RequestMappingHandlerMapping ,用于注解@Controller,@RequestMapping来定义controller.
1 @Controller 2 @RequestMapping(value = "books") 3 public class BookController { 4 5 @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}") 6 @ResponseBody 7 public String getBook(@PathVariable("id") String id) { 8 // ... 9 return id; 10 } 11 }

初始化时,3个类的大致分工如下:
AbstractHandlerMethodMapping定义整个算法流程;
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping提供匹配条件RequestMappingInfo的解析处理;
RequestMappingHandlerMapping根据@RequestMapping注解生成 RequestMappingInfo,同时提供isHandler实现
整个初始化工作由AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的initHandlerMethods主导.
1. 使用BeanFactoryUtils扫描应用下的Object或者直接从容器中获取Object
2. 迭代类,分别判断isHandler判断目标类是否Handler
2.1 RequestMappingHandlerMapping.isHandler根据@Controller或@RequestMapping注解判断(有任意一个)
3. 对handler解析出所有需要分发的方法detectHandlerMethods
3.1 获取原始的Class<?>
3.2 使用HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods过滤具体handler method,预留getMappingForMethod模板方法给子类
RequestMappingHandlerMapping.getMappingForMethod根据类,方法上的RequestMapping注解生成匹配条件RequestMappingInfo
3.3 对过滤到的每个method进行注册registerHandlerMethod
a, 使用createHandlerMethod封装处理器为HandlerMethod
b, 判断之前是否已经匹配条件对应的处理器是否冲突(相同的匹配条件只能有一个对应的处理器)
c, 设置匹配条件到handler method的映射关系
d, 从匹配条件中解析出url,并注册到urlMap(url到匹配条件的映射),这边由RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.getMappingPathPatterns实现
4. 对HandlerMethod进行初始化handlerMethodsInitialized,其实现在什么都没做
在讲初始化之前,我们先来聊聊使用到的一些概念
1. 映射关系,url到匹配条件RequestMappingInfo,匹配条件到HandlerMethod
2. 特殊的MultiValueMap,特别在value是个List
3. 使用到注解@Controller,@RequestMapping
4. 封装处理器信息的HandlerMethod
5. 封装各类匹配条件的RequestMappingInfo(诸如pattern,http method,request parameter等)
6. RequestCondition记录匹配条件
1. 进行request分发前,需要在初始化时准备好映射关系,这边AbstractHandlerMethodMapping中有两个属性保存了映射关系
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 // 匹配条件到HandlerMethod的映射 2 private final Map<T, HandlerMethod> handlerMethods = new LinkedHashMap<T, HandlerMethod>(); 3 // url到匹配条件的映射 4 private final MultiValueMap<String, T> urlMap = new LinkedMultiValueMap<String, T>();
2. 这边的MultiValueMap其实挺简单,就是map的值是个list
1 public interface MultiValueMap<K, V> extends Map<K, List<V>> { 2 // ... 3 }
3. 我们再来看看这边使用到的两个注解:
// @Controller
1 // org.springframework.stereotype.Controller 2 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) 3 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 4 @Documented 5 @Component 6 public @interface Controller { 7 8 /** 9 * The value may indicate a suggestion for a logical component name, 10 * to be turned into a Spring bean in case of an autodetected component. 11 * @return the suggested component name, if any 12 */ 13 String value() default ""; 14 15 }
// @RequestMapping
1 // org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping 2 @Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE}) 3 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 4 @Documented 5 @Mapping 6 public @interface RequestMapping { 7 8 /** 9 * url路径,如/myPath/*.do 10 */ 11 String[] value() default {}; 12 13 /** 14 * HTTP request methods 如:GET, POST, HEAD, OPTIONS, PUT, PATCH, DELETE, TRACE. 15 */ 16 RequestMethod[] method() default {}; 17 18 /** 19 * requeset parameter 有3种匹配方式,是否包含某个参数,参数值相等,参数值不等于某个值,如myParam!=myValue 20 */ 21 String[] params() default {}; 22 23 /** 24 * request的header 25 */ 26 String[] headers() default {}; 27 28 /** 29 * request的content type 30 */ 31 String[] consumes() default {}; 32 33 /** 34 * 返回内容的content type 35 */ 36 String[] produces() default {}; 37 38 } 39 }
4. HandlerMethod封装了处理器相关的全部信息,如类Object,方法Method,BeanFactory,参数MethodParameter[],原始方法Method
// HandlerMethod
1 // org.springframework.web.method.HandlerMethod 2 private final Object bean;// 因为final不可修改,所以下面每次需要修改信息时,都需要new一个 3 4 private final Method method; 5 6 private final BeanFactory beanFactory; 7 8 private final MethodParameter[] parameters; 9 10 private final Method bridgedMethod;
5. 这边匹配条件的范型只有一个实现,RequestMappingInfo.匹配条件里记录的是RequestCondition子类,用于诸如pattern,http method,request parameter等
// RequestMappingInfo
1 // javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest.RequestMappingInfo 2 public final class RequestMappingInfo implements RequestCondition<RequestMappingInfo> { 3 4 private final PatternsRequestCondition patternsCondition; 5 6 private final RequestMethodsRequestCondition methodsCondition; 7 8 private final ParamsRequestCondition paramsCondition; 9 10 private final HeadersRequestCondition headersCondition; 11 12 private final ConsumesRequestCondition consumesCondition; 13 14 private final ProducesRequestCondition producesCondition; 15 16 private final RequestConditionHolder customConditionHolder; 17 // ... 18 19 }
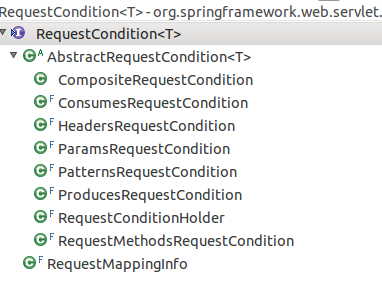
6. 最后再简单看看RequestCondition ,这边定义了3个方法
1 package org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.condition; 2 public interface RequestCondition<T> { 3 /** 4 * 拼接条件 5 */ 6 T combine(T other); 7 8 /** 9 * 查找匹配的条件,并返回 10 */ 11 T getMatchingCondition(HttpServletRequest request); 12 13 /** 14 * 用于排序 15 */ 16 int compareTo(T other, HttpServletRequest request); 17 }
看看继承体系吧,老套路,定义接口,然后模板方法实现主要逻辑,具体算法留给子类实现,还有正事要做,还是后期再细化吧.
正文
整个初始化工作由AbstractHandlerMethodMapping的initHandlerMethods主导.copy一段,省得回去比对看
1. 使用BeanFactoryUtils扫描应用下的Object或者直接从容器中获取Object
2. 迭代类,分别判断isHandler判断目标类是否Handler
2.1 RequestMappingHandlerMapping.isHandler根据@Controller或@RequestMapping注解判断(有任意一个)
3. 对handler解析出所有需要分发的方法detectHandlerMethods
3.1 获取原始的Class<?>
3.2 使用HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods过滤具体handler method,预留getMappingForMethod模板方法给子类
RequestMappingHandlerMapping.getMappingForMethod根据类,方法上的RequestMapping注解生成匹配条件RequestMappingInfo
3.3 对过滤到的每个method进行注册registerHandlerMethod
a, 使用createHandlerMethod封装处理器为HandlerMethod
b, 判断之前是否已经匹配条件对应的处理器是否冲突(相同的匹配条件只能有一个对应的处理器)
c, 设置匹配条件到handler method的映射关系
d, 从匹配条件中解析出url,并注册到urlMap(url到匹配条件的映射),这边由RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping.getMappingPathPatterns实现
4. 对HandlerMethod进行初始化handlerMethodsInitialized,其实现在什么都没做
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 /** 这个方法哪来的,具体看备注的InitializingBean 2 * Detects handler methods at initialization. 3 */ 4 public void afterPropertiesSet() { 5 initHandlerMethods(); 6 } 7 8 /**扫描ApplicationContext中的bean,然后筛选handler method 并注册 9 * Scan beans in the ApplicationContext, detect and register handler methods. 10 * @see #isHandler(Class) 11 * @see #getMappingForMethod(Method, Class) 12 * @see #handlerMethodsInitialized(Map) 13 */ 14 protected void initHandlerMethods() { 15 if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { 16 logger.debug("Looking for request mappings in application context: " + getApplicationContext()); 17 } 18 19 String[] beanNames = (this.detectHandlerMethodsInAncestorContexts ? 20 BeanFactoryUtils.beanNamesForTypeIncludingAncestors(getApplicationContext(), Object.class) : 21 getApplicationContext().getBeanNamesForType(Object.class)); 22 23 for (String beanName : beanNames) { 24 if (isHandler(getApplicationContext().getType(beanName))){ 25 detectHandlerMethods(beanName); 26 } 27 } 28 handlerMethodsInitialized(getHandlerMethods()); 29 }
预留给子类实现的判断handler,实际是由RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 /** 2 * Whether the given type is a handler with handler methods. 3 * @param beanType the type of the bean being checked 4 * @return "true" if this a handler type, "false" otherwise. 5 */ 6 protected abstract boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType);
// RequestMappingHandlerMapping
这边判断的逻辑很简单,类上使用Controller或RequestMapping其中至少一个注解就可以.
1 /** 2 * {@inheritDoc} 3 * Expects a handler to have a type-level @{@link Controller} annotation. 4 */ 5 @Override 6 protected boolean isHandler(Class<?> beanType) { 7 return ((AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(beanType, Controller.class) != null) || 8 (AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(beanType, RequestMapping.class) != null)); 9 }
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 /** 2 * Look for handler methods in a handler. 3 * @param handler the bean name of a handler or a handler instance 4 */ 5 protected void detectHandlerMethods(final Object handler) { 6 Class<?> handlerType = (handler instanceof String) ? 7 getApplicationContext().getType((String) handler) : handler.getClass(); 8 9 final Class<?> userType = ClassUtils.getUserClass(handlerType); 10 11 Set<Method> methods = HandlerMethodSelector.selectMethods(userType, new MethodFilter() { 12 public boolean matches(Method method) { 13 return getMappingForMethod(method, userType) != null; 14 } 15 }); 16 17 for (Method method : methods) { 18 T mapping = getMappingForMethod(method, userType); 19 registerHandlerMethod(handler, method, mapping); 20 } 21 }
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
这边具体的实现是由RequestMappingHandlerMapping实现,根据注解生产匹配关系,这边实现类是RequestMappingInfo,就是代码有点多,慢慢看
1 /** 2 * Provide the mapping for a handler method. A method for which no 3 * mapping can be provided is not a handler method. 4 * @param method the method to provide a mapping for 5 * @param handlerType the handler type, possibly a sub-type of the method's 6 * declaring class 7 * @return the mapping, or {@code null} if the method is not mapped 8 */ 9 protected abstract T getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType);
// RequestMappingHandlerMapping
1 /** 2 * Uses method and type-level @{@link RequestMapping} annotations to create 3 * the RequestMappingInfo. 4 * 5 * @return the created RequestMappingInfo, or {@code null} if the method 6 * does not have a {@code @RequestMapping} annotation. 7 * 8 * @see #getCustomMethodCondition(Method) 9 * @see #getCustomTypeCondition(Class) 10 */ 11 @Override 12 protected RequestMappingInfo getMappingForMethod(Method method, Class<?> handlerType) { 13 RequestMappingInfo info = null; 14 // 读取方法上的RequestMapping注解信息 15 RequestMapping methodAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(method, RequestMapping.class); 16 if (methodAnnotation != null) { 17 // 读取自定义的条件,这边没有使用 18 RequestCondition<?> methodCondition = getCustomMethodCondition(method); 19 // 根据方法上的RequsetMapping注解和自定义条件,生成匹配条件.这边的匹配条件包括http method,request parameter,request header等 20 info = createRequestMappingInfo(methodAnnotation, methodCondition); 21 // 读取类上的RequestMapping注解信息 22 RequestMapping typeAnnotation = AnnotationUtils.findAnnotation(handlerType, RequestMapping.class); 23 if (typeAnnotation != null) { 24 RequestCondition<?> typeCondition = getCustomTypeCondition(handlerType); 25 // 生成类上的匹配条件,并合并方法上的 26 info = createRequestMappingInfo(typeAnnotation, typeCondition).combine(info); 27 } 28 } 29 return info; 30 }
// RequestMappingHandlerMapping
1 /** 2 * Created a RequestMappingInfo from a RequestMapping annotation. 3 */ 4 private RequestMappingInfo createRequestMappingInfo(RequestMapping annotation, RequestCondition<?> customCondition) { 5 String[] patterns = resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(annotation.value()); 6 return new RequestMappingInfo( 7 new PatternsRequestCondition(patterns, getUrlPathHelper(), getPathMatcher(), 8 this.useSuffixPatternMatch, this.useTrailingSlashMatch, this.fileExtensions), 9 new RequestMethodsRequestCondition(annotation.method()), 10 new ParamsRequestCondition(annotation.params()), 11 new HeadersRequestCondition(annotation.headers()), 12 new ConsumesRequestCondition(annotation.consumes(), annotation.headers()), 13 new ProducesRequestCondition(annotation.produces(), annotation.headers(), getContentNegotiationManager()), 14 customCondition); 15 } 16 17 /** 18 * Resolve placeholder values in the given array of patterns. 19 * @return a new array with updated patterns 20 */ 21 protected String[] resolveEmbeddedValuesInPatterns(String[] patterns) { 22 if (this.embeddedValueResolver == null) { 23 return patterns; 24 } 25 else { 26 String[] resolvedPatterns = new String[patterns.length]; 27 for (int i=0; i < patterns.length; i++) { 28 resolvedPatterns[i] = this.embeddedValueResolver.resolveStringValue(patterns[i]); 29 } 30 return resolvedPatterns; 31 } 32 }
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 /** 2 * Register a handler method and its unique mapping. 3 * @param handler the bean name of the handler or the handler instance 4 * @param method the method to register 5 * @param mapping the mapping conditions associated with the handler method 6 * @throws IllegalStateException if another method was already registered 7 * under the same mapping 8 */ 9 protected void registerHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method, T mapping) { 10 HandlerMethod newHandlerMethod = createHandlerMethod(handler, method); 11 HandlerMethod oldHandlerMethod = handlerMethods.get(mapping); 12 if (oldHandlerMethod != null && !oldHandlerMethod.equals(newHandlerMethod)) { 13 throw new IllegalStateException("Ambiguous mapping found. Cannot map '" + newHandlerMethod.getBean() 14 + "' bean method " + newHandlerMethod + " to " + mapping + ": There is already '" 15 + oldHandlerMethod.getBean() + "' bean method " + oldHandlerMethod + " mapped."); 16 } 17 18 this.handlerMethods.put(mapping, newHandlerMethod);// 匹配条件requestMappingInfo 到处理器HandlerMethod 19 if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { 20 logger.info("Mapped "" + mapping + "" onto " + newHandlerMethod); 21 } 22 23 Set<String> patterns = getMappingPathPatterns(mapping); 24 for (String pattern : patterns) { 25 if (!getPathMatcher().isPattern(pattern)) { 26 this.urlMap.add(pattern, mapping);// url到匹配条件RequestMappingInfo 27 } 28 } 29 }
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 /** 2 * Create the HandlerMethod instance. 3 * @param handler either a bean name or an actual handler instance 4 * @param method the target method 5 * @return the created HandlerMethod 6 */ 7 protected HandlerMethod createHandlerMethod(Object handler, Method method) { 8 HandlerMethod handlerMethod; 9 if (handler instanceof String) { 10 String beanName = (String) handler; 11 handlerMethod = new HandlerMethod(beanName, getApplicationContext(), method); 12 } 13 else { 14 handlerMethod = new HandlerMethod(handler, method); 15 } 16 return handlerMethod; 17 }
// AbstractHandlerMethodMapping
1 /** 2 * Extract and return the URL paths contained in a mapping. 3 */ 4 protected abstract Set<String> getMappingPathPatterns(T mapping);
RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping会实现这个模板方法
// RequestMappingInfoHandlerMapping
1 /** 2 * Get the URL path patterns associated with this {@link RequestMappingInfo}. 3 */ 4 @Override 5 protected Set<String> getMappingPathPatterns(RequestMappingInfo info) { 6 return info.getPatternsCondition().getPatterns(); 7 }
备注:
1. 这边的afterPropertiesSet是因为实现了InitializingBean接口
// org.springframework.beans.factory.InitializingBean
1 /** 2 * Interface to be implemented by beans that need to react once all their 3 * properties have been set by a BeanFactory: for example, to perform custom 4 * initialization, or merely to check that all mandatory properties have been set. 5 * 6 * <p>An alternative to implementing InitializingBean is specifying a custom 7 * init-method, for example in an XML bean definition. 8 * For a list of all bean lifecycle methods, see the BeanFactory javadocs. 9 * 10 * @author Rod Johnson 11 * @see BeanNameAware 12 * @see BeanFactoryAware 13 * @see BeanFactory 14 * @see org.springframework.beans.factory.support.RootBeanDefinition#getInitMethodName 15 * @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware 16 */ 17 public interface InitializingBean { 18 19 /** 20 * Invoked by a BeanFactory after it has set all bean properties supplied 21 * (and satisfied BeanFactoryAware and ApplicationContextAware). 22 * <p>This method allows the bean instance to perform initialization only 23 * possible when all bean properties have been set and to throw an 24 * exception in the event of misconfiguration. 25 * @throws Exception in the event of misconfiguration (such 26 * as failure to set an essential property) or if initialization fails. 27 */ 28 void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception; 29 30 }