 0, keepdims=True) 77 78 #update 79 beta -= first_order * lr 80 z = X.dot(beta.T) 81 82 l = np.sum(-y*z + np.log( 1+np.exp(z) ) ) 83 print l 84 return beta 85 86 if __name__=="__main__": 87 88 #read data from xlsx file 89 workbook = xlrd.open_workbook("3.0alpha.xlsx") 90 sheet = workbook.sheet_by_name("Sheet1") 91 X1 = np.array(sheet.row_values(0)) 92 X2 = np.array(sheet.row_values(1)) 93 #this is the extension of x 94 X3 = np.array(sheet.row_values(2)) 95 y = np.array(sheet.row_values(3)) 96 X = np.vstack([X1, X2, X3]).T 97 y = y.reshape(-1, 1) 98 99 #plot training data 100 for i in range(X1.shape[0]): 101 if y[i, 0] == 0: 102 plt.plot(X1[i], X2[i], 'r+') 103 104 else: 105 plt.plot(X1[i], X2[i], 'bo') 106 107 #get optimal params beta with newton method 108 beta = newton(X, y) 109 newton_left = -( beta[0, 0]*0.1 + beta[0, 2] ) / beta[0, 1] 110 newton_right = -( beta[0, 0]*0.9 + beta[0, 2] ) / beta[0, 1] 111 plt.plot([0.1, 0.9], [newton_left, newton_right], 'g-') 112 113 #get optimal params beta with gradient descent method 114 beta = gradDescent(X, y) 115 grad_descent_left = -( beta[0, 0]*0.1 + beta[0, 2] ) / beta[0, 1] 116 grad_descent_right = -( beta[0, 0]*0.9 + beta[0, 2] ) / beta[0, 1] 117 plt.plot([0.1, 0.9], [grad_descent_left, grad_descent_right], 'y-') 118 119 plt.xlabel('density') 120 plt.ylabel('sugar rate') 121 plt.title("LR") 122 plt.show()