1.事物的声明阶段
@EnableTransactionManagement,是我们开启注解事物的第一步,我们来看下这个类为我们干了什么
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Import(TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector.class) public @interface EnableTransactionManagement { boolean proxyTargetClass() default false; AdviceMode mode() default AdviceMode.PROXY; int order() default Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE; }
我们主要看 TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector 干了件什么事情。它主要往spring 容器中导入了 AutoProxyRegistrar , ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration两个对象。
public class TransactionManagementConfigurationSelector extends AdviceModeImportSelector<EnableTransactionManagement> { @Override protected String[] selectImports(AdviceMode adviceMode) { switch (adviceMode) { case PROXY: return new String[] {AutoProxyRegistrar.class.getName(), ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration.class.getName()}; case ASPECTJ: return new String[] {TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ASPECT_CONFIGURATION_CLASS_NAME}; default: return null; } } }
ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration的作用,我们可以看到此类是一个配置类,主要为spring容器中导入了3个bean。这三个bean分别的作用,我们下来详说
@Configuration public class ProxyTransactionManagementConfiguration extends AbstractTransactionManagementConfiguration { @Bean(name = TransactionManagementConfigUtils.TRANSACTION_ADVISOR_BEAN_NAME) @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE) public BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor transactionAdvisor() { BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisor = new BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor(); advisor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource()); advisor.setAdvice(transactionInterceptor()); advisor.setOrder(this.enableTx.<Integer>getNumber("order")); return advisor; } @Bean @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE) public TransactionAttributeSource transactionAttributeSource() { return new AnnotationTransactionAttributeSource(); } @Bean @Role(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE) public TransactionInterceptor transactionInterceptor() { TransactionInterceptor interceptor = new TransactionInterceptor(); interceptor.setTransactionAttributeSource(transactionAttributeSource()); if (this.txManager != null) { interceptor.setTransactionManager(this.txManager); } return interceptor; } }
AutoProxyRegistrar 这个类,实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口,主要是为容器中注入了 InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator 这个bean。
public class AutoProxyRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar { private final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(getClass()); @Override public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { boolean candidateFound = false; Set<String> annoTypes = importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationTypes(); for (String annoType : annoTypes) { AnnotationAttributes candidate = AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, annoType); if (candidate == null) { continue; } Object mode = candidate.get("mode"); Object proxyTargetClass = candidate.get("proxyTargetClass"); if (mode != null && proxyTargetClass != null && AdviceMode.class == mode.getClass() && Boolean.class == proxyTargetClass.getClass()) { candidateFound = true; if (mode == AdviceMode.PROXY) { AopConfigUtils.registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry); if ((Boolean) proxyTargetClass) { AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry); return; } } } } }
public static BeanDefinition registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
return registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry, null);
}
public static BeanDefinition registerAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(InfrastructureAdvisorAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
}
}
我们首先来看一下这个类的继承关系图。
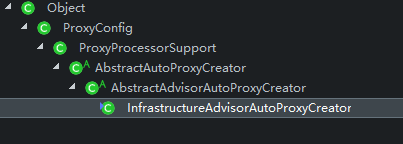
这个类首先是beanpostprocessor的实现类,他会对所有的bean做一次后置增强处理,我们在AbstractAutoProxyCreator中的 postProcessAfterInitialization 方法中可以看到,他会根据规则去对bean包装从而创造满足条件的代理。
/** * Create a proxy with the configured interceptors if the bean is * identified as one to proxy by the subclass. * @see #getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean */ @Override public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException { if (bean != null) { Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName); if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) { return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey); } } return bean; }
我们接下来进入 wrapIfNecessary 方法
// 如果需要的话,包装给定的bean,也就是说它是否有资格代理。 protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { return bean; } if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { return bean; } if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } // Create proxy if we have advice. Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null); if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; }
我们着重关注一下 getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean 方法
@Override protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource targetSource) { List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName); if (advisors.isEmpty()) { return DO_NOT_PROXY; } return advisors.toArray(); }
这个方法没什么说的,主要表达的意思是为bean找到合格的增强器。
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// 找到所有的候选者
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors(); // 从候选者中找到合格的
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName); extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) { eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors); } return eligibleAdvisors; }
在 findCandidateAdvisors 方法中,我们可以看到我们上文中注入的三个bean中的其中一个 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor,这个bean可以理解为我们的事物增强器。
public List<Advisor> findAdvisorBeans() { // Determine list of advisor bean names, if not cached already. String[] advisorNames = null; synchronized (this) { advisorNames = this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames; if (advisorNames == null) { // 找到上文注入的 BeanFactoryTransactionAttributeSourceAdvisor advisorNames = BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors( this.beanFactory, Advisor.class, true, false); this.cachedAdvisorBeanNames = advisorNames; } } if (advisorNames.length == 0) { return new LinkedList<Advisor>(); }return advisors; }
接下来我们看 findAdvisorsThatCanApply 方法,这个方法主要实现了,候选的增强器是否可以对当前bean使用。
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) { if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) { return candidateAdvisors; } List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty(); for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) { if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { // already processed continue; } if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) { eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate); } } return eligibleAdvisors; }
我们进入方法走到canApply处,继续往下跟。
public static boolean canApply(Advisor advisor, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) { return ((IntroductionAdvisor) advisor).getClassFilter().matches(targetClass); } else if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) { PointcutAdvisor pca = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor; return canApply(pca.getPointcut(), targetClass, hasIntroductions); } else { // It doesn't have a pointcut so we assume it applies. return true; } }
先判断类型后做一次转化,再次进入canApply方法
public static boolean canApply(Pointcut pc, Class<?> targetClass, boolean hasIntroductions) { Assert.notNull(pc, "Pointcut must not be null"); if (!pc.getClassFilter().matches(targetClass)) { return false; } MethodMatcher methodMatcher = pc.getMethodMatcher(); if (methodMatcher == MethodMatcher.TRUE) { // No need to iterate the methods if we're matching any method anyway... return true; } IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher introductionAwareMethodMatcher = null; if (methodMatcher instanceof IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) { introductionAwareMethodMatcher = (IntroductionAwareMethodMatcher) methodMatcher; } Set<Class<?>> classes = new LinkedHashSet<Class<?>>(ClassUtils.getAllInterfacesForClassAsSet(targetClass)); classes.add(targetClass); for (Class<?> clazz : classes) { Method[] methods = ReflectionUtils.getAllDeclaredMethods(clazz); for (Method method : methods) { if ((introductionAwareMethodMatcher != null && introductionAwareMethodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass, hasIntroductions)) || methodMatcher.matches(method, targetClass)) { return true; } } } return false; }
进入matches方法,下来的代码我会合并的连贯一些
@Override public boolean matches(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) { if (targetClass != null && TransactionalProxy.class.isAssignableFrom(targetClass)) { return false; } TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource(); return (tas == null || tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) != null); }
// 进入AbstractFallbackTransactionAttributeSource.getTransactionAttribute()
TransactionAttribute txAttr = computeTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass);
TransactionAttribute txAttr = findTransactionAttribute(specificMethod);
进入解析的流程
public class SpringTransactionAnnotationParser implements TransactionAnnotationParser, Serializable { @Override public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotatedElement ae) { AnnotationAttributes attributes = AnnotatedElementUtils.getMergedAnnotationAttributes(ae, Transactional.class); if (attributes != null) { return parseTransactionAnnotation(attributes); } else { return null; } } public TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(Transactional ann) { return parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationUtils.getAnnotationAttributes(ann, false, false)); } protected TransactionAttribute parseTransactionAnnotation(AnnotationAttributes attributes) { RuleBasedTransactionAttribute rbta = new RuleBasedTransactionAttribute(); Propagation propagation = attributes.getEnum("propagation"); rbta.setPropagationBehavior(propagation.value()); Isolation isolation = attributes.getEnum("isolation"); rbta.setIsolationLevel(isolation.value()); rbta.setTimeout(attributes.getNumber("timeout").intValue()); rbta.setReadOnly(attributes.getBoolean("readOnly")); rbta.setQualifier(attributes.getString("value")); ArrayList<RollbackRuleAttribute> rollBackRules = new ArrayList<RollbackRuleAttribute>(); Class<?>[] rbf = attributes.getClassArray("rollbackFor"); for (Class<?> rbRule : rbf) { RollbackRuleAttribute rule = new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule); rollBackRules.add(rule); } String[] rbfc = attributes.getStringArray("rollbackForClassName"); for (String rbRule : rbfc) { RollbackRuleAttribute rule = new RollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule); rollBackRules.add(rule); } Class<?>[] nrbf = attributes.getClassArray("noRollbackFor"); for (Class<?> rbRule : nrbf) { NoRollbackRuleAttribute rule = new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule); rollBackRules.add(rule); } String[] nrbfc = attributes.getStringArray("noRollbackForClassName"); for (String rbRule : nrbfc) { NoRollbackRuleAttribute rule = new NoRollbackRuleAttribute(rbRule); rollBackRules.add(rule); } rbta.getRollbackRules().addAll(rollBackRules); return rbta; } }
此方法会先拿到标记为 Transcantional 注解的方法,然后遍历属性。最后返回attr,如果解析到的attr不为空,则会将此增强器对待增强的bean做增强处理。
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) { if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) { return bean; } if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) { return bean; } if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; } // Create proxy if we have advice. Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null); if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) { this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE); Object proxy = createProxy( bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean)); this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass()); return proxy; } this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE); return bean; }
我们回到 wrapIfNecessary方法,如果返回的advisor不为空,我们会为他生成代理对象。
Object proxy = createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
这里就跟我们的使用AOP创建代理无缝融合,在找到当前bean确定要进行增强处理和增强的advisor后,使用动态代理的方式创建代理对象。