shell 脚本的函数
#!/usr/bin/env bash
function cpu_load() {
echo " cpu 负载监控"
}
function main() {
cpu_load
}
main
LAB1:监控nginx服务,挂了就重启
#!/bin/bash # # 获取脚本子进程的pid,如果脚本名称中带nginx,也会当成nginx进程 this_pid=$$ while true do ps -ef | grep nginx | grep -v grep | grep -v $this_pid &> /dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ];then echo "Nginx is running well" sleep 5 else systemctl start nginx echo "Nginx is down,Start it..." fi done
系统下后台运行
nohup sh nginx_daemon.sh &
#查看日志
tailf nohup.out
函数返回值
返回值有两种方式:
- return
- echo


LAB1:判断nginx进程是否存在
- 函数使用return返回值,通常只是用来供其他地方调用获取状态,因此通常仅返回0或1;0表示成功,1表示失败
nginx.sh
1 #!/bin/bash 2
3
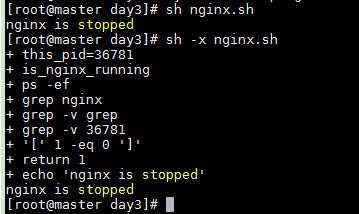
4 this_pid=$$ 5 6 function is_nginx_running 7 { 8 ps -ef | grep nginx | grep -v grep | grep -v $this_pid &> /dev/null 9 if [ $? -eq 0 ];then 10 return 0 11 else 12 return 1 13 fi 14 } 15 16 is_nginx_running && echo "nginx is running" || echo "nginx is stopped"
查看脚本进程的执行过程
bash -x nginx.sh
案例2 获取系统中的用户
- 使用echo返回值 使用echo可以返回任何字符串结果 通常用于返回数据,比如一个字符串值或者列表值
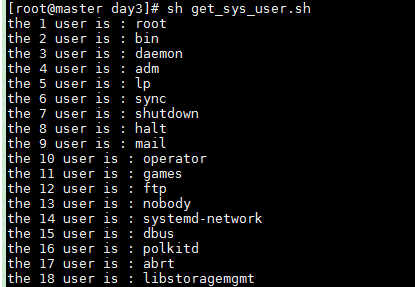
get_sys_user.sh
1 #!/bin/bash 2 3 # 获取系统所有的用户名 4 function get_users 5 { 6 users=`cat /etc/passwd | cut -d: -f1` 7 echo $users 8 } 9 10 # 定义一个变量将获取用户列表赋值给这个变量 11 user_list=`get_users` 12 13 index=1 14 for u in $user_list 15 do 16 echo "the $index user is : $u" 17 index=$(($index+1)) 18 done
执行脚本,输出如下
注:
return 常用来返回 0 and 1 用于其他函数或变量调用
echo 常用与输出