1.第一个struts2项目
参考官方配置 http://struts.apache.org/getting-started/
github地址:https://github.com/unbelievableme/maven_hibernate-struts-spring/tree/master/struts2/first
建议:参考官方配置操作一遍,因为技术不断更新,不同版本的struts的类可能不同,老版本的多个类可能在新版本中集成了一个
2.struts2工作流程原理
2.1步骤
1.创建Web Project
2.导入Jar(使用maven控制的话,配置pom.xml)
<!--pom配置见http://www.cnblogs.com/kundeg/p/7152846.html -->
3.在web.xml配置struts2的过滤器
<filter> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <!--该类会因struts版本不同而变化,在struts2.0-2.1.2为org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.FilterDispatcher,在之后版本为下述--> <filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <!-- 所有的url都会被url过滤器解析 --> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>
4.创建Struts核心xml文件
5.创建action类继承与ActionSupport
6.配置struts.xml
<!--详细配置及介绍见:http://www.cnblogs.com/kundeg/p/7188699.html-->
2.2流程
1、客户端浏览器发出HTTP请求
2、该请求被StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter接收
3、根据struts.xml配置,找到需要调用的Action类和方法, 并通过IoC方式,将值注入给Aciton
4、Action调用业务逻辑组件处理业务逻辑
5、Action执行完毕,根据struts.xml中的配置找到对应的返回结果result,并跳转到相应页面
6、返回HTTP响应到客户端浏览器
2.3原理
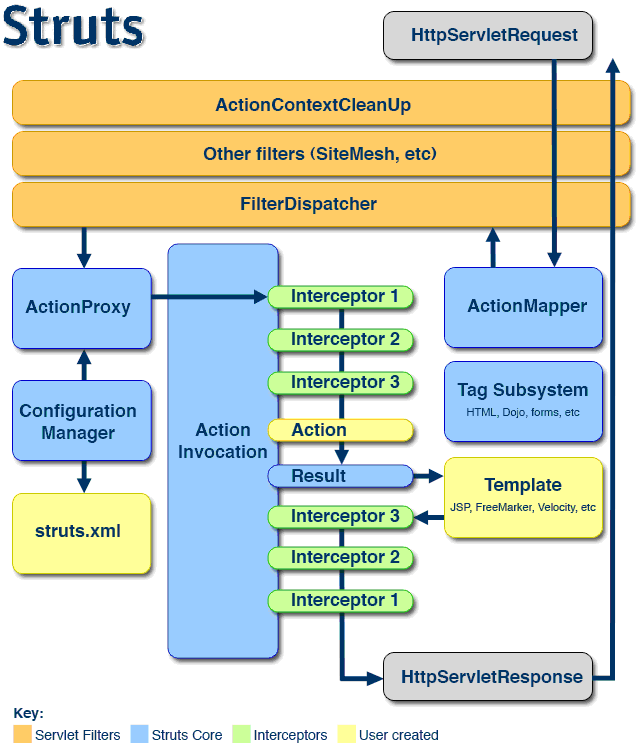
注意:在struts2.1.2后FilterDispatcher被替换为了StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter
1、 客户端初始化一个指向Servlet容器(例如Tomcat)的请求
2、 这个请求经过一系列的过滤器(Filter)(这些过滤器中有一个叫做ActionContextCleanUp的可选过滤器,这个过滤器对于Struts2和其他框架的集成很有帮助,例如:SiteMesh Plugin)
3、 接着被StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter(能够拦截请求对象ServletRequest和ServletResponse结合Struts.xml构建独立于servlet的ActionContxt)调用,StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter询问ActionMapper(含有struts.xml中Action配置的name,namespce,result等的HashMap)来决定这个请是否需要调用某个Action
4、 如果ActionMapper决定需要调用某个Action,StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter把请求的处理交给ActionProxy
5、 ActionProxy通过Configuration Manager询问框架的配置文件struts.xml,找到需要调用的Action类
6、 ActionProxy创建一个ActionInvocation的实例。
7、 ActionInvocation实例使用命名模式来调用,在调用Action的过程前后,涉及到相关拦截器(Intercepter)的调用。
8、 一旦Action执行完毕,ActionInvocation负责根据struts.xml中的配置找到对应的返回结果。返回结果通常是(但不总是,也可 能是另外的一个Action链)一个需要被表示的JSP或者FreeMarker的模版。在表示的过程中可以使用Struts2 框架中继承的标签。在这个过程中需要涉及到ActionMapper
3.拦截器介绍
3.1Interceptor基础介绍
拦截器基础介绍以及与过滤器的对比见StrutsPreparedAndExcuteFilter与Interceptor
3.2 计时拦截器实例
TimerAction.java
public class TimerAction extends ActionSupport{ public String excute(){ //下面为耗时代码段 int sum = 0; for(int i =0;i<10000;i++){ sum+=i; } return SUCCESS; } }
TimerInterceptor.java
public class TimerInterceptor extends AbstractInterceptor{ public String intercept(ActionInvocation invocation) throws Exception { //1.执行action之前 long start = System.currentTimeMillis(); //2.执行下一个拦截器,如果已经是最后一个拦截器,则执行目标Aciton String result = invocation.invoke(); //3.执行Action之后 long end = System.currentTimeMillis(); System.out.println("执行Action花费时间:"+(end-start+"ms")); return result; } }
struts.xml配置
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.5//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.5.dtd"> <struts> <constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="true" /> <package name="/" extends="struts-default" strict-method-invocation="false"> <!--注册拦截器--> <interceptors> <interceptor name="myTimer" class="Interceptor.TimerInterceptor"> </interceptor> </interceptors> <action name="TimerAction" method="excute" class="action.TimerAction"> <result name="success">/success.jsp</result> <!-- 引用拦截器 --> <interceptor-ref name="myTimer"></interceptor-ref> </action> </package> </struts>
项目路径(maven管理):
4.深入struts
4.1 Action搜索顺序
http://localhost:8080/struts2/path1/path2/path3/student.action
第一步:判断package是否存在,如:path1/path2/path3/
第二步:如果package存在,则判断该package中action是否存在,如果不存在则去默认namespace的package里面寻找action
第三步:如果package不存在,检查上一级路径的package是否存在(直到默认namespace),重复第一步 第三步:如果没有则报错
4.2 动态方法调用
目的:一个action对应多个请求的处理,避免action过多
举例:下述为类为action.helloworld的action,该action可以处理请求../add.action和../update.action,下面介绍动态调用的几种常见方法
public class helloworld extends ActionSupport{ public String add(){ /* */ return SUCCESS; } public String update(){ /* */ return SUCCESS; } }
4.2.1 method方法
在struts.xml中的配置如下:
<struts> <package name="defalut" extends="struts-default"> <action name="addAction" class="action.helloworld" method="add"> <result name="success">/add.jsp</result> </action> <action name="updateAction" class="action.helloworld" method="update"> <result name="success">/update.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
访问方式:http://localhost:8080/工程名/addAction.action(addAction可以换成updateAction)
缺点:当一个action中方法过多的时候哦,配置过于冗余
4.4.2 感叹号方式
修改entity为:
public class helloworld extends ActionSupport{ public String add(){ /* */ return "add"; } public String update(){ /* */ return "update"; } }
在struts.xml中配置如下
<struts> <constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="true" /> <package name="default" extends="struts-default" strict-method-invocation="false"> <action name="helloworldAction" class="action.helloworld"> <!--result的name属性值和action.helloworld类中方法处理的返回值相同--> <result name="add">/add.jsp</result> <result name="update">/update.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
访问方式:http://localhost:8080/工程名/helloworldAction!add.action(!后面的add表示方法,可以换成update)
4.4.3 通配符方式(推荐使用)
在struts.xml中配置如下
<struts> <constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="true" /> <package name="default" extends="struts-default" strict-method-invocation="false"> <!--{1}表示*的内容--> <action name="helloworld_*" method="{1}" class="action.helloworld"> <result name="success">/{1}.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
或者如下:
<struts> <constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="true" /> <package name="default" extends="struts-default" strict-method-invocation="false"> <!--{1}代表第一个*的内容,{2}代表第二个*的内容--> <action name="*_*" method="{2}" class="action.{1}"> <result name="success">/{2}.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
访问方式:http://localhost:8080/工程名/helloworld_add.action(add表示方法)
4.3 指定多个配置文件
目的:为了解决在struts.xml中配置过多,或者为了在不同的xml中配置实现更好的分类
要求:多个xml配置都必须遵守struts的dtd规范,同时要注意编码方式要相同
举例:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.5//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.5.dtd"> <struts> <constant name="struts.devMode" value="true" /> <package name="/" extends="struts-default"> <action name="index"> <result>/index.jsp</result> </action> <action name="hello" class="action.hello" method="execute"> <result name="success">/HelloWorld.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
可以用下述两个xml文件来表示:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.5//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.5.dtd"> <struts> <constant name="struts.devMode" value="true" /> <include file="helloworld.xml"></include> </struts>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.5//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.5.dtd"> <struts> <package name="/" extends="struts-default"> <action name="index"> <result>/index.jsp</result> </action> <action name="hello" class="action.hello" method="execute"> <result name="success">/HelloWorld.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
4.4 默认Action(主要讨论通配符配置方式)
目的:为了改进用户体验,解决http404和500错误(不能完全解决)
举例 :
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.5//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.5.dtd"> <struts> <constant name="struts.enable.DynamicMethodInvocation" value="true" /> <package name="/" extends="struts-default" strict-method-invocation="false"> <default-action-ref name="index"></default-action-ref> <action name="index"> <result>/error.jsp</result> </action> <action name="helloworld_*" method="{1}" class="action.helloworld"> <result name="success">/{1}.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
注意:非默认action的name属性值一定不要以*为开头进行通配。否则错误的action地址不能由默认action进行响应处理,会进入以*开头的action。
缺点:但即使是不以*开头的action也存在与它匹配的但工程中不存在的action地址,例如在上述配置的基础上访问http://localhost:8080/工程名/helloworld_ad.action还是会出现异常界面(下图所示)。
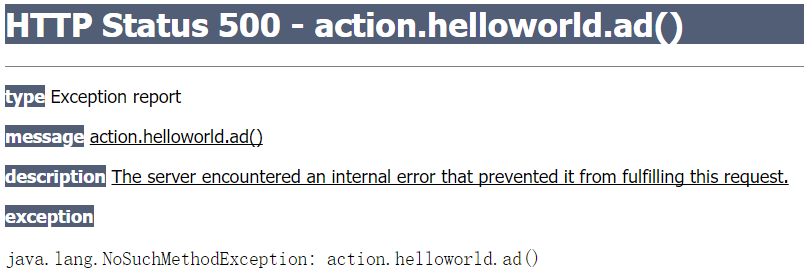
解决:通过method配置可以完全解决404或500错误,感叹号方式不行(不再详述)
4.4 struts后缀
目的:为了看起来xx,比如访问xx.html很容易以为静态页面,掩盖了本质:经过action处理跳转后的jsp页面
配置方式(三种):
1.在struts.xml中加上
<constant name="struts.action.extension" value="action,do,struts2"></constan
2.在struts.properties中加上
struts.action.extension=action,do,struts2
3.在web.xml中加上
<filter> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <filter-class>org.apache.struts2.dispatcher.filter.StrutsPrepareAndExecuteFilter</filter-class> <!--添加内容--> <init-param> <param-name>struts.action.extension</param-name> <param-value>do,action,strtus2</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>
4.5 struts传参
4.5.1 直接用Action属性
下列代码依次为:前端jsp,后台action(省略struts.xml配置)

<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <form action="./login.action" method="post"> 用户名:<input name="username" type="text"><br> 密码: <input name="password" type="password"><br> <input type="submit" value="登陆"> </form> </body> </html>

public class User extends ActionSupport{ private String username; public String excute(){ System.out.println(username); return SUCCESS; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } }
4.5.2 DomainModel
下列代码依次为:前端jsp,后台Action,实体类model

<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <form action="./login.action" method="post"> <!-- 要指明那个对象的object.xxx --> 用户名:<input name="user.username" type="text"><br> 密码: <input name="user.password" type="password"><br> <input type="submit" value="登陆"> </form> </body> </html>

public class loginAction extends ActionSupport{ private User user; public String excute(){ System.out.println(user.getUsername()); return SUCCESS; } public User getUser() { return user; } public void setUser(User user) { this.user = user; } }

public class User extends ActionSupport{ private String username; private String password; public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
4.5.3 ModelDriven
同上

<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <form action="./login.action" method="post"> 用户名:<input name="username" type="text"><br> 密码: <input name="password" type="password"><br> <!-- 为后台list传参 --> 爱好 1: <input name="hobby[0]" type="text"><br> 爱好 2: <input name="hobby[1]" type="text"><br> <input type="submit" value="登陆"> </form> </body> </html>

public class loginAction extends ActionSupport implements ModelDriven<User>{ private User user = new User(); public String excute(){ System.out.println(user.getUsername()); System.out.println(user.getHobby().get(0)); System.out.println(user.getHobby().get(1)); return SUCCESS; } public User getModel() { // TODO Auto-generated method stub return user; } }

public class User extends ActionSupport{ private String username; private String password; private List<String> hobby; public List<String> getHobby() { return hobby; } public void setHobby(List<String> hobby) { this.hobby = hobby; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }
4.6 result
4.6.1Action中五种内置属性(com.opensymphony.xwork2.Action)
1. SUCCESS Action正确的执行完成,返回相应的视图,success是name属性的默认值。
2. NONE 表示Action正确的执行完成,但并不返回任何事视图。
3. ERROR 表示Action执行失效,返回错误处理视图。
4. LOGIN Action因为用户没有登录的原因没有正确执行,将返回该登录视图,要求用户进行登录验证
5. INPUT Action的执行,需要从前端界面获取参数,INPUT就是代表这个参数输入界面,一般在应用中,会对这些 参数进行验证,如果验证没有通过,将自动返回该视图。
注意:内置属性的意思是说可以直接return,不需要加上引号,内置属性可以方便标识与说明,除此之外action在执行过程中可能内部return内置属性进行跳转,下述Input实例说明了这点。
4.6.2 Input实例
代码(依次为前端jsp,后台action,实体类entity,struts.xml):

<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> <html> <head> <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> <title>Insert title here</title> </head> <body> <form action="./login.action" method="post"> 用户名:<input name="username" type="text"><br> 密码: <input name="password" type="password"><br> <!-- 为后台list传参 --> 爱好 1: <input name="hobby[0]" type="text"><br> 爱好 2: <input name="hobby[1]" type="text"><br> 年龄:<input name="age" type="text"><br> <input type="submit" value="登陆"> </form> </body> </html>

public class loginAction extends ActionSupport implements ModelDriven<User> { private User user = new User(); public String excute() { System.out.println(user.getUsername()); System.out.println(user.getHobby().get(0)); System.out.println(user.getHobby().get(1)); System.out.println(user.getAge()); return SUCCESS; } public User getModel() { return user; } public void validate() { //如果不显式添加return INPUT,下述代码段必须放在validat函数内 if(user.getUsername()==null||"".equals(user.getUsername())){ this.addFieldError("username", "用户名不能为空"); } } }

public class User extends ActionSupport{ private String username; private String password; private int age; private List<String> hobby; public List<String> getHobby() { return hobby; } public void setHobby(List<String> hobby) { this.hobby = hobby; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } }

<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <!DOCTYPE struts PUBLIC "-//Apache Software Foundation//DTD Struts Configuration 2.5//EN" "http://struts.apache.org/dtds/struts-2.5.dtd"> <struts> <package name="/" extends="struts-default" strict-method-invocation="false"> <action name="login" method="excute" class="action.loginAction"> <result name="success">/success.jsp</result> <result name="input">/login.jsp</result> </action> </package> </struts>
测试:
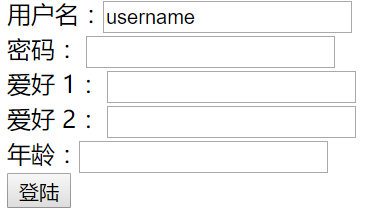

图一 图二 图三
1.图一可以通过action验证返回success,跳转到success.jsp页面
2.图二不可以通过action验证,返回login.jsp页面,因为前端传入的age属性为String类型与后台age的int类型不符,虽然没有显示判断,但系统会自动检查并return Input
3.图三不可以通过action验证,返回login.jsp页面,因为前端的username为空后,台有关于username的判断。
本质:
Action类的父类ActionSupport中有一个收集错误信息的容器Map,错误信息是名称fieldName和描述信息errorMessage的键值对,只要该Map中有值表示校验不通过,返回INPUT,系统可以自动addFileError("",""),也可以手动添加
4.6.3 result-type属性(chain,redirect,dispatcher)
type的默认值为dispatcher(请求转发),其他常用见的有三个:chain,redirect,plaintext。
1、chain:将action和另外一个action链接起来,result属性取action名字但是不要action后缀
<package name="students" namespace="/students" extends="struts-default" strict-method-invocation="false"> <action name="*_*" method="{2}" class="action.{1}Action"> <result name="Students_query_success">/students/Students_query_success.jsp</result> <!-- chain相当于内部转发,下述实例去执行action.StudentsAction的query方法 --> <result name="delete_success" type="chain">Students_query</result> </action> </package>
2、redirect:重定向(重新发起一次请求,原来的请求数据会丢失)
3、plaintext:返回网页源代码
4、stream:返回inputstream用于文件下载
注意:chain和dispatcher都属于服务器内部转发,这些转发默认不经过filter(即转发的action请求将无法响应)
原因:filter默认过滤来自客户端的符合url-pattern的请求而内部转发不在此范畴内
解决:因此使用这些type需要在web.xml中增加配置(如下)。
<filter-mapping> <filter-name>struts2</filter-name> <!-- 所有的url都会被url过滤器解析 --> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> <!--forward表示只过滤内部转发的请求--> <dispatcher>FORWARD</dispatcher> <!--request表示只过滤客户端的请求--> <dispatcher>REQUEST</dispatcher> </filter-mapping>
