数组
- 删除有序数组的重复元素
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
int id = 1; //id是要返回的处理后的数组大小
for(int i =1;i<nums.length;i++){
//状态转移逻辑,相等什么都不做,不相等更新nums[id]的值并且id+1
if(nums[i]!=nums[i-1]){
nums[id++] = nums[i];
}
}
return id;
}
- 删除指定元素
//和删除重复的元素有异曲同工之处
public int removeElement(int[] nums, int val) {
int id = 0;
for(int i =0;i<nums.length;i++){
//状态转移逻辑,相等什么都不做,不相等更新nums[id]的值并且id+1
if(nums[i]!=val){
nums[id++] = nums[i];
}
}
return id;
}
- 数组加1
public int[] plusOne(int[] digits) {
int n = digits.length;
for(int i = n-1;i>=0;i--){
if(digits[i]<9){
digits[i]++;
return digits;
}
digits[i]=0;
}
int new_array[] = new int[n+1];
new_array[0]=1;
return new_array;
}
- 数组是否包含重复
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
//运用了hashset
HashSet<Integer> hashSet = new HashSet<Integer>();
for(int i =0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(!hashSet.add(nums[i])){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//变试:在数组下标差距为k之内是否有重复
public boolean containsNearbyDuplicate(int[] nums, int k) {
HashSet<Integer>hashSet = new HashSet<Integer>();
for(int i =0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(i>k){
hashSet.remove(nums[i-k-1]);
}
if(!hashSet.add(nums[i])){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
- 合并两个有序数组(nums1的空间足够大)
public void merge(int[] nums1, int[] nums2,) {
int i = nums1.length-1;
int j = nums2.length-1;
int k = i+j+1;
while(i>=0&&j>=0){
if(nums1[i]<nums2[j]){
nums1[k--] = nums2[j--];
}
else nums1[k--] = nums1[i--];
}
while(j>=0){
nums1[k--] = nums2[j--];
}
}
- 将0移到数组末尾
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
int insertPos = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(nums[i]!=0){
nums[insertPos++] = nums[i];
}
}
while(insertPos<nums.length){
nums[insertPos++] = 0;
}
}
- 杨辉三角
public List<List<Integer>> generate(int numRows) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
List<Integer> row,pre = null;
for(int i =1;i<=numRows;i++){
row = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int j = 0;j<i;j++){
if(j==0||j==i-1){
row.add(1);
}
else{
row.add(pre.get(j-1)+pre.get(j));
}
}
pre = row;
list.add(row);
}
return list;
}
- 找出第三大的数
public int thirdMax(int[] nums) {
Integer[] max = new Integer[] { null, null, null };
//习惯应用这种迭代方式
for (Integer num : nums) {
//区别==和equals的用法
if (num.equals(max[0]) || num.equals(max[1]) || num.equals(max[2])) {
continue;
}
if (max[0] == null || max[0] < num) {
max[2] = max[1];
max[1] = max[0];
max[0] = num;
} else if (max[1] == null || max[1] < num) {
max[2] = max[1];
max[1] = num;
} else if (max[2] == null || max[2] < num)
max[2] = num;
}
return (max[2] == null ? max[0] : max[2]);
}
- 和为s的两个数的下标
//数组没有排序
public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
int [] res = new int[2];
if(numbers==null||numbers.length<2)
return res;
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
for(int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++){
if(!map.containsKey(target-numbers[i])){
map.put(numbers[i],i);
}else{
res[0]= map.get(target-numbers[i])+1;
res[1]= i+1;
break;
}
}
return res;
}
//数组排好了序
public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
int[] result = new int[2];
int left = 0;
int right = numbers.length-1;
//元素不能重复所以left<right
while(left<right){
int v = numbers[left]+numbers[right];
if(v == target){
result[0] = left+1;
result[1] = right+1;
break;
}
else if(v>target)
right--;
else
left++;
}
return result;
}
- 数组中出现次数超过一半的数字
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Solution {
public int MoreThanHalfNum_Solution(int [] array) {
int result = array[0];
int count =1;
for(int i = 1;i<array.length;i++){
if(array[i] == result){
count++;
}
else count--;
if(count == 0){
result = array[i];
count = 1;
}
}
count = 0;
for(int i = 0 ;i<array.length;i++){
if(array[i] == result) count++;
}
return count >(array.length / 2.0)?result:0;
}
}
- 最长连续1的个数
public int findMaxConsecutiveOnes(int[] nums) {
int count = 0;
int num = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<nums.length;i++){
if(nums[i]==1){
num = Math.max(num,++count);
}
else count=0;
}
return num;
}
- 连续子序列的最大和
//思想:到达array中的某个数值时,如果sum<0,则认为前面的sum无用丢弃,重新开始计算sum,如果sum>0,则认为sum继续更新中,之后与ret比较更新ret
public int FindGreatestSumOfSubArray(int[] array) {
if(array.length == 0) return 0;
int ret = Integer.MIN_VALUE; //用来记录最终的最大和
int sum = 0; //用来记录当前移动的最大和
for(int num : array) {
if(sum <= 0) sum = num;
else sum += num;
ret = Math.max(ret, sum);
}
return ret;
}
字符串
- 字符流中第一个不重复的字符
private int[] cnts = new int[256]; //char的取值范围为-128~127 所以创建256大小的数组用来标记
private Queue<Character> queue = new LinkedList<>();
public void Insert(char ch) {
cnts[ch]++;
queue.add(ch);
while (!queue.isEmpty() && cnts[queue.peek()] > 1) { //我们只关注第一个
queue.poll();
}
}
public char FirstAppearingOnce() {
if (queue.isEmpty()) return '#';
return queue.peek();
}
- 第一个只出现一次的字符位置
//与“字符流中第一个不重复的字符”的区别是:此处有str可以操作,而前者只有char可以操作,也可以理解为静态与动态
public int FirstNotRepeatingChar(String str) {
int[] cnts = new int[256];
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) cnts[str.charAt(i)]++;
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) if (cnts[str.charAt(i)] == 1) return i;
return -1;
}
- 最长不含重复字符的子字符串(字符串范围a~z)
public int longestSubStringWithoutDuplication(String str) {
int curLen = 0;
int maxLen = 0;
int[] position = new int[26]; //大小为26的数组用来记录字符在字符串中的位置
for(int i = 0;i<position.length;i++){
position[i]=-1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++) {
int c = str.charAt(i) - 'a'; //计算字符在数组中的位置
int preIndex = position[c];
if (preIndex == -1 || i - preIndex > curLen) {
curLen++; //连续长度+1
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, curLen);
} else curLen = i - preIndex; //例如 dabcae 就是4-1
position[c] = i;//记录字符在字符串中的位置
}
return maxLen;
}
- 字符串括号匹配
public boolean isValid(String s) {
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<Character>();
for(char a : s.toCharArray()){
switch(a){
case '(':stack.push(')');break;
case '{':stack.push('}');break;
case '[':stack.push(']');break;
default:
if(stack.empty()||!stack.pop().equals(a))return false;
}
}
return stack.empty();
}
链表
- 反转链表:输入一个链表,反转链表后,输出链表的所有元素。
public class Solution {
public ListNode ReverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head == null) return null;
ListNode pre,next;
pre = next = null;
while(head!=null){
next = head.next;
head.next = pre;
pre = head;
head = next;
}
return pre;
}
}
- 合并链表:输入两个单调递增的链表,输出两个链表合成后的链表,当然我们需要合成后的链表满足单调不减规则。
public class Solution {
public ListNode Merge(ListNode list1,ListNode list2) {
ListNode list = new ListNode(0);
ListNode head = list;
while(list1!=null&&list2!=null){
if(list1.val<=list2.val){
list.next = list1;
list1 = list1.next;
}
else {
list.next = list2;
list2 = list2.next;
}
list = list.next;
}
list.next = list1!=null?list1:list2;
return head.next;
}
}
- 反向遍历:输入一个链表,从尾到头打印链表每个节点的值。
import java.util.Stack;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Solution {
public ArrayList<Integer> printListFromTailToHead(ListNode listNode) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
while (listNode != null) {
stack.push(listNode.val);
listNode = listNode.next;
}
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
list.add(stack.pop());
}
return list;
}
}
- 链表中倒数第k个结点:输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
public class Solution {
public ListNode FindKthToTail(ListNode head,int k) {
ListNode p,q;
p = q = head;
int i = 0;
for(;p!=null;i++){
if(i>=k)
q = q.next;
p = p.next;
}
return i<k?null:q;
}
}
- 两个链表的第一个公共结点
public ListNode FindFirstCommonNode(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) {
ListNode l1 = pHead1, l2 = pHead2;
//每次遍历链表,差距就缩小1
while (l1 != l2) {
if (l1 == null) l1 = pHead2;
else l1 = l1.next;
if (l2 == null) l2 = pHead1;
else l2 = l2.next;
}
return l1;
}
/**
另一种简单思路:首先遍历两个链表得到它们的长度,获得两个链表的长度差值。在第二次遍历的时候,在较长的链表上先走差值步,接着再同时在两个链表上遍历,找到的第一个相同的结点就是它们的第一个公共结点。
**/
- 删除链表结点
//第一种:传入node
public void deleteNode(ListNode node) {
node.val = node.next.val;
node.next = node.next.next;
}
//第二种:传入val
public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) {
//处理第一个节点为空的情况,并且保证第一个节点的值不为val
while(head!=null && head.val == val){
head = head.next;
}
ListNode curr = head;
while(curr!=null && curr.next!=null){
if(curr.next.val ==val){
curr.next = curr.next.next;
}
else{
curr = curr.next;
}
}
return head;
}
- 删除链表中重复的结点
//第一种:1->1->2->3 处理后变为2->3
public ListNode deleteDuplication(ListNode pHead) {
ListNode first = new ListNode(-1);//设置一个trick
first.next = pHead;
ListNode p = pHead;//p记住当前结点
ListNode last = first;//last记住前面的结点
while (p != null && p.next != null) {
if (p.val == p.next.val) {
int val = p.val;
while (p!= null&&p.val == val)
p = p.next;
last.next = p; //更新p
} else {
last = p; //更新last
p = p.next; //更新p
}
}
return first.next;
}
//第二种:1->1->2->3 处理后变为1->2->3
public ListNode deleteDuplicates(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null)return head;
ListNode node = head;
while(node!=null && node.next!=null){
if(node.val == node.next.val){
node.next = node.next.next;
}
else node = node.next;
}
return head;
}
- 链表中环的入口结点
/**
第一步,找环中相汇点。分别用p1,p2指向链表头部,p1每次走一步,p2每次走二步,直到p1==p2找到在环中的相汇点。
第二步,找环的入口。接上步,当p1==p2时,p2所经过节点数为2x,p1所经过节点数为x,设环中有n个节点 ,p2比p1多走一圈有2x=n+x; n=x;可以看出p1实际走了一个环的步数,再让p2指向链表头部,p1位置不变,p1,p2每次走一步直到p1==p2; 此时p1指向环的入口。
**/
public ListNode EntryNodeOfLoop(ListNode pHead) {
if (pHead == null) return null;
ListNode slow = pHead, fast = pHead;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (slow == fast) {
fast = pHead;
while (slow != fast) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
}
return slow;
}
}
return null;
}
栈与队列
- 栈实现队列
/**
思路:栈的特点是先进后出,push的元素进入一个栈A,要满足队列先进先出
的特点,还需要另外一个栈B,pop时将栈A元素出栈到栈B,之后栈B在进行出
栈,就有了队列先进先出的效果
**/
import java.util.Stack;
public class Solution {
Stack<Integer> stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
Stack<Integer> stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
stack1.push(node);
}
public int pop() {
if(stack1.empty()&&stack2.empty()){
throw new RuntimeException("Queue is empty!");
}
if(stack2.empty()){
while(!stack1.empty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
}
- 队列实现栈
/**
思路:假设有两个队列Q1和Q2,当二者都为空时,入栈操作可以用入队操作来模拟,可以随便选一个空队列,假设选Q1进行入栈操作,现在假设a,b,c依次入栈了(即依次进入队列Q1),这时如果想模拟出栈操作,则需要将c出栈,因为在栈顶,这时候可以考虑用空队列Q2,将a,b依次从Q1中出队,而后进入队列Q2,将Q1的最后一个元素c出队即可,此时Q1变为了空队列,Q2中有两个元素,队头元素为a,队尾元素为b,接下来如果再执行入栈操作,则需要将元素进入到Q1和Q2中的非空队列,即进入Q2队列,出栈的话,就跟前面的一样,将Q2除最后一个元素外全部出队,并依次进入队列Q1,再将Q2的最后一个元素出队即可
**/
public class Solution {
Queue<Integer> queue1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
Queue<Integer> queue2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
public void push(int node) {
if (queue1.isEmpty()&&queue2.isEmpty()) {
queue1.add(node);
return;
}
if (queue1.isEmpty()) {
queue2.add(node);
return;
}
if (queue2.isEmpty()) {
queue1.add(node);
return;
}
}
public int pop() {
if (queue1.isEmpty()&&queue2.isEmpty()) {
try {
throw new Exception("stack is empty");
} catch (Exception e) {
}
}
if (queue1.isEmpty()) {
while (queue2.size()>1) {
queue1.add(queue2.poll());
}
return queue2.poll();
}
if (queue2.isEmpty()) {
while (queue1.size()>1) {
queue2.add(queue1.poll());
}
return queue1.poll();
}
return (Integer) null;
}
- 栈的压入,弹出序列
//给出一个入栈序列和一个出栈序列,判断是否匹配
public boolean IsPopOrder(int[] pushA, int[] popA) {
int n = pushA.length;
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < n; i++) {
stack.push(pushA[i]);
while (j < n && stack.peek() == popA[j]) {
stack.pop();
j++;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
二叉树
- 先序遍历
//recursive
public void visit(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return ;
System.out.println(root.val);
visit(root.left);
visit(root.right);
}
//iterative
public void visit(TreeNode node){
Stack<TreeNode> stack =new Stack<TreeNode>();
while(root!=null || !stack.empty()){
while(root!=null){
System.out.println(root.val);
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
root = root.right;
}
}
- 中序遍历
//recursive
public void visit(TreeNode root){
if(root ==null)return;
visit(root.left);
System.out.println(root.val);
visit(root.right);
}
//iterative
public void visit(TreeNode node){
Stack<TreeNode> stack =new Stack<TreeNode>();
while(root!=null || !stack.empty()){
while(root!=null){
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
System.out.println(root.val);
root = root.right;
}
}
- 后序遍历
//recursive
public void visit(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return ;
visit(root.left);
visit(root.right);
System.out.println(root.val);
}
//iterativey
public void visit(TreeNode node){
Stack<TreeNode> stack = new Stack<TreeNode>();
Stack<TreeNode>stack1 = new Stack<TreeNode>();
while(root!=null || !stack.empty()){
while(root!=null){
stack.push(root);
stack1.push(root);
root = root.right;
}
root = stack.pop();
root = root.left;
}
while(!stack1.empty()){
System.out.println(stack1.pop().val);
}
}
- 层次遍历
public void visit(TreeNode root){
if(root == null)return;
Queue<TreeNode> q = new LinkedList<TTreeNode>();
q.offer(root);
while(!q.isEmpty()){
TreeNode node = q.poll();
System.out.println(node.val);
if(node.left!=null){
q.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right!=null){
q.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
- 二叉搜索树的第k个结点
//递归
public class Solution {
int cnt = 0;
TreeNode KthNode(TreeNode root, int k) {
return inorder(root, k);
}
private void inorder(TreeNode root, int k) {
if (root == null) return;
inorder(root.left, k);
cnt++;
if (cnt == k) return root;
inorder(root.right, k);
}
}
//递推
public TreeNode KthNode(TreeNode root,int k){
int cnt = 0;
Stack<TreeNode> stack =new Stack<TreeNode>();
while(root!=null || !stack.empty()){
while(root!=null){
stack.push(root);
root = root.left;
}
root = stack.pop();
cnt++;
if (cnt == k) return root;
root = root.right;
}
return null;
}
- 二叉树的深度
//递归
public int TreeDepth(TreeNode pRoot)
{
if(pRoot == null){
return 0;
}
int left = TreeDepth(pRoot.left);
int right = TreeDepth(pRoot.right);
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}
//递推(层次遍历)
public int TreeDepth(TreeNode pRoot)
{
if(pRoot == null){
return 0;
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<TreeNode>();
queue.add(pRoot);
//depth表示深度,count表示当前层已经遍历的结点个数,nextCount表示下一层的结点个数
int depth = 0, count = 0, nextCount = 1;
while(queue.size()!=0){
TreeNode top = queue.poll();
count++;
if(top.left != null){
queue.add(top.left);
}
if(top.right != null){
queue.add(top.right);
}
if(count == nextCount){//当前层次结点已经遍历完了
nextCount = queue.size(); //更新nextCount
count = 0; //count变为0
depth++;//深度+1
}
}
return depth;
}
- 平衡二叉树:输入一棵二叉树,判断该二叉树是否是平衡二叉树。
public class Solution {
//后续遍历时,遍历到一个节点,其左右子树已经遍历 依次自底向上判断,每个节点只需要遍历一次
private boolean isBalanced=true;
public boolean IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode root) {
getDepth(root);
return isBalanced;
}
public int getDepth(TreeNode root){
if(root==null)
return 0;
int left=getDepth(root.left);
int right=getDepth(root.right);
if(Math.abs(left-right)>1){
isBalanced=false;
}
return right>left ?right+1:left+1;
}
}
- 二叉树的镜像:操作给定的二叉树,将其变换为源二叉树的镜像。
//先序遍历的变型
public class Solution {
public void Mirror(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)return;
change(root);
Mirror(root.left);
Mirror(root.right);
}
private void change(TreeNode root){
TreeNode temp = root.left;
root.left = root.right;
root.right = temp;
}
}
- 二叉搜索树的后序遍历序列
public class Solution {
public boolean VerifySquenceOfBST(int [] sequence) {
int size = sequence.length;
int i =0 ;
if(size == 0)return false;
while(--size>0){
while(sequence[i++]<sequence[size]){
if(i==size)break;
};
while(sequence[i++]>sequence[size]){
if(i==size)break;
};
if(i<size)return false;
i = 0;
}
return true;
}
}
排序
重要概念(稳定性)排序算法稳定性的简单形式化定义为:如果Ai = Aj,排序前Ai在Aj之前,排序后Ai还在Aj之前,则称这种排序算法是稳定的。通俗地讲就是保证排序前后两个相等的数的相对顺序不变。
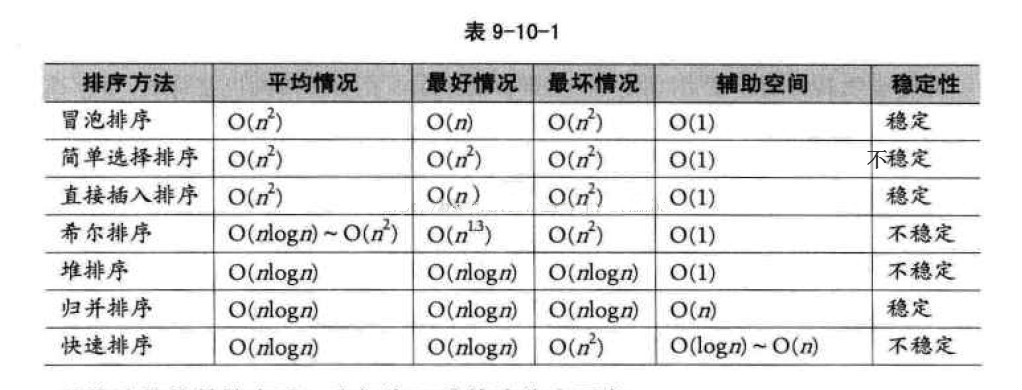
- 冒泡排序
//初始
public void BubbleSort(int[] a) {
for(int i = 0;i<a.length;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<a.length-1-i;j++) {
if(a[j]>a[j+1]) {
int tem=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=tem;
}
}
}
}
//优化:最优情况时间复杂度O(n)
public void BubbleSort(int[] a) {
boolean flag = true;
for(int i = 0;i<a.length;i++) {
flag = false;
for(int j=0;j<a.length-1-i;j++) {
if(a[j]>a[j+1]) {
int tem=a[j];
a[j]=a[j+1];
a[j+1]=tem;
flag = true;
}
}
if(!flag)break;
}
}
- 选择排序
/**
注意选择排序与冒泡排序的区别:冒泡排序通过依次交换相邻两个顺序不合法的元素位置,从而将当前最小(大)元素放到合适的位置;而选择排序每遍历一次都记住了当前最小(大)元素的位置,最后仅需一次交换操作即可将其放到合适的位置。
**/
public void SelectSort(int[] a) {
int minIndex = 0;
int temp = 0;
if ((a == null) || (a.length == 0))
return;
for (int i = 0; i < a.length - 1; i++) {
minIndex = i;
for (int j = i + 1; j < a.length; j++) {
if (a[j] < a[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
if (minIndex != i) {
temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[minIndex];
a[minIndex] = temp;
}
}
}
/**
选择排序是不稳定的排序算法,不稳定发生在最小元素与A[i]交换的时刻。
比如序列:{ 5, 8, 5, 2,9},一次选择的最小元素是2,然后把2和第一个5进行交换,从而改变了两个元素5的相对次序
**/
- 插入排序
public static void InsertSort(int[] arr)
{
int j;
int target;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
j = i;
target = arr[i];
while (j > 0 && target < arr[j - 1]){
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
j--;
}
arr[j] = target;
}
}
- 归并排序
public int[] sort(int[] a,int low,int high){
int mid = (low+high)/2;
if(low<high){
sort(a,low,mid);
sort(a,mid+1,high);
merge(a,low,mid,high);
}
return a;
}
public void merge(int[] a, int low, int mid, int high) {
int[] temp = new int[high-low+1];
int i= low;
int j = mid+1;
int k=0;
while(i<=mid && j<=high){
if(a[i]<a[j]){
temp[k++] = a[i++];
}else{
temp[k++] = a[j++];
}
}
while(i<=mid){
temp[k++] = a[i++];
}
while(j<=high){
temp[k++] = a[j++];
}
for(int x=0;x<temp.length;x++){
a[x+low] = temp[x];
}
}
- 快速排序
/**
基本思想:
快速排序使用分治的思想,通过一趟排序将待排序列分割成两部分,其中一部分记录的关键字均比另一部分记录的关键字小。之后分别对这两部分记录继续进行排序,以达到整个序列有序的目的。
快排的步骤:
(1)选择基准:在待排序列中,按照某种方式挑出一个元素,作为 “基准”(pivot)
(2)分割操作:以该基准在序列中的实际位置,把序列分成两个子序列。此时,在基准左边的元素都比该基准小,在基准右边的元素都比基准大
(3)递归地对两个序列进行快速排序,直到序列为空或者只有一个元素。
时间复杂度:
最好情况:平衡二叉树:T(n) <= 2*T(n/2) + O(n) 计算得O(nlgn)
最差情况:斜树直线:T(n)=T(n-1)+n-1 计算得O(n^2)
**/
public static void sort(int[] s, int lo, int hi){
int left = lo;
int right = hi;
int temp;
if(lo<hi){
while(left<right){
while(left<hi&&s[left]<=s[lo]){
left++;
}
while(right>lo&&s[right]>s[lo]){
right--;
}
if(left<right){//left<right是为了避免最后的重复交换
temp = s[left];
s[left] = s[right];
s[right] = temp;
}
}
//下面将s[0]的值与s[right]交换
temp = s[lo];
s[lo] = s[right];
s[right] = temp;
sort(s, lo, right-1);
sort(s, right+1, hi);
}
}
/**
快排的优化:
从快排的思想来看对于基准点的选取是至关重要的,因为他会将序列进行分割从而决定了递归的深度,而快排的时间复杂度是:depth*O(n),常见的优化方法有:随机选取基准,三数取中选取基准,当序列分割到一定大小时用插入排序,每次分割结束将key相等的元素聚在一起
**/
- 堆排序
/**
堆排序的思想:利用堆的特性,父结点值大于(或者小于)子结点值,依次取出堆顶的值,再维护成一个新堆,重复该过程,数据就被排序了
堆排序需要解决两个问题:
1.如何由一个无序序列建成一个堆?
2.如何在输出堆顶元素之后,调整剩余元素成为一个新的堆
堆排序的效率问题:
1.构建堆 O(n) 解法:递推公式为T(n) = 2*T(n/2) + O(lg n)
2.堆排序 O(nlgn) 解法:log(n-1)+log(n-2)+log(n-3)+...+lg1<nlgn
对排序是不稳定的:比如序列:{ 9, 5, 7, 5 },堆顶元素是9,堆排序下一步将9和第二个5进行交换,得到序列 { 5, 5, 7, 9 },再进行堆调整得到{ 7, 5, 5, 9 },重复之前的操作最后得到{ 5, 5, 7, 9 }从而改变了两个5的相对次序
**/
public static void sort(int[] a) {
//下标小于a.length/2的为非叶子结点,需要调整子结点建立堆
for (int i = a.length / 2; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustHeap(a, i, a.length - 1);
}
// 进行n-1次循环完成排序
for (int i = a.length - 1; i > 0; i--) {
// 最后一个元素和第一个元素进行交换
int temp = a[i];
a[i] = a[0];
a[0] = temp;
adjustHeap(a, 0, i);//调整根结点,维护成一个堆
}
}
//调整为大根堆
public static void adjustHeap(int[] a, int parent, int length) {
int temp = a[parent]; // temp保存父节点的值
int child = 2 * parent + 1; // 左子节点的索引
while (child < length) {// 如果child>=length说明不需要调整了
//比较左右结点记住最大结点的下标
if (child + 1 < length && a[child] < a[child + 1]) {
child ++;// child指向右结点
}
// 如果父结点的值大于子结点,直接返回
if (temp > a[child])
break;
//否则,将子节点的值赋值给父节点
a[parent] = a[child];
// 递推调整子结点的堆结构
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
//将开始记住父结点值的temp值赋给当前a[parent]
a[parent] = temp;
}
- 最小的k个数
/**
快排:利用快排的思想,寻找第k个位置上正确的数,k位置前面的数即是比k位置小的数组,k后面的数即是比k位置元素大的数组
**/
public void sort(int[] s, int lo, int hi, int k){
int left = lo;
int right = hi;
int temp;
if(lo<hi){
while(left<right){
while(left<hi&&s[left]<=s[lo]){
left++;
}
while(right>lo&&s[right]>s[lo]){
right--;
}
if(left<right){//left<right是为了避免最后的重复交换
temp = s[left];
s[left] = s[right];
s[right] = temp;
}
}
//下面将s[0]的值与s[right]交换
temp = s[lo];
s[lo] = s[right];
s[right] = temp;
while (right != k - 1) {
if (right > k - 1) {
hi = right-1;
sort( s, lo, hi, k);
} else {
lo = right+1;
sort( s, lo, hi, k);
}
}
}
}
//堆排序:先构造大小为k的堆,之后遍历数组调整堆
public static void sort(int[] a,int k) {
int []maxHeap = new int[k]; //储存堆的数组
for (in i = 0; i < maxHeap.lengtth; i++) {
maxHeap[i] = a[i]; //初始化
}
for (int i = a.length / 2; i >= 0; i--) {
adjustHeap(a, i, a.length - 1); //维护成一个最大堆
}
for (int i = k; i <a.length ; i++) {
if (maxHeap[0]>a[i]) {
maxHeap[0] = a[i];//如果a[i]中的元素比堆中根结点的数值小,入堆
adjustHeap(maxHeap, 0);
}
}
//调整为大根堆
public static void adjustHeap(int[] a, int parent, int length) {
int temp = a[parent]; // temp保存父节点的值
int child = 2 * parent + 1; // 左子节点的索引
while (child < length) {// 如果child>=length说明不需要调整了
//比较左右结点记住最大结点的下标
if (child + 1 < length && a[child] < a[child + 1]) {
child ++;// child指向右结点
}
// 如果父结点的值大于子结点,直接返回
if (temp > a[child])
break;
//否则,将子节点的值赋值给父节点
a[parent] = a[child];
// 递推调整子结点的堆结构
parent = child;
child = 2 * parent + 1;
}
//将开始记住父结点值的temp值赋给当前a[parent]
a[parent] = temp;
}
/**
两种思路对比:
快排
优点:节省空降,时间复杂度平均为O(n+n/2+n/(2^2)+...+n/(2^lgn))=O(n)
缺点:需要修改原始数组
堆排
优点:不用修改原始数组,适合海量数据
缺点:时间复杂度略高 O(k+(n-k)lgk)=O(nlogk)
**/
二分法及变形
- 有序数组中查找
//找到返回下标,否则返回应该插入的下标
public int searchInsert(int[] nums, int target) {
int low = 0;
//high = nums.length -1注意要减一
int high = nums.length-1;
//判断条件是小于等于
while(low<=high){
int mid = (low+high)/2;
if(nums[mid]==target){
return mid;
}
else if(nums[mid]<target){
low=mid+1;
}
else {
high=mid-1;
}
}
return low;
}
- 矩阵二分查找:在一个二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
public class Solution {
public boolean Find(int target, int [][] array) {
int row = 0;
int column = array[0].length-1;
while(row<array.length && column>=0){
if(array[row][column] == target){
return true;
}
else if(array[row][column]<target){
row++;
}
else column--;
}
return false;
}
}
- 数字在排序数组中出现的次数
public int GetNumberOfK(int[] array, int k) {
//下述二分找出一个k的下标
int l = 0, h = array.length - 1;
while (l <= h) {
int m = l + (h - l) / 2;
if (array[m] >= k) h = m - 1; //注意是>=
else l = m + 1;
}
int cnt = 0;
while (l < array.length && array[l++] == k) cnt++;
return cnt;
}
- 求x的开方
public int mySqrt(int x) {
if(x == 0) return 0;
int i = 1;
int j = x;
while(i<=j){
int mid = i + (j - i)/2;
if(mid>x/mid){
j = mid - 1;
}
else{
if((mid+1) > x/(mid+1))
return mid;
i = mid + 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
//变试:判断一个数是不是完全平方数
public boolean isPerfectSquare(int num) {
int low = 1, high = num;
while (low <= high) {
long mid = (low + high)/2;
if (mid * mid == num) {
return true;
} else if (mid * mid < num) {
low = (int) mid + 1;
} else {
high = (int) mid - 1;
}
}
return false;
}
动态规划
- 斐波那契数列:现在要求输入一个整数n,请你输出斐波那契数列的第n项。n<=39
//动态规划,每个数值都是由前两个数值决定的,具有最优子序列
//g+=f就是加上前两个数值
//f=g-f是为了记住当前g的前一个数值,对下一个g来说就是前第个数值了
public class Solution {
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
int f = 0, g = 1;
while(--n>=0) {
g += f;
f = g - f;
}
return f;
}
}
- 跳台阶:一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
public class Solution {
public int JumpFloor(int target) {
int f = 1 ; int g = 2;
while(--target>0){
g+=f;
f = g-f;
}
return f;
}
}
- 变态跳台阶:一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级……它也可以跳上n级。求该青蛙跳上一个n级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
public class Solution {
public int JumpFloorII(int target) {
int a [] = new int[target];
a[0]=1;
if(target>1){
a[1]=2;}
for(int i = 2;i<target;i++){
for(int j =0;j<i;j++){
a[i]+=a[j];
}
a[i]+=1;
}
return a[target-1];
}
}
其他
- 二进制中1的个数:输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中1的个数。其中负数用补码表示。
public class Solution {
public int NumberOf1(int n) {
int count = 0;
while(n!= 0){
count++;
n = n & (n - 1);
}
return count;
}
}