一、Collection
集合存放在java.util包中,可以看作是集成好的数据结构,供你调用,十分方便,集合经常拿来和数组对比,其实我觉得没啥可比性,不过还是简单来看看它们的区别:
1.数组长度固定,而集合长度不固定。
2.集合只能存储对象,但数组不仅能存储基本类型还有对象数组。
3.集合存储的是对象的引用,对象本身不连续(待证实),而数组元素与元素内存连续。
4.一个数组只能存相同的数据类型,集合能存不同的数据类型。(补充例子)
先来张图,话说好像是第一次上图。。。

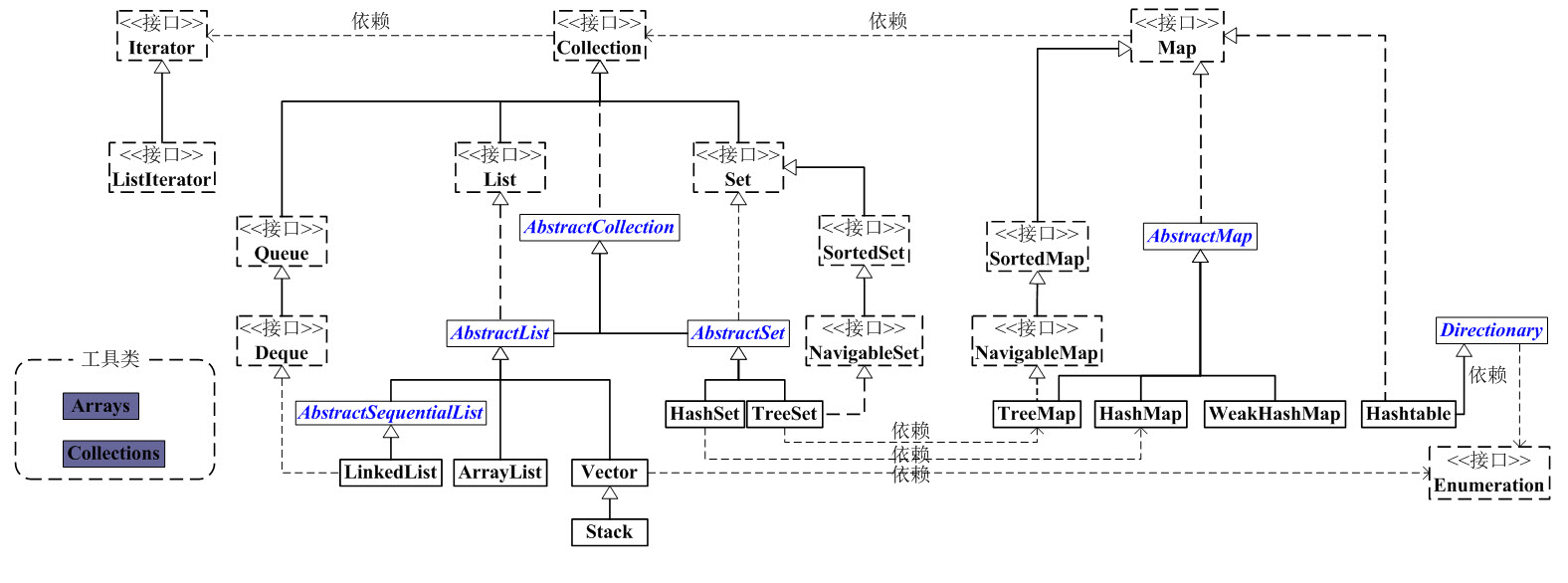
图1来源: http://www.cnblogs.com/taiwan/p/6954135.html
图2出处:http://www.cnblogs.com/skywang12345/p/io_07.html
这两个图展示了基本集合的关系,暂时也考虑按这个顺序来复习。Collection和Map是两个根接口,互不影响。
二、List
上篇也说到了List其实是一个接口,并且实现父接口Collection,实现它的类有ArrayList、Vector和LinkedList。
但基本上的使用方法都是:List l=new ArrayList(); List l=new Vector();
Collection和List的方法包括(均为JDK1.7的基本功能、例如Collection接口1.8版本新增4个功能 注:removeIf spliterator stream parallelStream,List接口新增3个功能 注:spliterator replaceAll sort):
abstract boolean add(E object) abstract boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection) abstract void clear() abstract boolean contains(Object object) abstract boolean containsAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract boolean equals(Object object) abstract int hashCode() //equal和hashCode两个方法Object也有,Collection和List都是覆盖过的。 abstract boolean isEmpty() //注:Vector也有覆盖,但ArrayList和LinkedList没有。 abstract Iterator<E> iterator() abstract boolean remove(Object object) abstract boolean removeAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract boolean retainAll(Collection<?> collection) abstract int size() abstract <T> T[] toArray(T[] array) abstract Object[] toArray()
————————————————上面是Collection,下面是List————————————————
abstract void add(int location, E object) abstract boolean addAll(int location, Collection<? extends E> collection) abstract E get(int location) abstract int indexOf(Object object) abstract int lastIndexOf(Object object) abstract ListIterator<E> listIterator(int location) abstract ListIterator<E> listIterator() abstract E remove(int location) abstract E set(int location, E object) abstract List<E> subList(int start, int end)
而对于实现List接口的主要三个数据结构分别是ArrayList、Vector、LinkedList,其中ArrayList和Vector是很类似的,都类似于可变长的对象数组,但是ArrayList不是线程安全的,而Vector是线程安全的,这个到学习线程部分再详说吧,暂时先理解为适合单线程和多线程。LinkedList则是链表(线程不安全,其实集合类中Vector、Stack、Hashtable和Enumeration是线程安全的,其余都是线程不安全的),适合增删操作较多时,那两个比较适合遍历操作,面向的任务不同。
1.对于ArrayList来说,新增的方法如下:
Object clone()
void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity)
void trimToSize()
void removeRange(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
ArrayList是一个类,实现List接口,成员域有两个,分别为:
private int size; // 实际元素个数
transient Object[] elementData; //数组存放内容
构造函数有3个,无参构造函数,capacity=10,size=0(但其实其中过程较为复杂,ArrayList是在添加第一个元素时才实现了初始容量为10的构造,
可以参考https://blog.csdn.net/jdsjlzx/article/details/52675726和https://blog.csdn.net/m0_37884977/article/details/80514809);
以initialCapacity 参数的构造函数,capacity=initialCapacity size=0;以Collection为参数的构造函数,size=capacity=原Collection的size;
1 package list; 2 3 import java.lang.reflect.Field; 4 import java.util.ArrayList; 5 6 public class Capacity { 7 8 public static void main(String[] args) { 9 // ArrayList <Integer> al=new ArrayList<Integer>(); 10 // ArrayList <Integer> al=new ArrayList<Integer>(4); 11 ArrayList <Integer> bl=new ArrayList<Integer>(); 12 for(int i=0;i<9;i++) 13 { 14 bl.add(i); 15 } 16 ArrayList <Integer> al=new ArrayList<Integer>(bl); 17 System.out.println(al.size()); 18 System.out.println(getArrayListCapacity(al)); 19 al.add(1); 20 System.out.println(al.size()); 21 System.out.println(getArrayListCapacity(al)); 22 for(int i=0;i<9;i++) 23 { 24 al.add(i); 25 } 26 System.out.println(al.size()); 27 System.out.println(getArrayListCapacity(al)); 28 al.add(11); 29 System.out.println(al.size()); 30 System.out.println(getArrayListCapacity(al)); 31 for(int i=0;i<5;i++) 32 { 33 al.add(i); 34 } 35 System.out.println(al.size()); 36 System.out.println(getArrayListCapacity(al)); 37 38 } 39 public static int getArrayListCapacity(ArrayList<?> arrayList) { 40 Class<ArrayList> arrayListClass = ArrayList.class; 41 try { 42 Field field = arrayListClass.getDeclaredField("elementData"); 43 field.setAccessible(true); 44 Object[] objects = (Object[])field.get(arrayList); 45 return objects.length; 46 } catch (NoSuchFieldException e) { 47 e.printStackTrace(); 48 return -1; 49 } catch (IllegalAccessException e) { 50 e.printStackTrace(); 51 return -1; 52 } 53 } 54 55 }
当容量不够时,ArrayList自动扩容到1.5倍的下取整10-15-22-33;4-6-9-13-19;这个样子
关于ArrayList的操作直接上代码:
/*ensureCapacity和trimToSize方法*/
al.ensureCapacity(38); //42 if parameter<1.5oldCapacity newCapacity=1.5Capacity else newCapacity=parameter System.out.println(getArrayListCapacity(al)); al.ensureCapacity(43); // 63 System.out.println(getArrayListCapacity(al)); al.trimToSize(); //使capacity=size System.out.println(al.size()); System.out.println(getArrayListCapacity(al));
package list; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Collection; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.List; import java.util.ListIterator; import java.util.Vector; //ArrayList Function public class collection { public static void main(String []args) { ArrayList <Integer> a=new ArrayList<Integer>(); ArrayList <Integer> b=new ArrayList<Integer>(); ArrayList <Integer> c=new ArrayList<Integer>(); /*四种Add操作*/ for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { c.add(i); } a.add(8); a.addAll(c); b.addAll(0, c); b.add(5,55); //插入在index前面一位 /*contains操作*/ System.out.println(b.contains(0)); //true System.out.println(b.contains(null)); //false // Object p=new Object(); // System.out.println(p.equals(null)); 永远false /*Iterator*/ Iterator <Integer> it=b.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { System.out.print(it.next()+" "); } System.out.println(); /*retainAll*/ b.retainAll(a); //只要b中元素不在a中(即a中没有),就删掉。 /*ListIterator<E> listIterator(int index) * 从下标index开始为第一个,而且可以向前previous()和hasPrevious()*/ ListIterator <Integer> it1=b.listIterator(0); while(it1.hasNext()) { System.out.print(it1.next()+" "); } System.out.println(); /*subList 形成一个视图*两者联动一个变,另一个也变/ List<Integer> d=b.subList(2, 7); d.set(0, 888); /*ForEach*/ for(int j:d) { System.out.print(j+" "); } System.out.println(); for(int j:b) { System.out.print(j+" "); } System.out.println(); d.remove(3); for(int j:d) { System.out.print(j+" "); } System.out.println(); for(int j:b) { System.out.print(j+" "); } System.out.println();
d.set(3,333);
for(int j:d)
{
System.out.print(j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
for(int j:b)
{
System.out.print(j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
/**/ } }
结果:
true
false
0 1 2 3 4 55 5 6 7 8 9
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
888 3 4 5 6
0 1 888 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 //d变b也变
888 3 4 6
0 1 888 3 4 6 7 8 9
888 333 4 6
0 1 888 333 4 6 7 8 9 //b变d也变
其他操作:
深层拷贝和浅层拷贝:深层拷贝是指完全复制,不指向同一元素;浅层拷贝指向同一元素
而ArrayList的clone()方法是一种浅层拷贝方法?(不知如何验证,所以也不确定)
package list; import java.util.ArrayList; public class arraylist { public static void main(String[] args) { // ArrayList <Integer> a=new ArrayList<Integer>(); //互不影响 ArrayList <String> a=new ArrayList<String>(); for(int i=0;i<9;i++) { a.add(String.valueOf(i)+"aa"); } ArrayList <String> b=(ArrayList<String>) a.clone(); //cast for(String j:a) { System.out.print(j+" "); } System.out.println(); for(String j:b) { System.out.print(j+" "); } System.out.println(); a.remove(0); for(String j:a) { System.out.print(j+" "); } System.out.println(); for(String j:b) { System.out.print(j+" "); } System.out.println(); b.remove(1); for(String j:a) { System.out.print(j+" "); } System.out.println(); for(String j:b) { System.out.print(j+" "); } System.out.println(); } }
总是互相不关联,看起来像是深度复制啊?还是实验设计有问题?
2.Vector
Vector有3个成员域:
int elementCount; // 实际元素个数
Object[] elementData; //动态数组存放内容
int capacityIncrement //
四个构造函数:
默认构造函数:Vector(); capacity=10,increment=0
单参数构造函数:Vector(int initCapacity); capacity=initCapacity,increment=0
双参数构造函数:Vector(int initCapacity,int capacityIncrement); capacity=initCapacity,increment=capacityIncrement
Collection构造函数:Vector(Collection c)
向量的大小大于其容量时,容量自动增加的量。如果在创建Vector时,指定了capacityIncrement的大小;则,每次当Vector中动态数组容量增加时,增加的大小都是capacityIncrement。如果容量的增量小于等于零,则每次需要增大容量时,向量的容量将增大一倍。若是ensureCapacity(int minCapacity)方法,首先判断capacityIncrement是否大于0,若大于0新容量newCapacity=oldCapacity+capacityIncrement。否则newCapacity=oldCapacity*2。之后选择newCapacity和minCapacity较大的那一个当作新的容量。ensureCapacirt(int minCapacity)核心代码:
private void grow(int minCapacity) { int oldCapacity = elementData.length; //旧容量 int newCapacity = oldCapacity + ((capacityIncrement > 0) ?capacityIncrement : oldCapacity); //capacity>0直接加,小于等于0翻倍 if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) newCapacity = minCapacity; //之后判断是否大于参数,选较大的 if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)// newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity); elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity); } public synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity > 0) { modCount++;// ensureCapacityHelper(minCapacity); } private static int hugeCapacity(int minCapacity) { if (minCapacity < 0) // overflow throw new OutOfMemoryError(); return (minCapacity > MAX_ARRAY_SIZE) ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : MAX_ARRAY_SIZE; } 原文:https://blog.csdn.net/zhangveni/article/details/51000873
Vector中的API:
synchronized boolean add(E object) //尾部增加元素@@@@
void add(int location, E object) //下标location之前插入元素@@@@
synchronized boolean addAll(Collection<? extends E> collection) //@@@@
synchronized boolean addAll(int location, Collection<? extends E> collection) //@@@@
synchronized void addElement(E object) //除返回值不同,其他和add一样
synchronized int capacity()
void clear() //@@@@
synchronized Object clone() ####
boolean contains(Object object) //@@@@
synchronized boolean containsAll(Collection<?> collection) //@@@@
synchronized void copyInto(Object[] elements) //***********//
synchronized E elementAt(int location)
Enumeration<E> elements() //***********//
synchronized void ensureCapacity(int minimumCapacity) #####
synchronized boolean equals(Object object) //@@@@
synchronized E firstElement()
E get(int location) //@@@@
synchronized int hashCode() //@@@@
synchronized int indexOf(Object object, int location) //***********//
int indexOf(Object object) //@@@@
synchronized void insertElementAt(E object, int location)
synchronized boolean isEmpty() //@@@@
synchronized E lastElement()
synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object object, int location)
synchronized int lastIndexOf(Object object) @@@@
synchronized E remove(int location) @@@@
boolean remove(Object object) @@@@
synchronized boolean removeAll(Collection<?> collection) @@@@
synchronized void removeAllElements()
synchronized boolean removeElement(Object object)
synchronized void removeElementAt(int location)
synchronized boolean retainAll(Collection<?> collection) @@@@
synchronized E set(int location, E object) @@@@
synchronized void setElementAt(E object, int location)
synchronized void setSize(int length) //************//
synchronized int size() @@@@
synchronized List<E> subList(int start, int end) @@@@
synchronized <T> T[] toArray(T[] contents) @@@@
synchronized Object[] toArray() @@@@
synchronized String toString() //******
synchronized void trimToSize() ####
add和addElement几乎一致,还有set和setElementAt、insertElementAt和add双参数、get和ElementAt、remove和removeElement [2]以及removeAllElement和clear。这几乎都是因为从List继承一些方法,然后本身又会自带一些,有些返回值不同,但实现的功能没有大差。上述列表中,带@是继承自List和Collection的方法,带#是和Arraylist一样方法(ensureCapacity其实也不一样)。剩下的好像只有Element那些重复的和为数不多的方法了。
因此主要实现上述带有标志 * 的及其相关的方法为示例:
package vector; import java.util.Enumeration; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Vector; public class vector { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Vector <String> vs=new Vector<String>(); String [] st=new String[20]; String [] st2=new String[20]; /*add*/ for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { vs.add(String.valueOf(i)); } /*capacity*/ System.out.println(vs.capacity()); vs.add(5, "5"); vs.addElement("am "); System.out.println(vs.capacity()); /*iterator*/ Iterator<String> it=vs.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { System.out.print(it.next()+" "); } System.out.println(); /*indexOf lastIndexOf*/ System.out.print(vs.indexOf("5")+" "); //第一个出现该元素的下标 System.out.print(vs.lastIndexOf("5")+" "); //最后一个出现该元素的下标 System.out.print(vs.lastIndexOf("10")+" "); //没有的元素返回-1 System.out.print(vs.indexOf("8",9)+" "); //返回的元素必须大于等于第二个参数 System.out.print(vs.lastIndexOf("5",5)+" "); //返回的参数小于等于第二个参数,否则返回-1 System.out.println(); /*setsize*/ vs.setSize(20); //若小于当前size,删除后面元素,若大于添加null /*enum*/ Enumeration<String> en=vs.elements(); while(en.hasMoreElements()) { System.out.print(en.nextElement()+' '); } System.out.println(); /*copyInto*/ vs.copyInto(st); for(String a:st) { System.out.print(a+" "); } System.out.println(); /*toString*/ System.out.println(vs.toString()); } }
20
0 1 2 3 4 5 5 6 7 8 9 am
5 6 -1 9 5
0 1 2 3 4 5 5 6 7 8 9 am null null null null null null null null
0 1 2 3 4 5 5 6 7 8 9 am null null null null null null null null
[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, am , null, null, null, null, null, null, null, null]
太多了LinkedList移到下一篇吧。