题解:当度数大于等于3的点最多只有一个时可以遍历,否则不行。一次dfs找出以那个点为根节点的所有叶子节点(配合vector遍历)
#include <map> #include <set> #include <stack> #include <cmath> #include <queue> #include <cstdio> #include <vector> #include <string> #include <cstring> #include <iostream> #include <algorithm> #define debug(a) cout << #a << " " << a << endl using namespace std; const int maxn = 1e5 + 10; const int mod = 1e9 + 7; typedef long long ll; ll n, u, v, vis[maxn]; vector<ll> V[maxn], ans; struct node { ll num, val; }deg[maxn]; bool cmp( node a, node b ) { return a.num > b.num; } void dfs( ll k, ll last ) { vis[k] = 1; if( V[k].size() == 1 && V[k][0] == last ) { ans.push_back(k); return ; } for( ll i = 0; i < V[k].size(); i ++ ) { if( !vis[V[k][i]] ) { dfs( V[k][i], k ) ; } } return ; } int main(){ std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false); cin >> n; memset( vis, 0, sizeof(vis) ); for( ll i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) { deg[i].val = i; } for( ll i = 1; i < n; i ++ ) { cin >> u >> v; deg[u].num ++, deg[v].num ++; V[u].push_back(v), V[v].push_back(u); } sort( deg+1, deg+n+1, cmp ); if( deg[2].num >= 3 ) { cout << "No" << endl; } else { cout << "Yes" << endl; dfs( deg[1].val, -1e9 ); cout << ans.size() << endl; for( ll i = 0; i < ans.size(); i ++ ) { cout << deg[1].val << " " << ans[i] << endl; } } return 0; }
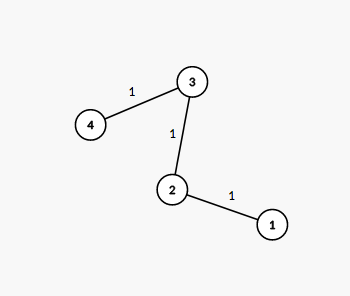 The number next to each edge corresponds to the path number in the decomposition. It is easy to see that this decomposition suits the required conditions.
The number next to each edge corresponds to the path number in the decomposition. It is easy to see that this decomposition suits the required conditions.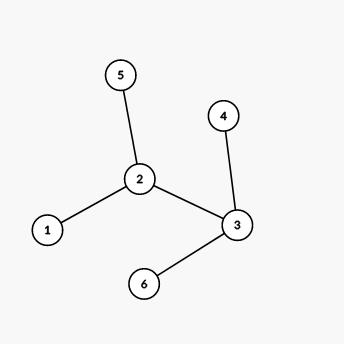 We can show that there are no valid decompositions of this tree.
We can show that there are no valid decompositions of this tree.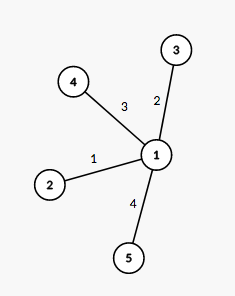 The number next to each edge corresponds to the path number in the decomposition. It is easy to see that this decomposition suits the required conditions.
The number next to each edge corresponds to the path number in the decomposition. It is easy to see that this decomposition suits the required conditions.