一、问题描述
1.遍历二叉树指定层次的所有结点
2.统计指定层的搜索结点个数
3.对二叉树进行层次遍历
4.找到二叉树中每一层的第一个结点或最后一个结点
二、问题分析
对树结构的问题我们首先会想到使用递归来解决,因为树结构完美适合递归,树的前序、中序、后序遍历使用递归很容易就可以解决,并且很容易理解。对于树结构的层次遍历则会稍微麻烦一点(当然,也很简单),基于层次遍历的问题也有很多,现在我们就着重来分析前面提到的3个问题。
什么是层次遍历 -- 即按照节点在每一层的顺序从上至下,由左到右进行遍历。
所有的结果都是基于如下的树结构:
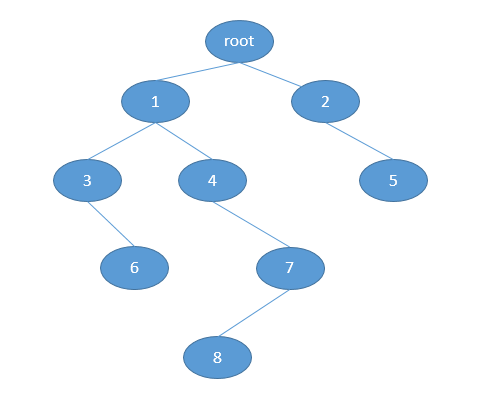
树的数据结构的具体代码如下:

class Node { private String data; private Node lChild; private Node rChild; public Node(String data) { this.data = data; } public Node(String data, Node lChild, Node rChild) { this.data = data; this.lChild = lChild; this.rChild = rChild; } public Node getLChild() { return lChild; } public Node getRChild() { return rChild; } public void setRChild(Node rChild) { this.rChild = rChild; } public void setLChild(Node lChild) { this.lChild = lChild; } @Override public String toString() { return data; } }
问题1分析 -- 如何遍历二叉树指定层次的所有结点?首先,我们考虑能不能使用递归进行遍历,因为树问题太适合用递归解决了,假定我们的函数名为traverseLevel,我们至少能够确定函数的参数应该会有树的根节点root,然后,仅仅只有这个参数还不足以解决问题,再添加一个int型的level参数,通过这两个参数能否解决问题呢?我们发现确实可以解决问题的。具体代码如下(其中树的数据结构需要自己建立,只给出了递归的核心代码):

public void traverseLevel(Node root, int level) { if(null == root) return; if (1 == level) { // 表示到达指定层 System.out.println(root.data); } else { traverseLevel(root.lChild, level - 1); traverseLevel(root.rChild, level - 1); } }
问题2分析 -- 基于问题1,我们已经可以遍历树的指定层,现在我们要统计指定层的所有结点个数,只需要简单的修改问题1中的代码即可,具体的代码如下:

public int levelNodeCount(Node root, int level) { if(null == root) return 0; if (1 == level) { // 表示到达指定层 System.out.println(root.data); return 1; } else { return levelNodeCount(root.lChild, level - 1) + levelNodeCount(root.rChild, level - 1); } }
问题3分析 -- 基于问题1的分析,我们可以进一步求解问题3,既然我们可以遍历指定层的所有结点,那么遍历按照层次结构遍历整棵树就只需要依次遍历第一层,第二层...最后一层(n)。
这时,我们只需要求出树有多少层,即n的大小(树的高度)即可解决整个问题。求解树的高度我们也可以采拥递归的方法来进行,具体代码如下:

public int treeHeight(Node root) { if (null == root) return 0; int lHeight = treeHeight(root.lChild); int rHeight = treeHeight(root.rChild); int max = -1; if (lHeight > rHeight) max = lHeight; else max = rHeight; return max + 1; }
既然求得了树的高度,那么问题2也就迎刃而解了,具体代码如下:

for (int i = 1; i <= treeHeight(root); i++) { traverseLevel(root, i); }
继续问题3分析 -- 如果我们不采拥递归的方法来解决,而使用队列的方式进行求解,可以得到如下的代码:

public static void levelOrder(Node root) { Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>(); if (null != root) { if (null != root.lChild) queue.offer(root.lChild); if (null != root.rChild) { queue.offer(root.rChild); } System.out.println(root.data); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Node node = queue.poll(); System.out.println(node.data); if (null != node.lChild) { queue.offer(node.lChild); } if (null != node.rChild) { queue.offer(node.rChild); } } } }
问题4分析 -- 有了解决问题1、问题2和问题3的基础,解决问题3也会容易很多,首先我们需要知道每一层的节点个数,然后使用一个计数器递增,当达到每一层的第一个结点时,进行遍历操作即可,具体代码如下:

public static void printFirstNodeOfEachLevel(Node root) { Queue<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>(); int preCount = 0; int levelNodeCount = 0; if (null != root) { System.out.println(root.data); if (null != root.lChild) { queue.offer(root.lChild); levelNodeCount++; } if (null != root.rChild) { queue.offer(root.rChild); levelNodeCount++; } int count = 0; preCount = levelNodeCount; levelNodeCount = 0; while (!queue.isEmpty()) { Node node = queue.poll(); count++; if (count == 1) { System.out.println(node.data); } if (null != node.lChild) { queue.offer(node.lChild); levelNodeCount++; } if (null != node.rChild) { queue.offer(node.rChild); levelNodeCount++; } if (count == preCount) { // 已经到了本层的最后一个结点 count = 0; preCount = levelNodeCount; levelNodeCount = 0; } } } }
同理,若理解了遍历每层的第一个结点的思路,那么遍历每层的最后一个结点就很简单了。只需要令count == preCount即可。
三、问题总结
对于树结构的相关问题我们首先应该想到的是使用递归来解决,然后思考能不能使用其他方法来解决。感谢各位园友观看,谢谢~
