前一篇博客,我总结了Tomcat对于生命周期组件的管理。在了解了容器的启动之后,我们开始剖析它的内部运行机制。今天我们来分析一下Tomcat如何处理Request。Socket作为网络通信的基础也是Request和Response的底层实现,有过Socket使用经验的读者一定不会对下面的伪代码陌生:
// Java伪代码 ... while(true) { Socket soc = ServerSocket.accept(); // 监听并阻塞 new Thread(new Runnable() { // 开辟新的线程处理Socket inputStream(soc); // 读取Socket中的数据 outputStream(soc); // 写入数据 }); } ...
一、从Socket到Request
Tomcat容器对Socket的处理思路与以上伪代码基本一致,只是更加复杂。下图展示了从Tomcat启动到Socket到来后,主要类的调动过程(虚线箭头表示有新的线程启动):
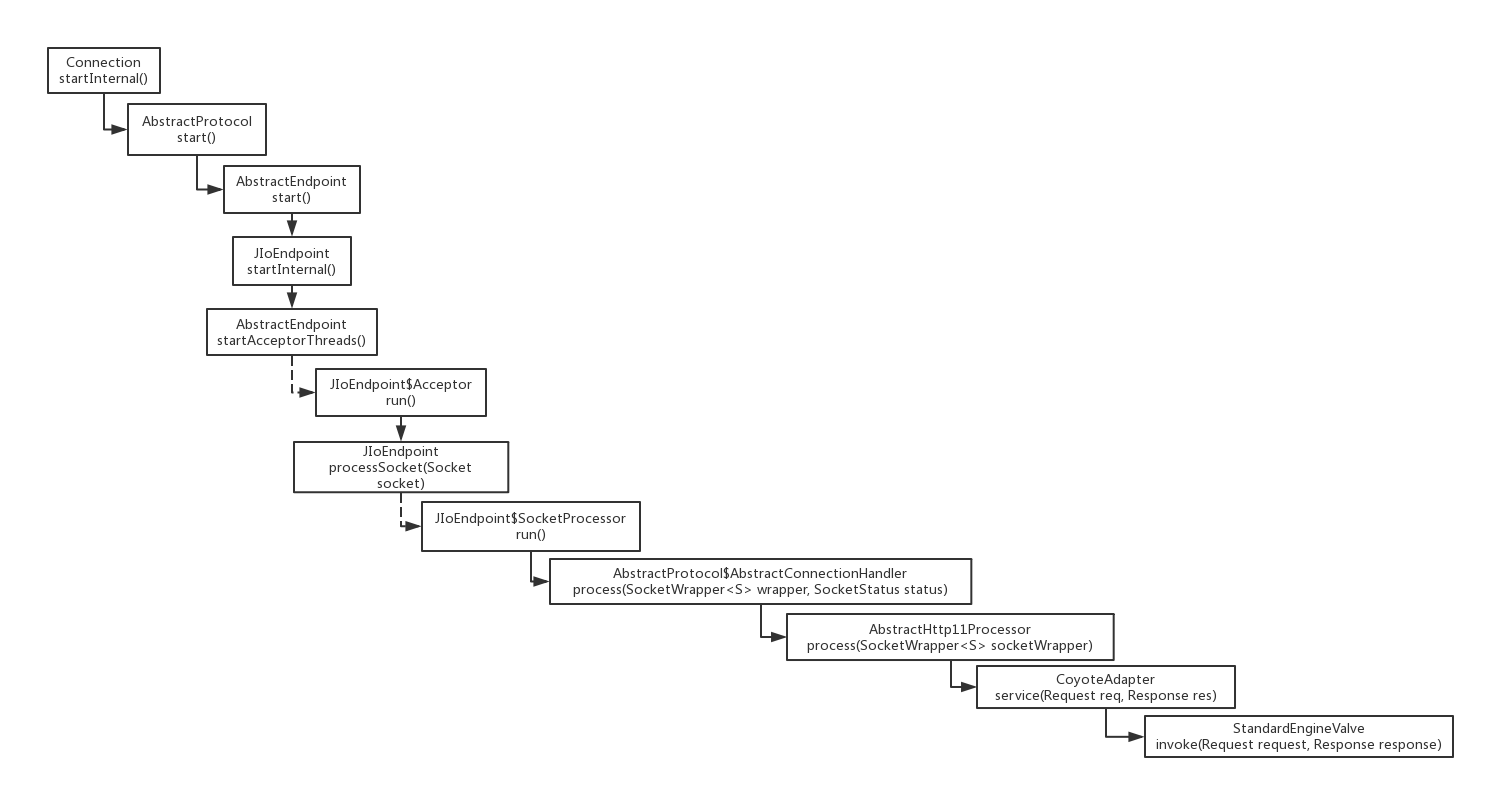
Acceptor是定义在JIoEndpoint中的内部类实现了Runnable接口。在run方法中定义了循环语句while (running){...}重点是ServerSocketFactory获取监听端口(默认8080)上的Socket请求
Socket socket = null; try { // Accept the next incoming connection from the server // socket socket = serverSocketFactory.acceptSocket(serverSocket); ...
然后,这个Socket对象会被封装成SocketWrapper对象并交给给JIoEndpoint的另一个内部类SocketProcessor处理。
protected boolean processSocket(Socket socket) { // Process the request from this socket try { SocketWrapper<Socket> wrapper = new SocketWrapper<Socket>(socket); wrapper.setKeepAliveLeft(getMaxKeepAliveRequests()); wrapper.setSecure(isSSLEnabled()); ...
一直到AbstractHttp11Processor.process方法,我们第一次见到了Request的身影。不过此时的Request实际上是org.apache.coyote.Request,它是Tomcat内部的定义类并且被final修饰。在CoyoteAdapter.service方法中,它又被处理成:org.apache.catalina.connector.Request,它继承了HttpServletRequest。直到这时,从Socket到Request才真正完成。
二、Pipeline、FilterChain以及设计模式
ContainerBase是Tomcat中的生命周期组件。它包含了4个标准的实现类:StandardContext、StandardEngine、StandardHost和StandardWrapper。每一个Container对象都含有各自的Pipeline和Valve。
/** * The Pipeline object with which this Container is associated. */ protected Pipeline pipeline = new StandardPipeline(this); /** * Create a new StandardContext component with the default basic Valve. */ public StandardContext() { super(); pipeline.setBasic(new StandardContextValve()); ... } ...
它们通过Container的构造函数被初始化,并负责处理Request。每一个Containner组件都实现了各自的invoke方法,具体的业务逻辑读者可以自己去分析。
经过4次invoke,Request会继续交给FilterChain(责任链模式的核心对象)处理。
ApplicationFilterChain filterChain = factory.createFilterChain(request, wrapper, servlet); try { if ((servlet != null) && (filterChain != null)) { if (context.getSwallowOutput()) { ... } else { if (request.isAsyncDispatching()) { ... } else if (comet) { ... } else { filterChain.doFilter(request.getRequest(), response.getResponse()); } } ...
经过多个Filter的处理,才会交到Servlet的手中。