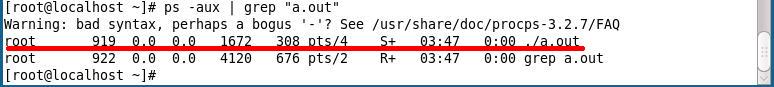
(1)用wait和waitpid函数清理僵尸进程,父进程可以阻塞等待子进程结束
(2)父进程在信号处理函数中wait()清理子进程
其实,子进程在终止时会给父进程发SIGCHLD信号,该信号的默认处理动作是忽略,父进程可以自定义SIGCHLD信号的处理函数,这样父进程只需专心处理自己的工作,不必关心子进程了,子进程终止时会通知父进程,父进程在信号处理函数中调用wait清理子进程即可。
例子1:
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <signal.h> void sig_child(int signo) { printf("handler child process! "); } int main (int argc, char *argv[]) { int i = 0; pid_t pid = fork(); if (pid == 0) { sleep(1); while (i++ < 6) { printf("child running... "); sleep(1); } } else if (pid > 0) { signal(SIGCHLD, sig_child); while (1) { printf("father running... "); sleep(1); } } else { printf("create failed "); exit(0); } printf("Main exit() "); return 0; }
程序输出: [root@localhost ~]# ./a.out father running... child running... father running... father running... child running... child running... father running... child running... father running... father running... child running... father running... child running... father running... Main exit() handler child process! father running... father running... father running...
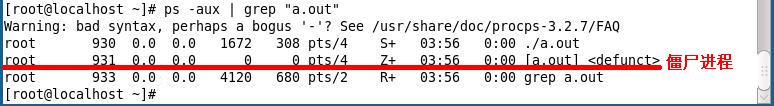
从输出来看这里验证了:
①子进程结束,会自动发送SIGCHLD信号给父进程。
②父进程可以在信号处理函数进行回收子进程资源,由于上面的程序并调用wait()或者waitpid()进行回收资源,故还是产生了僵尸进程。
例子2:
// 将上个例子加上wait()函数 void sig_child(int signo) { printf("handler child process! "); wait(); }
程序输出:
[root@localhost ~]# ./a.out father running... father running... child running... child running... father running... father running... child running... child running... father running... father running... child running... child running... father running... father running... Main exit() handler child process! father running... father running... father running...

在信号处理函数中调用wait()回收子进程的资源。
(3)让内核来回收子进程资源
如果父进程不关心子进程什么时候结束,那么可以用signal(SIGCLD, SIG_IGN)或signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_IGN)通知内核,自己对子进程的结束不感兴趣,那么子进程结束后,内核会回收,并不再给父进程发送信号。
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <signal.h> int main (int argc, char *argv[]) { int i = 0; pid_t pid = fork(); if (pid == 0) { sleep(1); while (i++ < 6) { printf("child running... "); sleep(1); } } else if (pid > 0) { //signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_IGN); // 通知内核来回收子进程资源 signal(SIGCLD, SIG_IGN); // 通知内核来回收子进程资源 while (1) { printf("father running... "); sleep(1); } } else { printf("create failed "); exit(0); } printf("Main exit() "); return 0; }
程序输出:
[root@localhost ~]# ./a.out father running... child running... father running... child running... father running... child running... father running... child running... father running... child running... father running... child running... father running... Main exit() father running... father running... father running... father running... father running... father running...