关于图的搜索问题可以看我的另一篇博客二分图的判定点击打开链接
L2-023. 图着色问题
时间限制
300 ms
内存限制
65536 kB
代码长度限制
8000 B
判题程序
Standard
作者
陈越
图着色问题是一个著名的NP完全问题。给定无向图 G = (V, E),问可否用K种颜色为V中的每一个顶点分配一种颜色,使得不会有两个相邻顶点具有同一种颜色?
但本题并不是要你解决这个着色问题,而是对给定的一种颜色分配,请你判断这是否是图着色问题的一个解。
输入格式:
输入在第一行给出3个整数V(0 < V <= 500)、E(>= 0)和K(0 < K <= V),分别是无向图的顶点数、边数、以及颜色数。顶点和颜色都从1到V编号。随后E行,每行给出一条边的两个端点的编号。在图的信息给出之后,给出了一个正整数N(<= 20),是待检查的颜色分配方案的个数。随后N行,每行顺次给出V个顶点的颜色(第i个数字表示第i个顶点的颜色),数字间以空格分隔。题目保证给定的无向图是合法的(即不存在自回路和重边)。
输出格式:
对每种颜色分配方案,如果是图着色问题的一个解则输出“Yes”,否则输出“No”,每句占一行。
输入样例:6 8 3 2 1 1 3 4 6 2 5 2 4 5 4 5 6 3 6 4 1 2 3 3 1 2 4 5 6 6 4 5 1 2 3 4 5 6 2 3 4 2 3 4输出样例:
Yes Yes No No
我自己的解答最后一个测试点会超时,最后是我参考的别人的代码,觉得很巧妙
先来看一下最后一个点超时的代码,作参考
import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
public class Main {
public static int V, E, C;
public static List<Integer>[] list;
public static int[] color = new int[501];
public static int[][] book; // 标记数组,避免往回走,成往返回路死在递归了
public static int[] checked; // 做剪枝用,如果某个顶点在之前相邻顶点的邻接数组用过,说明走过一遍了,就没必要走了
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner cin = new Scanner(new BufferedInputStream(System.in));
V = cin.nextInt();
E = cin.nextInt();
C = cin.nextInt();
list = (ArrayList<Integer>[]) new ArrayList[V + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= V; ++i) {
list[i] = new ArrayList<Integer>();
}
book = new int[V + 1][V + 1];
checked = new int[V + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < E; ++i) {
int a = cin.nextInt();
int b = cin.nextInt();
list[a].add(b);
list[b].add(a);
}
int n = cin.nextInt();
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
set.clear();
for (int j = 1; j <= V; ++j) {
color[j] = cin.nextInt();
set.add(color[j]);
}
if (set.size() != C) { // 用例的第三个点,3种颜色却给出6种,不合规范
System.out.println("No");
continue;
}
solve();
}
cin.close();
}
public static void solve() {
clear();
for (int i = 1; i <= V; ++i) {
if (checked[i] != 1 && !dfs(i)) { // 题目没说图是连通的,所以要每个顶点走一遍
System.out.println("No");
return;
}
}
System.out.println("Yes");
}
public static void clear() {
for (int i = 0; i < V + 1; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < V + 1; ++j) {
book[i][j] = 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < V + 1; ++i) {
checked[i] = 0;
}
}
public static boolean dfs(int v) {
int size = list[v].size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
int vv = list[v].get(i);
checked[vv] = 1; // 下一次返回solve()可以剪枝
if (book[v][vv] != 1) {
if (color[vv] == color[v])
return false;
book[v][vv] = 1;
book[vv][v] = 1;
if (!dfs(vv))
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}接着是正确的代码:
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int V, E, C;
int v[250000]; // 起点的顶点,每个点的终点可以是另外499个点
int w[250000]; // 终点的顶点
int color[501];
int visit[501]; // 辅助标记数组
void clear()
{
for (int i = 0; i < 501; ++i)
{
visit[i] = 0;
}
}
int main()
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &V, &E, &C);
for (int i = 1; i <= E; ++i)
{
scanf("%d %d", &v[i], &w[i]);
}
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
int count = 0;
bool flag = true;
clear();
for (int j = 1; j <= V; ++j)
{
scanf("%d", &color[j]);
if (visit[color[j]])
continue;
visit[color[j]] = 1; // 这个颜色已经有了
++count; // 记录颜色种数
}
if (count != C) {
printf("No
");
continue;
}
for (int k = 1; flag && k <= E; ++k) {
if (color[v[k]] == color[w[k]]) {
printf("No
");
flag = false;
}
}
if (flag) {
printf("Yes
");
}
}
return 0;
}
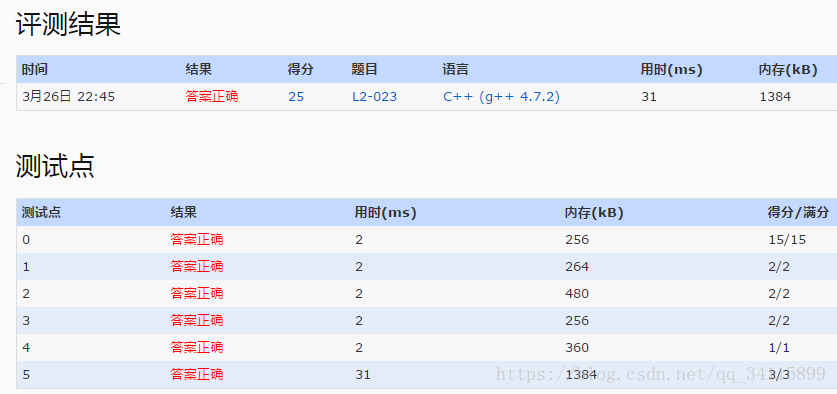
题目链接地址https://www.patest.cn/contests/gplt/L2-023
========================================Talk is cheap, show me the code=======================================