专门开一篇用来记录实际面试过程中遇到的各种题目及经验总结,不定期更新。
(更新时间:2020/05/27)
准备面试:
1.题目准备
第一大类:基础知识(html+css)
① 请简述一下em,rem,px的区别
参考网站(https://www.jianshu.com/p/f5248dda87c2)
答:
(px)是固定长度单位,不随其他元素的变化而变化。
(em)是相对长度单位,相对父级元素的变化而变化。浏览器默认比例是1em=16px,此单位一旦父元素单位变化,就需要不停的修改子元素的值, 不推荐使用。
(rem)也是相对长度单位,相对根节点(html节点)变化而变化。浏览器默认比例是1rem=16px,解决了em元素的使用弊端。一般使用方法如下:
html,body{
font-size:62.5%; //比例调整成1:10
}
扩展:参考网站(https://www.jianshu.com/p/a0bdd3e9133d)
移动端适配法则:
以下代码px与rem的尺寸比例是1:100,例如设计稿width:100px; font-size:20px,换算成rem为1rem;font-size:0.2rem
(function (doc, win) { 'use strict'; var docEl = doc.documentElement, //根元素html resizeEvt = 'orientationchange' in window ? 'orientationchange' : 'resize',//判断窗口有没有orientationchange这个方法,有就赋值给一个变量,没有就返回resize方法。 recalc = function () { var clientWidth = docEl.clientWidth; if (!clientWidth) { return; } if (clientWidth >= 560) { clientWidth = 560; //把document的fontSize大小设置成跟窗口成一定比例的大小,从而实现响应式效果。 } docEl.style.fontSize = 100 * (clientWidth / 750) + 'px'; //这里的尺寸(750)可以根据设计稿尺寸调整,例如(640)等 }; if (!doc.addEventListener) { return; } recalc(); win.addEventListener(resizeEvt, recalc, false); //addEventListener事件方法接受三个参数:第一个是事件名称比如点击事件onclick,第二个是要执行的函数,第三个是布尔 doc.addEventListener('DOMContentLoaded', recalc, false); //绑定浏览器缩放与加载时间 })(document, window);
② 请问css的哪些属性可以继承,哪些不可以继承
参考网站:(https://www.jianshu.com/p/896caadce2e7)
答:
一、能继承的属性
1. 字体系列属性:font、font-family、font-weight、font-size、font-style;
2. 文本系列属性:
(1)内联元素:color、line-height、word-spacing、letter-spacing、text-transform;
(2)块级元素:text-indent、text-align;
3. 元素可见性:visibility
4. 表格布局属性:caption-side、border-collapse、border-spacing、empty-cells、table-layout;
5. 列表布局属性:list-style
6. 生成内容属性:quotes
7. 光标属性:cursor
8. 页面样式属性:page、page-break-inside、windows、orphans;
9. 声音样式属性:speak、speech-rate、volume、voice-family、pitch、stress、elevation;
二、不能继承的属性
1. display:规定元素应该生成的框的类型;
2. 文本属性:vertical-align、text-decoration;
3. 盒子模型的属性:width、height、margin 、border、padding;
4. 背景属性:background、background-color、background-image;
5. 定位属性:float、clear、position、top、right、bottom、left、min-width、min-height、max-width、max-height、overflow、clip;
6. 生成内容属性:content、counter-reset、counter-increment;
7. 轮廓样式属性:outline-style、outline-width、outline-color、outline;
8. 页面样式属性:size、page-break-before、page-break-after;
9. 声音样式属性:pause、cue、play-during;
③ 请简述一下盒子模型。
参考网站(https://www.jianshu.com/p/afb119b66e7b)
答:盒模型分两种:标准盒模型(w3c盒模型)和怪异盒模型(ie盒模型)
W3C标准盒子模式包括内容(content)、填充(padding)、边框(border)、边界(margin)
IE盒子模型的范围也包括内容(content)、填充(padding)、边框(border)、边界(margin),但是content包含了border和padding
切换标准模式和怪异模式
box-sizing:border-box(ie盒模型)
box-sizing:content-box(默认:标准盒模型)
(更新时间:2020/05/29)
④ 清除浮动的方法
答:以下列举4种办法清楚浮动。
第一种:写一个空标签;
<style> .son{ 200px;height: 50px;float:left;} .clear{clear:both;} </style> <div class="dad"> <div class="son"></div> <div class="son"></div> <div class="clear"></div> </div>
缺点:多余添加标签,语义化不友好,不推荐使用。
第二种:父元素设置overflow属性触发BFC;
<style> .dad{overflow: hidden;} .son{ 200px;height: 50px;float:left;} .clear{clear:both;} </style> <div class="dad"> <div class="son"></div> <div class="son"></div> </div>
缺点:超出隐藏,简单粗暴,但是会隐藏点子元素超出部分,并且文字内容无法换行等问题,不推荐使用。
第三种:添加伪类;
<style> .dad:after{content:'';display: block;clear: both;height: 0;line-height: 0;visibility: hidden;} /* IE6 */ .dad{*zoom: 1;} .son{ 200px;height: 50px;float:left;} .clear{clear:both;} </style> <div class="dad"> <div class="son"></div> <div class="son"></div> </div>
缺点:ie6-7不支持伪元素after,需要使用zoom来触发hasLayout,但是结构简单,符合闭合浮动思想,推荐使用。
第四种:添加双伪类;
<style> .dad:before,.dad:after{content:'';display: table;} .dad:after{clear: both;} /* IE6 */ .dad{*zoom: 1;} .son{ 200px;height: 50px;float:left;} .clear{clear:both;} </style> <div class="dad"> <div class="son"></div> <div class="son"></div> </div>
缺点:与上述一样,效果更完善,推荐使用。
(更新时间:2020/06/01)
⑤ css中transition和animation的区别
参考网站:https://www.cnblogs.com/mufc/p/11468742.html
答:1.两个都是css3属性,transition可以看做hover的延伸,animation可以看做flash的延伸;
2.transition: property(规定设置效果的属性如width或height) duration(规定过渡需要完成的时间) timing-function(规定速度效果的速度曲线) delay(定义何时开始过渡);
3.animation: name(规定要绑定到选择器的 keyframe名称) duration(规定动画时间) timing-function(规定动画曲线) delay(规定动画开始前延迟) iteration-count(规定播放次数) direction(是否轮流反向播放);
4.transition 是过渡,是样式值的变化的过程,只有开始和结束;animation 其实也叫关键帧,通过和 keyframe 结合可以设置中间帧的一个状态;
5.animation 配合 @keyframe 可以不触发时间就触发这个过程,而 transition 需要通过 hover 或者 js 事件来配合触发;
6.在性能方面:浏览器有一个主线程和排版线程;主线程一般是对 js 运行的、页面布局、生成位图等等,然后把生成好的位图传递给排版线程,而排版线程会通过 GPU 将位图绘制到页面上,也会向主线程请求位图等等;我们在用使用 aniamtion 的时候这样就可以改变很多属性,像我们改变了 width、height、postion 等等这些改变文档流的属性的时候就会引起,页面的回流和重绘,对性能影响就比较大,但是我们用 transition 的时候一般会结合 tansfrom 来进行旋转和缩放等不会生成新的位图,当然也就不会引起页面的重排了,所以,如果可以使用transition属性完成效果就可以尽量少的使用animation。
(更新时间:2020/06/02)
⑥ 实现一个两边大小固定中间随宽度自适应的布局
实现效果如下:
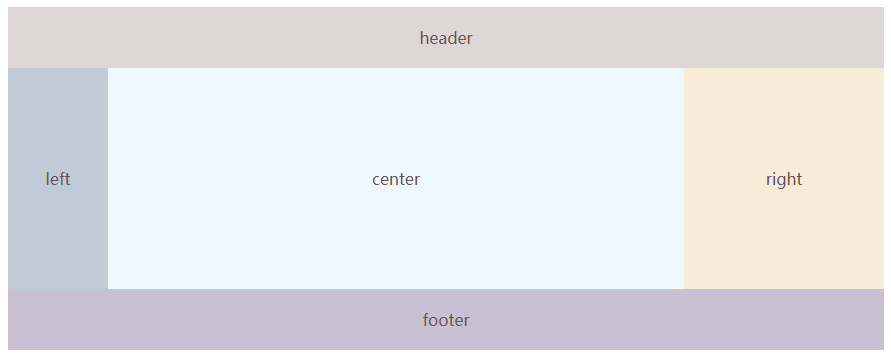
答:三种写法:
1.圣杯布局
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>圣杯布局</title>
</head>
<style>
/* 圣杯布局 */
body {
min- 500px;
text-align: center;
color: #6b5152;
}
header {
background: #dfd7d7;
padding: 20px 0;
}
.main {
padding-left: 100px;
padding-right: 200px;
clear: both;
}
.fl {
float: left;
}
.left {
100px;
background: #c1cbd7;
margin-left: -100%;
position: relative;
right: 100px;
padding: 100px 0;
}
.right {
200px;
background: #f8ebd8;
margin-right: -200px;
padding: 100px 0;
}
.center {
100%;
background: aliceblue;
padding: 100px 0;
}
footer {
clear: both;
background: #c9c0d3;
padding: 20px 0;
}
</style>
<body>
<header>header</header>
<div class="main">
<div class="fl center">
center
</div>
<div class="fl left">
left
</div>
<div class="fl right">
right
</div>
</div>
<footer>footer</footer>
</body>
</html>
2.双飞翼布局
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>双飞翼布局</title>
</head>
<style>
/* 双飞翼布局 */
body{
min- 500px;
text-align: center;
}
header {
background: #dfd7d7;
padding: 20px 0;
}
.main {
100%;
}
.fl {
float: left;
}
.center {
background: aliceblue;
margin-left: 100px;
margin-right: 200px;
padding: 100px 0;
}
.left {
100px;
background: #c1cbd7;
margin-left: -100%;
padding: 100px 0;
}
.right {
200px;
background: #f8ebd8;
margin-left: -200px;
padding: 100px 0;
}
footer {
clear: both;
background: #c9c0d3;
padding: 20px 0;
}
</style>
<body>
<header>header</header>
<div class="main fl">
<div class="center">
center
</div>
</div>
<div class="fl left">
left
</div>
<div class="fl right">
right
</div>
<footer>footer</footer>
</body>
</html>
3.flex布局
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>flex布局</title>
</head>
<style>
/* flex布局 */
body {
min- 500px;
text-align: center;
}
header {
background: #dfd7d7;
padding: 20px 0;
}
.main {
display: flex;
}
.center {
flex: 1;
background: aliceblue;
padding: 100px 0;
}
.left {
100px;
background: #c1cbd7;
flex: 0 0 100px;
padding: 100px 0;
order: -1;
}
.right {
200px;
background: #f8ebd8;
flex: 0 0 200px;
padding: 100px 0;
}
footer {
clear: both;
background: #c9c0d3;
padding: 20px 0;
}
</style>
<body>
<header>header</header>
<div class="main">
<div class="center">
center
</div>
<div class="left">
left
</div>
<div class="right">
right
</div>
</div>
<footer>footer</footer>
</body>
</html>
⑦ 列出几种实现水平垂直居中的方法
1.块级元素的水平垂直居中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>块级元素水平垂直居中</title>
<style>
/* 第一种*/
.content {
300px;
height: 300px;
background: #faead3;
margin: auto;
position: absolute;
left: 0;
right: 0;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
}
/* 第二种*/
.content {
300px;
height: 300px;
background: #faead3;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
margin-top: -150px;
margin-left: -150px;
}
/* 第三种*/
.content {
300px;
height: 300px;
background: #faead3;
position: absolute;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="content"></div>
</body>
</html>
2.行内元素的水平垂直居中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>行内元素水平垂直居中</title>
<style>
/* 单行文本水平垂直居中 */
/* 第一种 */
.wrapper {
300px;
height: 300px;
background: #faead3;
text-align: center;
word-break: break-all;
}
.content {
line-height: 300px;
}
/* 多行文本水平垂直居中 */
/* 第一种 */
.wrapper {
300px;
height: 300px;
background: #faead3;
text-align: center;
word-break: break-all;
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
}
.content {
display: inline-block;
/* IE7 */
/* display: inline;
zoom:1; */
}
/* 第二种 */
.wrapper {
300px;
height: 300px;
background: #faead3;
text-align: center;
word-break: break-all;
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
}
.content {
display: table;
margin: 0 auto;
}
/* 图片元素水平垂直居中 */
/* 第一种 */
.wrapper {
300px;
height: 300px;
background: #faead3;
text-align: center;
line-height: 300px;
font-size: 0;
}
img {
80%;
height: auto;
vertical-align: middle;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content">88888888888888888888</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
3.通用水平垂直居中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>通用水平垂直居中</title>
<style>
/* 通用规则 */
/* 第一种 */
.wrapper {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
align-items: center;
}
.content {
300px;
height: 300px;
background: #faead3;
}
/* 第二种 */
.wrapper {
300px;
height: 300px;
background: #faead3;
text-align: center;
word-break: break-all;
display: flex;
}
.content {
margin: auto;
}
/* 第三种 */
.wrapper {
300px;
height: 300px;
background: #faead3;
text-align: center;
word-break: break-all;
display: grid;
}
.content {
align-self: center;
justify-self: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="wrapper">
<div class="content">88888888888888888888</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
⑧ css预处理用的什么以及预处理的时候写过什么方法
⑨ flex布局的方法以及写法
⑩ ES5中, 除了函数,什么能够产生作用域
⑪ 简述一下你了解到的选择器
⑫ 什么是无样式内容闪烁,应该如何避免
⑬ 浏览器的内核问题
⑭ 浏览器兼容问题
⑮ CSS3的新特性(粘性定位 斜切)
⑯ 说出使用过的ui框架
第二大类:JS
⑰ 简述js的数据类型
⑱ 简述一下闭包
⑲ 简述一下 for in,for of,for each,map 的用法以及区别
⑳ 实现模糊查询的时候怎么让他发送的请求减少(事件节流)