字典实例:建立学生学号成绩字典,做增删改查遍历操作。
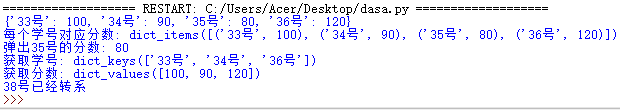
sno=['33号','34号','35号','36号'] grade=[100,90,80,120] d={'33号':100,'34号':90,'35号':80,'36号':120} print(d) print('每个学号对应分数:',d.items()) print('弹出35号的分数:',d.pop('35号')) print('获取学号:',d.keys()) print('获取分数:',d.values()) print(d.get('38号','38号已经转系'))
二、列表,元组,字典,集合的遍历。
总结列表,元组,字典,集合的联系与区别。
代码:
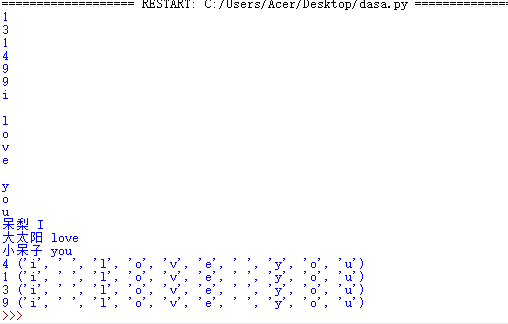
list=['1','3','1','4','9','9'] for i in list: print(i) tu=tuple('i love you') for i in tu: print(i) d={'呆梨':'I','大太阳':'love','小呆子':'you'} for i in d: print(i,d[i]) set=set(list) for i in set: print(i,tu)
- 列表是Python中最具灵活性的有序集合对象类型,与字符串不同的是,列表可以包含任何种类的对象:数字,字符串,甚至是其他列表.并且列表都是可变对象,它支持在原处修改的操作.也可以通过指定的索引和分片获取元素.列表就可元组的可变版本,用[]来定义
- .元祖可以包含不同类型的对象,但是是不可变的,不可以在增减元素,用()来定义.
- 字典(Dictionary) 是 Python 的内置数据类型之一,它定义了键和值之间一对一的关系,但它们是以无序的方式储存的,具有极快的查找速度,dict的key必须是不可变对象。定义 Dictionary 使用一对大(花)括号” { } ”。
- 集合(set)和其他语言类似, 是一个无序不重复元素集, 基本功能包括关系测试和消除重复元素. 集合对象还支持union(联合), intersection(交), difference(差)和sysmmetric difference(对称差集)等数学运算.由于集合是无序的,所以,sets 不支持 索引, 分片, 或其它类序列(sequence-like)的操作。
三、英文词频统计实例
待分析字符串
分解提取单词
- 大小写 txt.lower()
- 分隔符'.,:;?!-_’
- 单词列表
单词计数字典
代码:
girl='''Remembering me, Discover and see All over the world, She's known as a girl To those who a free, The mind shall be key Forgotten as the past 'Cause history will last God is a girl, Wherever you are, Do you believe it, can you recieve it? God is a girl, Whatever you say, Do you believe it, can you recieve it? God is a girl.''' girl=girl.lower() for i in ',?': girl=girl.replace(i,' ') words=girl.split(' ') print(words) dict={} for i in words: dict[i]=words.count(i) print(dict)
结果:
