SpringBoot启动过程流程图
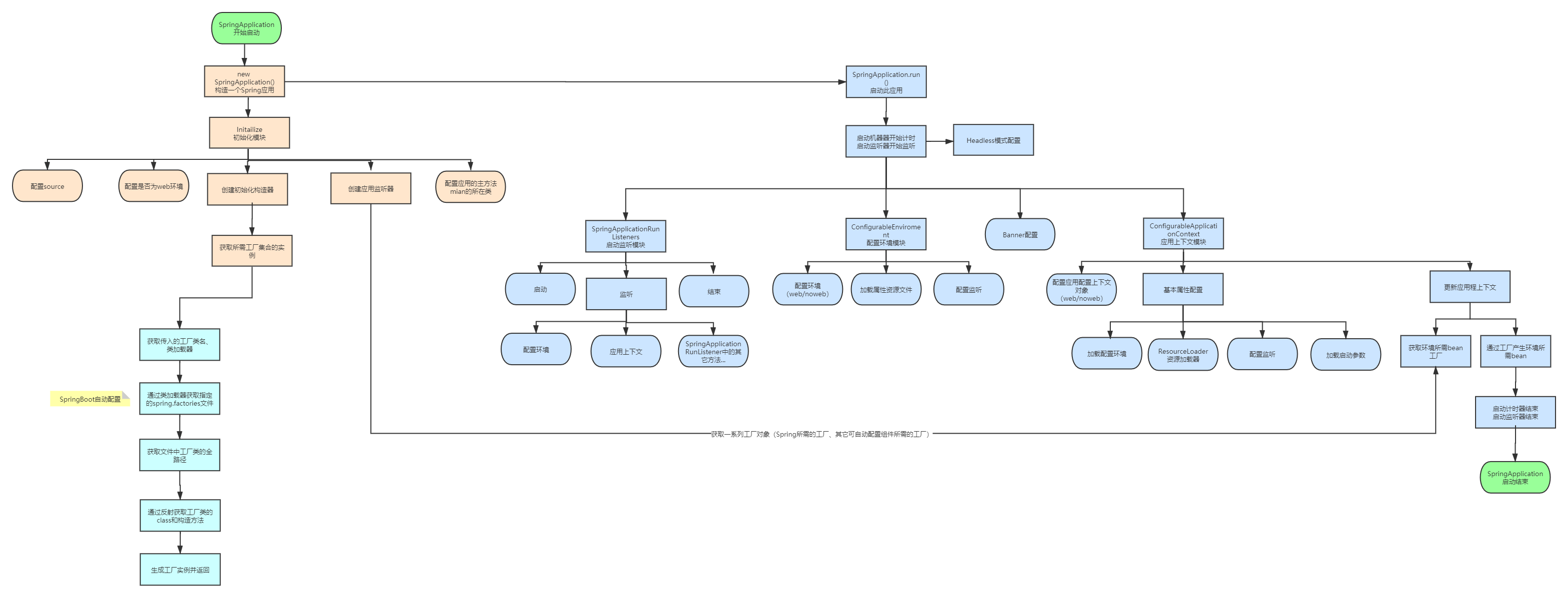
源码解析
首先,我们先来看下SpringBoot项目的启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
一个是@SpringBootApplication,参考另一篇文章SpringBoot自动配置实现原理及源码解析(2.3.x)
另一个关键点是SpringApplication.run()方法,这是一个静态方法,我们详细看下代码:
/**
* 静态方法
*/
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
return run(new Class<?>[]{primarySource}, args);
}
/**
* 调用此方法启动会使用默认设置和用户提供的参数args
*/
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
// 实例化SpringApplication,然后调用run
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
可以看到代码new SpringApplication(),new了一个这个对象,然后调用run,我们先看看SpringApplication构造函数:
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
this(null, primarySources);
}
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
// 把SpringDemoApplication作为primarySources属性存储起来
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 从classpath中推断是否为web应用
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
// 获取启动加载器
this.bootstrappers = new ArrayList<>(getSpringFactoriesInstances(Bootstrapper.class));
// 设置初始化器(Initializer),最后会调用这些功能
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// 设置监听器(Listener)
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
// 获取main方法所在的类
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
基本就是做如下几件事情:
- 配置primarySources
- 配置环境是否为web环境
- 创建初始化构造器setInitializers
- 创建应用监听器
- 配置应用主方法所在类(就是main方法所在类)
基本上就是做一些必要的属性初始化和赋值,接下来我们看下关键方法run

/**
* 运行spring应用程序,创建并刷新一个新的 {@link ApplicationContext}.
*
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 计时工具
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// 创建启动上下文对象
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext = createBootstrapContext();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 第一步:获取并启动监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(bootstrapContext, this.mainApplicationClass);
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 第二步:准备环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, bootstrapContext, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 第三步:打印banner,就是启动的时候在console的spring图案
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 第四步:创建spring容器
context = createApplicationContext();
context.setApplicationStartup(this.applicationStartup);
// 第五步:spring容器前置处理
prepareContext(bootstrapContext, context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// 第六步:刷新容器
refreshContext(context);
// 第七步:spring容器后置处理
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop(); // 结束计时器并打印,这就是我们启动后console的显示的时间
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 发出启动结束事件
listeners.started(context);
// 执行runner的run方法
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 异常处理,如果run过程发生异常
handleRunFailure(context, ex, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// 异常处理,如果run过程发生异常
handleRunFailure(context, ex, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
// 返回最终构建的容器对象
return context;
}
基本流程如下:
启动一个计时器,启动完成后会打印耗时
获取并启动监听器 SpringApplicationRunListeners
配置环境 ConfigurableEnvironment
Banner配置,就是控制台的那个spirng
应用上下文模块(前置处理、刷新、后置处理) ConfigurableApplicationContext
发出启动结束事件并结束计时
这里的每一个方法都是做了很多事情,接下来我们一步步深入看下
run方法第一步:获取并启动监听器
这里的启动监听就是我们需要监听SpringBoot的启动流程监听,实现SpringApplicationRunListener类即可监听
/**
* 获取运行监听的监听者们,在对应的阶段会发送对应的事件到监听者
* @param args
* @return
*/
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[]{SpringApplication.class, String[].class};
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger,
getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args),
this.applicationStartup);
}
1
SpringApplicationRunListener类如下:
public interface SpringApplicationRunListener {
/**
* 当调用run方法后会立即调用,可以用于非常早期的初始化
*/
default void starting(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext) {
starting();
}
/**
* 环境准备好之后调用
*/
default void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableBootstrapContext bootstrapContext,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
environmentPrepared(environment);
}
/**
* 在加载资源之前,ApplicationContex准备好之后调用
*/
default void contextPrepared(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
/**
* 在加载应用程序上下文但在其刷新之前调用
*/
default void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
/**
* 上下文已经刷新且应用程序已启动且所有{@link CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner}
* 和{@link ApplicationRunner ApplicationRunners}未调用之前调用
*/
default void started(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
/**
* 当应用程序上下文被刷新并且所有{@link CommandLineRunner commandLineRunner}
* 和{@link ApplicationRunner ApplicationRunners}都已被调用时,在run方法结束之前立即调用。
*/
default void running(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
}
/**
* 在启动过程发生失败时调用
*/
default void failed(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception) {
}
}
run方法第二步:准备环境
/**
* 创建并配置SpringBooty应用j将要使用的Environment
*
* @param listeners
* @param bootstrapContext
* @param applicationArguments
* @return
*/
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// 根据不同的web类型创建不同实现的Environment对象
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 配置环境
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 发送环境已准备完成事件
listeners.environmentPrepared(bootstrapContext, environment);
DefaultPropertiesPropertySource.moveToEnd(environment);
// 根据命令行参数中spring.profiles.active属性配置Environment对象中的activeProfile(比如dev、prod、test)
configureAdditionalProfiles(environment);
// 绑定环境中spring.main属性绑定到SpringApplication对象中
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
// 如果用户使用spring.main.web-application-type属性手动设置了webApplicationType
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
// 将环境对象转换成用户设置的webApplicationType相关类型,他们是继承同一个父类,直接强转
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
这里主要有如下过程:
- 创建配置环境 ConfigurableEnvironment
- 加载属性文件资源
- 配置监听
run方法第三步:打印banner
/**
* 打印banner
*
* @param environment
* @return
*/
private Banner printBanner(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
// banner模式,可以是console、log、off
if (this.bannerMode == Banner.Mode.OFF) {
return null;
}
ResourceLoader resourceLoader = (this.resourceLoader != null) ? this.resourceLoader
: new DefaultResourceLoader(null);
SpringApplicationBannerPrinter bannerPrinter = new SpringApplicationBannerPrinter(resourceLoader, this.banner);
if (this.bannerMode == Mode.LOG) {
return bannerPrinter.print(environment, this.mainApplicationClass, logger);
}
return bannerPrinter.print(environment, this.mainApplicationClass, System.out);
}基本就是依据不同情况打印banner而已,比较简单
run方法第四步:创建spring容器
最终获取到ConfigurableApplicationContext上下文对象run方法第五步:spring容器前置处理
/**
* Spring容器准备
*/
private void prepareContext(DefaultBootstrapContext bootstrapContext, ConfigurableApplicationContext context,
ConfigurableEnvironment environment, SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
// 设置上下文环境
context.setEnvironment(environment);
//
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
// 执行所有ApplicationContextInitializer对象的initialize方法(这些对象是通过读取spring.factories加载)
applyInitializers(context);
// 发布上下文准备完成事件到所有监听器
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
bootstrapContext.close(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
//
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
// 加载bean到上下文
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
// 发送上下文加载完成事件
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}run方法第六步:刷新容器【关键】
/**
* 刷新应用程序上下文
*
* @param context
*/
private void refreshContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 注册一个关闭钩子,在jvm停止时会触发,然后退出时执行一定的退出逻辑
if (this.registerShutdownHook) {
try {
// 添加:Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook()
// 移除:Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(this.shutdownHook)
context.registerShutdownHook();
} catch (AccessControlException ex) {
// Not allowed in some environments.
}
}
// ApplicationContext真正开始初始化容器和创建bean的阶段
refresh((ApplicationContext) context);
}
protected void refresh(ApplicationContext applicationContext) {
Assert.isInstanceOf(ConfigurableApplicationContext.class, applicationContext);
refresh((ConfigurableApplicationContext) applicationContext);
}protected void refresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext applicationContext) {
applicationContext.refresh();
}调用应用上下文对象的refresh()方法,接下来我i门到ConfigurableApplicationContext类中去看下这个方法
public interface ConfigurableApplicationContext extends ApplicationContext, Lifecycle, Closeable {
void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException;
} -
这是一个接口,且这个类是在spring框架中,非springboot,它的实现类共有三个
-
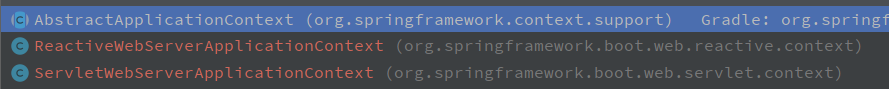
AbstractApplicationContext是一个抽象类,其余两个类都继承了它,我们来看看这个抽象类的代码:
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
StartupStep contextRefresh = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.refresh");// 第一步:准备更新上下时的预备工作
prepareRefresh();// 第二步:获取上下文内部BeanFactory
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();// 第三步:对BeanFactory做预备工作
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);try {
// 第四步:允许在上下文子类中对bean工厂进行post-processing
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);StartupStep beanPostProcess = this.applicationStartup.start("spring.context.beans.post-process");
// 第五步:调用上下文中注册为bean的工厂 BeanFactoryPostProcessor
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);// 第六步:注册拦截bean创建的拦截器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
beanPostProcess.end();// 第七步:初始化MessageSource(国际化相关)
initMessageSource();// 第八步:初始化容器事件广播器(用来发布事件)
initApplicationEventMulticaster();// 第九步:初始化一些特殊的bean
onRefresh();// 第十步:将所有监听器注册到前两步创建的事件广播器中
registerListeners();// 第十一步:结束bean的初始化工作(主要将所有单例BeanDefinition实例化)
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);// 第十二步:afterRefresh(上下文刷新完毕,发布相应事件)
finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
} finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
contextRefresh.end();
}
}
}这里有非常多的步骤,上下文对象主要的bean也是在这里进行处理的,具体的说明可以看注释
@Override
public final void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
try {
super.refresh();
}
catch (RuntimeException ex) {
WebServer webServer = this.webServer;
if (webServer != null) {
webServer.stop();
}
throw ex;
}
}主要还是调用父类方法,没有什么特殊的
run方法/第七步:spring容器后置处理 afterRefresh()
protected void afterRefresh(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
}这是一个空的方法
run方法启动后
主要做如下几件事情:发出启动结束事件
执行实现ApplicationRunner、CommandLineRunner的run方法
发布应用程序已启动(ApplicationStartedEvent)事件
run方法异常处理
如果run方法的处理过程中发生异常,则对exitCode进行相应处理private void handleRunFailure(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, Throwable exception,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners) {
try {
try {
handleExitCode(context, exception);
if (listeners != null) {
listeners.failed(context, exception);
}
} finally {
reportFailure(getExceptionReporters(context), exception);
if (context != null) {
context.close();
}
}
} catch (Exception ex) {
logger.warn("Unable to close ApplicationContext", ex);
}
ReflectionUtils.rethrowRuntimeException(exception);
}
至此,所有SpringBoot的启动流程已经完成,你的项目也顺利的跑起来了