Valera has got a rectangle table consisting of n rows and m columns. Valera numbered the table rows starting from one, from top to bottom and the columns – starting from one, from left to right. We will represent cell that is on the intersection of row x and column y by a pair of integers (x, y).
Valera wants to place exactly k tubes on his rectangle table. A tube is such sequence of table cells (x1, y1), (x2, y2), ..., (xr, yr), that:
- r ≥ 2;
- for any integer i (1 ≤ i ≤ r - 1) the following equation |xi - xi + 1| + |yi - yi + 1| = 1 holds;
- each table cell, which belongs to the tube, must occur exactly once in the sequence.
Valera thinks that the tubes are arranged in a fancy manner if the following conditions are fulfilled:
- no pair of tubes has common cells;
- each cell of the table belongs to some tube.
Help Valera to arrange k tubes on his rectangle table in a fancy manner.
The first line contains three space-separated integers n, m, k (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 300; 2 ≤ 2k ≤ n·m) — the number of rows, the number of columns and the number of tubes, correspondingly.
Print k lines. In the i-th line print the description of the i-th tube: first print integer ri (the number of tube cells), then print 2ri integersxi1, yi1, xi2, yi2, ..., xiri, yiri (the sequence of table cells).
If there are multiple solutions, you can print any of them. It is guaranteed that at least one solution exists.
3 3 3
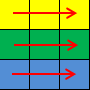
3 1 1 1 2 1 3 3 2 1 2 2 2 3 3 3 1 3 2 3 3
2 3 1
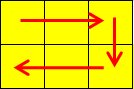
6 1 1 1 2 1 3 2 3 2 2 2 1
Picture for the first sample:
Picture for the second sample:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int mmap[310][310];
int main()
{
int n,m,k;
while(cin>>n>>m>>k)
{
int t=n*m-(k-1)*2;
int x=1,y=1;
printf("%d",t);
while(t--)
{
printf(" %d %d",x,y);
mmap[x][y]=1;
if(y+1<=m&&!mmap[x][y+1])
{
y++;
}
else if(y-1>=1&&!mmap[x][y-1])
y--;
else x++;
}
k--;
while(k--)
{
printf("
2");
t=2;
while(t--)
{
printf(" %d %d",x,y);
mmap[x][y]=1;
if(y+1<=m&&!mmap[x][y+1])
{
y++;
}
else if(y-1>=1&&!mmap[x][y-1])
y--;
else x++;
}
}
printf("
");
}
}