霍夫曼编码(Huffman Coding)是一种编码方法,霍夫曼编码是可变字长编码(VLC)的一种。
霍夫曼编码使用变长编码表对源符号(如文件中的一个字母)进行编码,其中变长编码表是通过一种评估来源符号出现机率的方法得到的,出现机率高的字母使用较短的编码,反之出现机率低的则使用较长的编码,这便使编码之后的字符串的平均长度、期望值降低,从而达到无损压缩数据的目的。
霍夫曼编码的具体步骤如下:
1)将信源符号的概率按减小的顺序排队。
2)把两个最小的概率相加,并继续这一步骤,始终将较高的概率分支放在右边,直到最后变成概率1。
3)画出由概率1处到每个信源符号的路径,顺序记下沿路径的0和1,所得就是该符号的霍夫曼码字。
4)将每对组合的左边一个指定为0,右边一个指定为1(或相反)。
例:现有一个由5个不同符号组成的30个符号的字符串:
BABACAC ADADABB CBABEBE DDABEEEBB
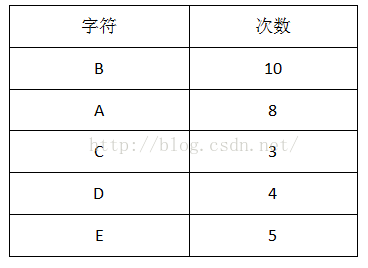
1首先计算出每个字符出现的次数(概率):
2把出现次数(概率)最小的两个相加,并作为左右子树,重复此过程,直到概率值为1

第一次:将概率最低值3和4相加,组合成7:
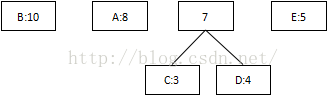
第二次:将最低值5和7相加,组合成12:

第三次:将8和10相加,组合成18:
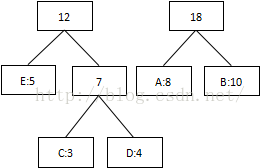
第四次:将最低值12和18相加,结束组合:
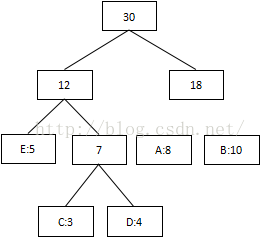
3 将每个二叉树的左边指定为0,右边指定为1

4 沿二叉树顶部到每个字符路径,获得每个符号的编码
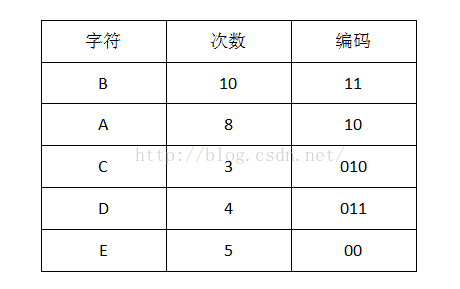
我们可以看到出现次数(概率)越多的会越在上层,编码也越短,出现频率越少的就越在下层,编码也越长。当我们编码的时候,我们是按“bit”来编码的,解码也是通过bit来完成,如果我们有这样的bitset “10111101100″ 那么其解码后就是 “ABBDE”。所以,我们需要通过这个二叉树建立我们Huffman编码和解码的字典表。
这里需要注意的是,Huffman编码使得每一个字符的编码都与另一个字符编码的前一部分不同,不会出现像’A’:00, ’B’:001,这样的情况,解码也不会出现冲突。
霍夫曼编码的局限性
利用霍夫曼编码,每个符号的编码长度只能为整数,所以如果源符号集的概率分布不是2负n次方的形式,则无法达到熵极限;输入符号数受限于可实现的码表尺寸;译码复杂;需要实现知道输入符号集的概率分布;没有错误保护功能。
霍夫曼编码实现 (C++实现):
- int main()
- {
- int n, w;
- char c;
- string s;
- cout << "input size of char : ";
- cin >> n;
- BinartNodes bn;
- for(int i = 0; i != n; ++i)
- {
- cout << "input char and weight: ";
- cin >> c >> w;
- bn.add_Node((Node(c, w)));
- cin.clear();
- }
- while(bn.size() != 1)
- {
- Node n1 = bn.pop(), //获取前两个权重最小的结点
- n2 = bn.pop();
- Node h(' ', n1.get_weight() + n2.get_weight()); //新建结点,权重为前两个结点权重和
- if( n1.get_weight() < n2.get_weight()) //权重较小的结点在新结点左边
- {
- h.set(n1, n2); //设置新结点左右子结点
- }
- else
- {
- h.set(n2, n1);
- }
- bn.add_Node(h); //将新结点插入到multiset中
- }
- encodeing(bn.get_Node(), s); //编码
- cout << "input huffman code: ";
- cin >> s;
- cout << "decoded chars: ";
- decoding(bn.get_Node(), s); //解码
- }
Handle.h句柄类:
- /*Handle.h*/
- //句柄模型类
- template <class Type> class Handle{
- public:
- Handle(Type *ptr = 0): pn(ptr), use(new size_t(1)) {}
- Type& operator*(); //重载操作符*
- Type* operator->(); //重载操作符->
- const Type& operator*() const;
- const Type* operator->() const;
- Handle(const Handle &h): pn(h.pn), use(h.use) { ++*use; } //复制操作
- Handle& operator=(const Handle &h); //重载操作符=,赋值操作
- ~Handle() {rem_ref(); } //析构函数
- private:
- Type *pn; //对象指针
- size_t *use; //使用次数
- void rem_ref()
- {
- if (--*use == 0)
- {delete pn; delete use; }
- }
- };
- template <class Type> inline Type& Handle<Type>::operator*()
- {
- if (pn) return *pn;
- throw runtime_error("dereference of unbound Handle");
- }
- template <class Type> inline const Type& Handle<Type>::operator*() const
- {
- if (pn) return *pn;
- throw runtime_error("dereference of unbound Handle");
- }
- template <class Type> inline Type* Handle<Type>::operator->()
- {
- if (pn) return pn;
- throw runtime_error("access through unbound handle");
- }
- template <class Type> inline const Type* Handle<Type>::operator->() const
- {
- if (pn) return pn;
- throw runtime_error("access through unbound handle");
- }
- template <class Type> inline Handle<Type>& Handle<Type>::operator=(const Handle &rhs)
- {
- ++*rhs.use;
- rem_ref();
- pn = rhs.pn;
- use = rhs.use;
- return *this;
- }
- /*Node.h*/
- template <class T> class Handle;
- class Node{
- friend class Handle<Node>; //句柄模型类
- public:
- Node():ch(' '),wei(0), bits(), lc(), rc(){}
- Node(const char c, const int w):
- ch(c), wei(w), bits(), lc(), rc(){}
- Node(const Node &n){ch = n.ch; wei = n.wei; bits = n.bits;
- lc = n.lc; rc = n.rc; }
- virtual Node* clone()const {return new Node( *this);}
- int get_weight() const {return wei;} //获取权重
- char get_char() const {return ch; } //获得字符
- Node &get_lchild() {return *lc; } //获得左结点
- Node &get_rchild() {return *rc; } //获得右结点
- void set(const Node &l, const Node &r){ //设置左右结点
- lc = Handle<Node>(new Node(l));
- rc = Handle<Node>(new Node(r));}
- void set_bits(const string &s){bits = s; } //设置编码
- private:
- char ch; //字符
- int wei; //权重
- string bits; //编码
- Handle<Node> lc; //左结点句柄
- Handle<Node> rc; //右结点句柄
- };
- inline bool compare(const Node &lhs, const Node &rhs); //multiset比较函数
- inline bool compare(const Node &lhs, const Node &rhs)
- {
- return lhs.get_weight() < rhs.get_weight();
- }
- class BinartNodes{
- typedef bool (*Comp)(const Node&, const Node&);
- public:
- BinartNodes():ms(compare) {} //初始化ms的比较函数
- void add_Node(Node &n){ms.insert(n); } //增加Node结点
- Node pop(); //出结点
- size_t size(){return ms.size(); } //获取multiset大小
- Node get_Node() {return *ms.begin();} //获取multiset第一个数据
- private:
- multiset<Node, Comp> ms;
- };
- /*Node.cpp*/
- #include "Node.h"
- Node BinartNodes::pop()
- {
- Node n = *ms.begin(); //获取multiset第一个数据
- ms.erase(ms.find(*ms.begin())); //从multiset中删除该数据
- return n;
- }
霍夫曼编码实现 (C语言实现):
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include<stdlib.h>
- #include<string>
- #include <iostream>
- #define MAXBIT 100
- #define MAXVALUE 10000
- #define MAXLEAF 30
- #define MAXNODE MAXLEAF*2 -1
- typedef struct
- {
- int bit[MAXBIT];
- int start;
- } HCodeType; /* 编码结构体 */
- typedef struct
- {
- int weight;
- int parent;
- int lchild;
- int rchild;
- char value;
- } HNodeType; /* 结点结构体 */
- /* 构造一颗哈夫曼树 */
- void HuffmanTree (HNodeType HuffNode[MAXNODE], int n)
- {
- /* i、j: 循环变量,m1、m2:构造哈夫曼树不同过程中两个最小权值结点的权值,
- x1、x2:构造哈夫曼树不同过程中两个最小权值结点在数组中的序号。*/
- int i, j, m1, m2, x1, x2;
- /* 初始化存放哈夫曼树数组 HuffNode[] 中的结点 */
- for (i=0; i<2*n-1; i++)
- {
- HuffNode[i].weight = 0;//权值
- HuffNode[i].parent =-1;
- HuffNode[i].lchild =-1;
- HuffNode[i].rchild =-1;
- HuffNode[i].value=' '; //实际值,可根据情况替换为字母
- } /* end for */
- /* 输入 n 个叶子结点的权值 */
- for (i=0; i<n; i++)
- {
- printf ("Please input char of leaf node: ", i);
- scanf ("%c",&HuffNode[i].value);
- getchar();
- } /* end for */
- for (i=0; i<n; i++)
- {
- printf ("Please input weight of leaf node: ", i);
- scanf ("%d",&HuffNode[i].weight);
- getchar();
- } /* end for */
- /* 循环构造 Huffman 树 */
- for (i=0; i<n-1; i++)
- {
- m1=m2=MAXVALUE; /* m1、m2中存放两个无父结点且结点权值最小的两个结点 */
- x1=x2=0;
- /* 找出所有结点中权值最小、无父结点的两个结点,并合并之为一颗二叉树 */
- for (j=0; j<n+i; j++)
- {
- if (HuffNode[j].weight < m1 && HuffNode[j].parent==-1)
- {
- m2=m1;
- x2=x1;
- m1=HuffNode[j].weight;
- x1=j;
- }
- else if (HuffNode[j].weight < m2 && HuffNode[j].parent==-1)
- {
- m2=HuffNode[j].weight;
- x2=j;
- }
- } /* end for */
- /* 设置找到的两个子结点 x1、x2 的父结点信息 */
- HuffNode[x1].parent = n+i;
- HuffNode[x2].parent = n+i;
- HuffNode[n+i].weight = HuffNode[x1].weight + HuffNode[x2].weight;
- HuffNode[n+i].lchild = x1;
- HuffNode[n+i].rchild = x2;
- printf ("x1.weight and x2.weight in round %d: %d, %d ", i+1, HuffNode[x1].weight, HuffNode[x2].weight); /* 用于测试 */
- printf (" ");
- } /* end for */
- } /* end HuffmanTree */
- //解码
- void decodeing(char string[],HNodeType Buf[],int Num)
- {
- int i,tmp=0,code[1024];
- int m=2*Num-1;
- char *nump;
- char num[1024];
- for(i=0;i<strlen(string);i++)
- {
- if(string[i]=='0')
- num[i]=0;
- else
- num[i]=1;
- }
- i=0;
- nump=&num[0];
- while(nump<(&num[strlen(string)]))
- {tmp=m-1;
- while((Buf[tmp].lchild!=-1)&&(Buf[tmp].rchild!=-1))
- {
- if(*nump==0)
- {
- tmp=Buf[tmp].lchild ;
- }
- else tmp=Buf[tmp].rchild;
- nump++;
- }
- printf("%c",Buf[tmp].value);
- }
- }
- int main(void)
- {
- HNodeType HuffNode[MAXNODE]; /* 定义一个结点结构体数组 */
- HCodeType HuffCode[MAXLEAF], cd; /* 定义一个编码结构体数组, 同时定义一个临时变量来存放求解编码时的信息 */
- int i, j, c, p, n;
- char pp[100];
- printf ("Please input n: ");
- scanf ("%d", &n);
- HuffmanTree (HuffNode, n);
- for (i=0; i < n; i++)
- {
- cd.start = n-1;
- c = i;
- p = HuffNode[c].parent;
- while (p != -1) /* 父结点存在 */
- {
- if (HuffNode[p].lchild == c)
- cd.bit[cd.start] = 0;
- else
- cd.bit[cd.start] = 1;
- cd.start--; /* 求编码的低一位 */
- c=p;
- p=HuffNode[c].parent; /* 设置下一循环条件 */
- } /* end while */
- /* 保存求出的每个叶结点的哈夫曼编码和编码的起始位 */
- for (j=cd.start+1; j<n; j++)
- { HuffCode[i].bit[j] = cd.bit[j];}
- HuffCode[i].start = cd.start;
- } /* end for */
- /* 输出已保存好的所有存在编码的哈夫曼编码 */
- for (i=0; i<n; i++)
- {
- printf ("%d 's Huffman code is: ", i);
- for (j=HuffCode[i].start+1; j < n; j++)
- {
- printf ("%d", HuffCode[i].bit[j]);
- }
- printf(" start:%d",HuffCode[i].start);
- printf (" ");
- }
- printf("Decoding?Please Enter code: ");
- scanf("%s",&pp);
- decodeing(pp,HuffNode,n);
- getchar();
- return 0;
- }