一、solr搜索流程介绍
1. 前面我们已经学习过Lucene搜索的流程,让我们再来回顾一下

流程说明:
首先获取用户输入的查询串,使用查询解析器QueryParser解析查询串生成查询对象Query,使用所有搜索器IndexSearcher执行查询对象Query得到TopDocs,遍历TopDocs得到文档Document
2. Solr搜索的工作流程:
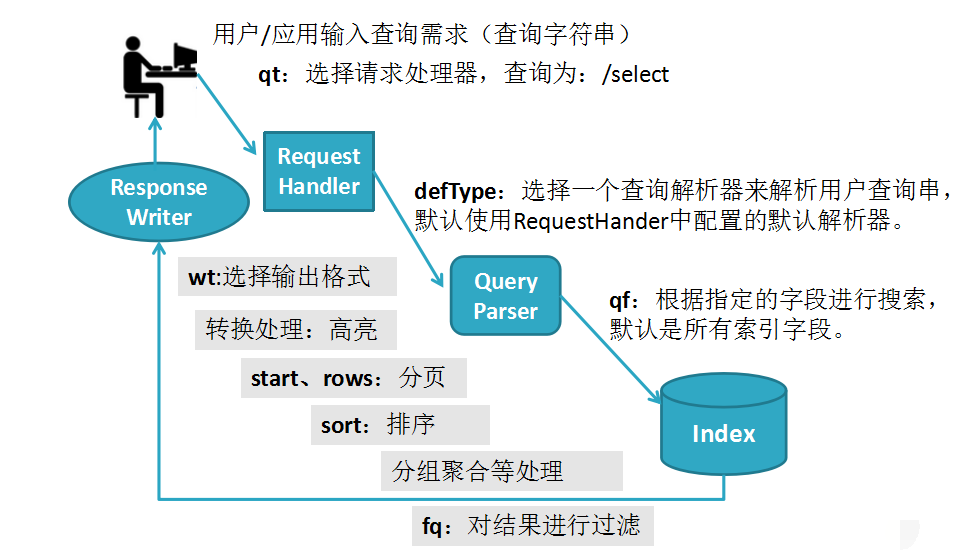
流程说明:
用户输入查询字符串,根据用户的请求类型qt(查询为/select)选择请求处理器RequestHandler,根据用户输入的参数defType来选择一个查询解析器解析用户的查询串(默认使用RequestHander中配置的默认查询解析器),查询解析器解析完以后根据用户输入的参数qf指定的字段进行搜索(默认是所有索引字段),查询到结果以后做一些特殊的处理(fq,sort,start,rows,wt)以后使用响应处理器ResponseWriter返回给用户
3. 查看内核的solrconfig.xml文件,了解搜索的请求处理器配置
<requestHandler name="/select" class="solr.SearchHandler"> <lst name="defaults"> <str name="echoParams">explicit</str> <int name="rows">10</int> <bool name="preferLocalShards">false</bool> </lst> </requestHandler>
<requestHandler name="/query" class="solr.SearchHandler"> <lst name="defaults"> <str name="echoParams">explicit</str> <str name="wt">json</str> <str name="indent">true</str> <str name="df">text</str> </lst> </requestHandler>
<requestHandler name="/browse" class="solr.SearchHandler"> <lst name="defaults"> <str name="echoParams">explicit</str> <!-- VelocityResponseWriter settings --> <str name="wt">velocity</str> <str name="v.template">browse</str> <str name="v.layout">layout</str> <str name="title">Solritas</str> <!-- Query settings --> <str name="defType">edismax</str> <str name="qf"> text^0.5 features^1.0 name^1.2 sku^1.5 id^10.0 manu^1.1 cat^1.4 title^10.0 description^5.0 keywords^5.0 author^2.0 resourcename^1.0 </str> <str name="mm">100%</str> <str name="q.alt">*:*</str> <str name="rows">10</str> <str name="fl">*,score</str> <str name="mlt.qf"> text^0.5 features^1.0 name^1.2 sku^1.5 id^10.0 manu^1.1 cat^1.4 title^10.0 description^5.0 keywords^5.0 author^2.0 resourcename^1.0 </str> <str name="mlt.fl">text,features,name,sku,id,manu,cat,title,description,keywords,author,resourcename</str> <int name="mlt.count">3</int> <!-- Faceting defaults --> <str name="facet">on</str> <str name="facet.missing">true</str> <str name="facet.field">cat</str> <str name="facet.field">manu_exact</str> <str name="facet.field">content_type</str> <str name="facet.field">author_s</str> <str name="facet.query">ipod</str> <str name="facet.query">GB</str> <str name="facet.mincount">1</str> <str name="facet.pivot">cat,inStock</str> <str name="facet.range.other">after</str> <str name="facet.range">price</str> <int name="f.price.facet.range.start">0</int> <int name="f.price.facet.range.end">600</int> <int name="f.price.facet.range.gap">50</int> <str name="facet.range">popularity</str> <int name="f.popularity.facet.range.start">0</int> <int name="f.popularity.facet.range.end">10</int> <int name="f.popularity.facet.range.gap">3</int> <str name="facet.range">manufacturedate_dt</str> <str name="f.manufacturedate_dt.facet.range.start">NOW/YEAR-10YEARS</str> <str name="f.manufacturedate_dt.facet.range.end">NOW</str> <str name="f.manufacturedate_dt.facet.range.gap">+1YEAR</str> <str name="f.manufacturedate_dt.facet.range.other">before</str> <str name="f.manufacturedate_dt.facet.range.other">after</str> <!-- Highlighting defaults --> <str name="hl">on</str> <str name="hl.fl">content features title name</str> <str name="hl.preserveMulti">true</str> <str name="hl.encoder">html</str> <str name="hl.simple.pre"><b></str> <str name="hl.simple.post"></b></str> <str name="f.title.hl.fragsize">0</str> <str name="f.title.hl.alternateField">title</str> <str name="f.name.hl.fragsize">0</str> <str name="f.name.hl.alternateField">name</str> <str name="f.content.hl.snippets">3</str> <str name="f.content.hl.fragsize">200</str> <str name="f.content.hl.alternateField">content</str> <str name="f.content.hl.maxAlternateFieldLength">750</str> <!-- Spell checking defaults --> <str name="spellcheck">on</str> <str name="spellcheck.extendedResults">false</str> <str name="spellcheck.count">5</str> <str name="spellcheck.alternativeTermCount">2</str> <str name="spellcheck.maxResultsForSuggest">5</str> <str name="spellcheck.collate">true</str> <str name="spellcheck.collateExtendedResults">true</str> <str name="spellcheck.maxCollationTries">5</str> <str name="spellcheck.maxCollations">3</str> </lst> <!-- append spellchecking to our list of components --> <arr name="last-components"> <str>spellcheck</str> </arr> </requestHandler>
通过查看内核techproducts 内核的solrconfig.xml文件发现/select, /query, /browse三个请求处理器都是使用的solr.SearchHandler这个类来完成搜索的各项工作的,请求处理器里面的各项参数类型介绍:
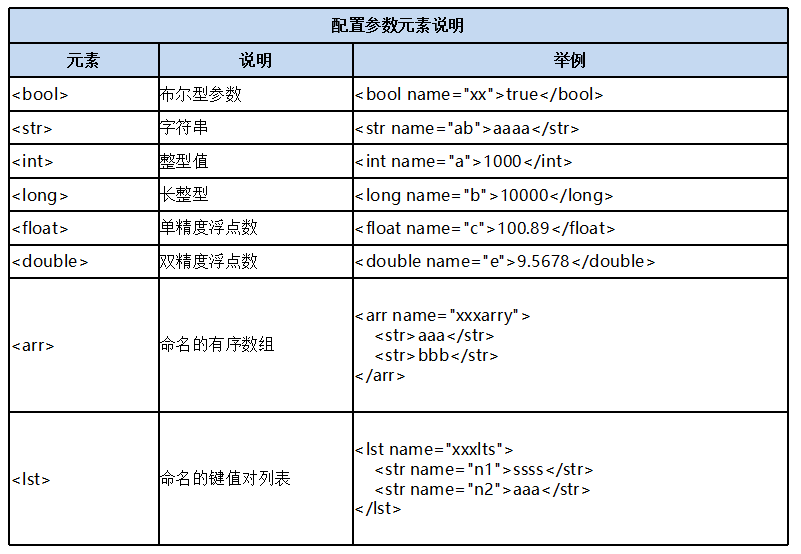
4. SearchHandler介绍
查询请求在SearcheHandler这个request handler中完成,各个步骤的工作由SearchHandler中组合的组件来完成了(可自定义,在该查询的requesthandler配置元素内配置)。示例,自定义组件组合:
<arr name="components"> <str>query</str> <str>facet</str> <str>mlt</str> <str>highlight</str> <str>debug</str> <str>someothercomponent</str> </arr>
说明:
"query" (usually QueryComponent)
"facet" (usually FacetComponent)
"mlt" (usually MoreLikeThisComponent)
"highlight" (usually HighlightComponent)
"stats" (usually StatsComponent)
"debug" (usually DebugComponent)
还可在主组件组合前、后加入组件:
<arr name="first-components"> <str>mycomponent</str> </arr> <arr name="last-components"> <str>myothercomponent</str> </arr>
SearchHandler的详细介绍见官方文档:https://wiki.apache.org/solr/SearchHandler
注意:如果你有这样的默认查询参数需要,可在<lst name="defaults"></lst>里面配置
二、查询语法及解析器详解
1. 通用查询参数详解见官方文档
http://lucene.apache.org/solr/guide/7_3/common-query-parameters.html
2. 查询解析器介绍
Standard Query Parser
DisMax Query Parser
Extended DisMax Query parser
默认使用的是 Standard Query Parser 。通过defType参数可指定。
3. Standard Query Parser
solr标准查询解析器。关键优点:它支持一个健壮且相当直观的语法,允许我们创建各种结构的查询。这个我们在学习lucene时已学过。最大的缺点:它不能容忍语法错误。
Standard Query Parser 请求参数:
除了通用参数外,标准查询解析器还支持的参数有:
q:用标准查询语法定义的查询表达式(查询串、主查询),必需。
q.op:指定查询表达式的默认操作, “AND” or “OR”,覆盖默认配置值。
df:指定默认查询字段
sow: Split on whitespace 按空格分割,如果设置为true,则会分别对分割出的文本进行分词处理。默认false。
3.1 Standard Query Parser 响应内容格式
在浏览器输入地址:http://localhost:8983/solr/techproducts/select?q=id:SP2514N&wt=xml

Standard Query Parser 响应内容格式-练习:
1、加上debug=all参数看看返回什么
http://localhost:8983/solr/techproducts/select?q=cat:book&wt=xml&debug=all

说明:加入debug参数后显示在浏览器地址后查询的过程
2、加上explainOther参数看看返回什么
http://localhost:8983/solr/techproducts/select?q=cat:book&wt=xml&debug=all&explainOther=id:055357342X
3.2 Solr Standard Query Parser 对传统 lucene语法的增强
在范围查询的边界两端都可以用*
field:[* TO 100] finds all field values less than or equal to 100
field:[100 TO *] finds all field values greater than or equal to 100
field:[* TO *] matches all documents with the field
允许纯非的查询(限顶级字节)
-inStock:false finds all field values where inStock is not false
-field:[* TO *] finds all documents without a value for field
支持嵌入solr查询(子查询),切入查询可以使用任意的solr查询解析器
inStock:true OR {!dismax qf='name manu' v='ipod'}
支持特殊的filter(…) 语法来说明某个字句的结果要作为过滤查询进行缓存
q=features:songs OR filter(inStock:true)
q=+manu:Apple +filter(inStock:true)
q=+manu:Apple & fq=inStock:true
如果过滤查询中的某个字句需要独立进行过滤缓存,也可用
q=features:songs & fq=+filter(inStock:true) +filter(price:[* TO 100])
q=manu:Apple & fq=-filter(inStock:true) -filter(price:[* TO 100])
查询中的时间表示语法
createdate:1976-03-06T23:59:59.999Z
createdate:"1976-03-06T23:59:59.999Z"
createdate:[1976-03-06T23:59:59.999Z TO *]
createdate:[1995-12-31T23:59:59.999Z TO 2007-03-06T00:00:00Z]
timestamp:[* TO NOW]
pubdate:[NOW-1YEAR/DAY TO NOW/DAY+1DAY]
createdate:[1976-03-06T23:59:59.999Z TO 1976-03-06T23:59:59.999Z+1YEAR]
createdate:[1976-03-06T23:59:59.999Z/YEAR TO 1976-03-06T23:59:59.999Z]
4. DisMax Query Parser
最大分离查询器,DisMax:Maximum Disjunction 最大分离
说明:一个查询,可以为不同字段设置评分权重,在合并它的查询字句的命中文档时,每个文档的分值取各个字句中的最大得分值。
DisMax Query Parser 是设计用于处理用户输入的简单短语查询的,它的特点:
只支持查询语法的一个很小的子集:简单的短语查询、+ - 修饰符、AND OR 布尔操作;
简单的语法,不抛出语法错误异常给用户。
可以在多个字段上进行短语查询。
可以灵活设置各个查询字段的相关性权重。
可以灵活增加满足某特定查询文档的相关性权重
4.1 DisMax Query Parser官方详细说明文档
http://lucene.apache.org/solr/guide/7_3/the-dismax-query-parser.html#the-dismax-query-parser
5. Extended DisMax Query Parser
扩展 DisMax Query Parse 使支标准查询语法(是 Standard Query Parser 和 DisMax Query Parser 的复合)。也增加了不少参数来改进disMax。
强烈建议:使用 edismax 来进行查询解析,因为它有如下特点
支持的语法很丰富;
很好的容错能力;
灵活的加权评分设置。
5.1 Extended DisMax Query Parser官方详细说明文档
http://lucene.apache.org/solr/guide/7_3/the-extended-dismax-query-parser.html#the-extended-dismax-query-parser
6. 函数查询
solr查询也可使用函数,可用来过滤文档、提高相关性值、根据函数计算结果进行排序、以及返回函数计算结果。在标准查询解析器、dismax、edismax中都可以使用函数。
函数可以是:
常量:数值或字符串字面值,如 10、”lucene solr” 字段: name title 另一个函数:functionName(…) 替代参数: q={!func}min($f1,$f2)&f1=sqrt(popularity)&f2=1
6.1 solr提供的函数官方详细说明文档
http://lucene.apache.org/solr/guide/7_3/function-queries.html#function-queries
主要有数据转换函数,数学函数,相关性函数,布尔函数,距离函数
6.2 函数的使用方式
用作函数查询,查询参数值是一个函数表达式,来计算相关性得分或过滤
q={!func}div(popularity,price)&fq={!frange l=1000}customer_ratings
在排序中使用
sort=div(popularity,price) desc, score desc
在结果中使用
&fl=sum(x, y),id,a,b,c,score&wt=xml
在加权参数 bf、boost中使用来计算权重
q=dismax&bf="ord(popularity)^0.5 recip(rord(price),1,1000,1000)^0.3"
在设置评分计算函数的特殊关键字 _val_ 中使用
q=_val_:mynumericfield _val_:"recip(rord(myfield),1,2,3)"
6.3 Function Query 函数查询说明
函数查询:指我们在查询参数q、fq中使用了函数来改变相关性得分或过滤的一类特殊查询。函数对所有匹配的文档分别进行计算得到一个值作为一个加分值,加入到文档的相关性得分中。
改变评分:
方式一:整个查询就是一个函数表达式,匹配所有文档,文档的得分就是函数值
q=*:* q={!func}div(popularity,price)&debug=all
说明:{!func} 说明q参数需要用func查询解析器来解析,func:Function Query Parser
方式二:值挂接,加入一个评分项,文档的得分=其他关键字得分 + 函数值
q=ipod AND _val_:"div(popularity,price)"&debug=all
方式三:查询解析器挂接(显示嵌套查询)
q=ipod AND _query_:"{!func}div(popularity,price)"&debug=all
方式四:查询解析器挂接(隐式嵌套查询)
q=ipod AND {!func v ="div(popularity,price)"}&debug=all
6.4 通过函数来过滤文档
如果需要对搜索结果进行过滤,只留下函数计算产生特定值的文档,可以选择函数区间解析器(Function Range query parser,简称frange)。在q/fq参数中应用frange 执行一个特定的函数查询,然后过滤掉函数值落在最低值和最高值范围之外的文档。
q={!frange l=0.01 u=0.1}div(popularity,price)&debug=all
q=ipod&fq={!frange l=0.05 u=0.1}div(popularity,price)&debug=all
第一个查询说明:相除的结果在0.01到0.1之间的
7. 查询中使用本地参数
7.1 什么是本地参数?
作为查询参数值的前缀,用来为查询参数添加元数据说明用的参数。看下面的查询:
q=solr rocks
如需要为这个查询说明是进行 AND 组合及默认查询字段是title:
q={!q.op=AND df=title}solr rocks
7.2 本地参数语法说明用的参数。看下面的查询:
作为查询参数值的前缀,用 {!key=value key=value} 包裹的多个key=value
7.3 本地参数用法示例
Query Type 的简写形式,type指定查询解析器
q={!dismax qf=myfield}solr rocks
q={!type=dismax qf=myfield}solr rocks
通过v 关键字指定参数值
q={!dismax qf=myfield}solr rocks
q={!type=dismax qf=myfield v='solr rocks'}
参数引用
q={!dismax qf=myfield}solr rocks q={!type=dismax qf=myfield v=$qq}&qq=solr rocks
8. 其他查询解析器见官方文档
https://lucene.apache.org/solr/guide/7_3/other-parsers.html
其他查询解析器,让我们可以在查询中灵活根据需要以本地参数的方式选用
三、总结
如何来写一个查询? 掌握语法 q
如何指定查询字段? Field: df(标准查询解析器) qf (dismax查询解析器)
如何添加过滤条件?Fq , {!frange}
如何指定返回字段? fl
如何指定排序? sort
如何为某个词项、短语加权?词项、短语^5
如何为字段加权? qf=title^10 pf pf2 pf3
如何用字段值来进行加权,如流行度、销量? _val_ _query_ 函数查询
如何查看某个查询的调试信息? debug