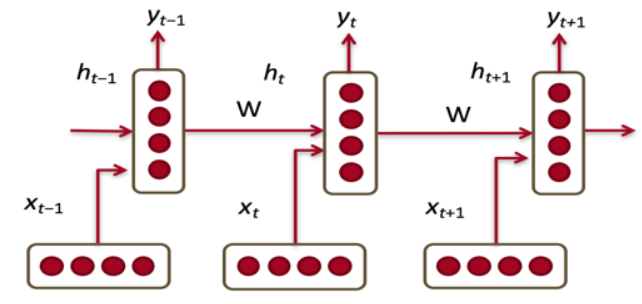
0、循环神经网络 (Recurrent Neural Network)
每一步的参数W是固定的
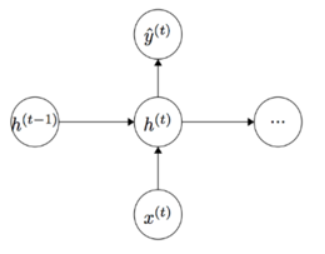
当前隐状态包含了所有前面出现的单词信息
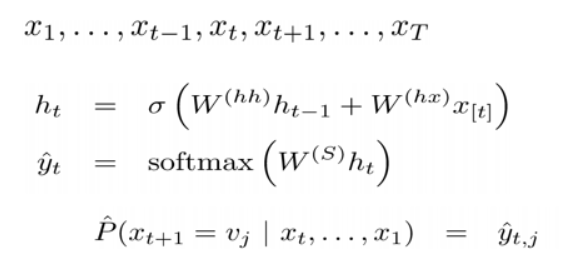
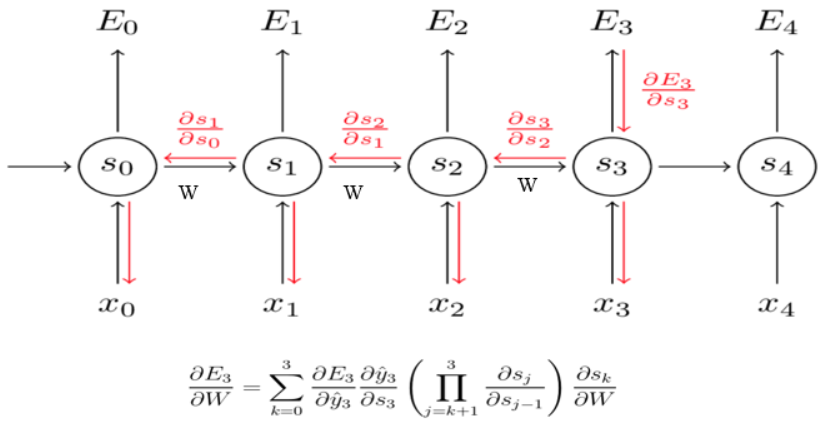
对于RNN,如何训练Train:
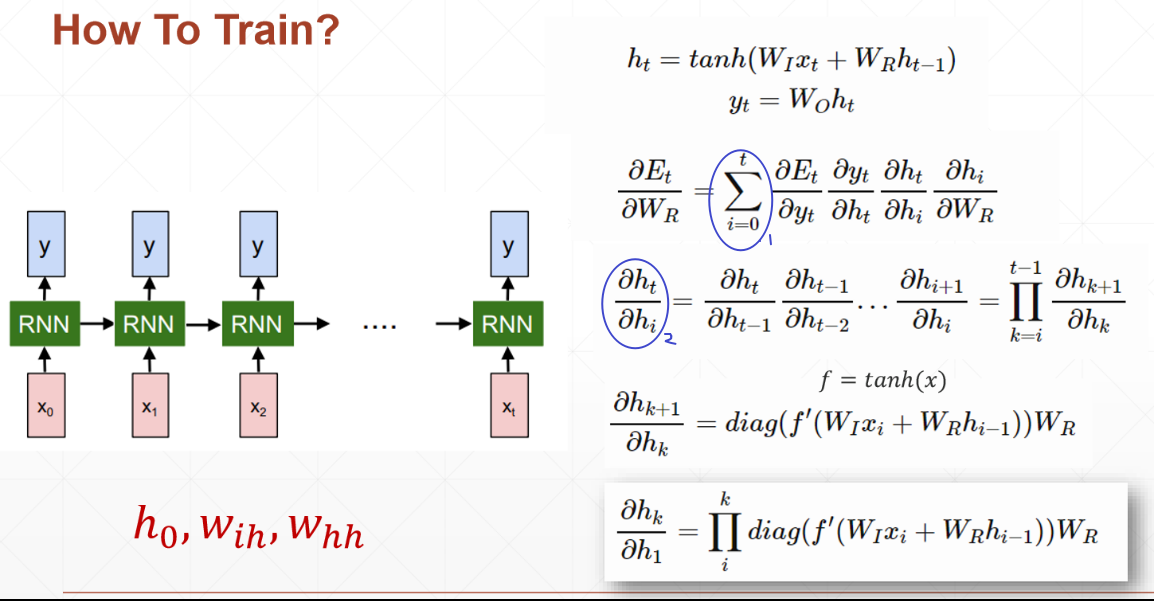
①:每一时刻的输出误差Et都有之前所有时刻的隐状态ht有关,因此是求和符号
②:对于隐状态之间的求导,链式法则的使用会出现,WR的连乘,这亦是根据反向传播(链式法则),梯度会不断相乘,很容易梯度消失或者爆炸
训练RNN很难
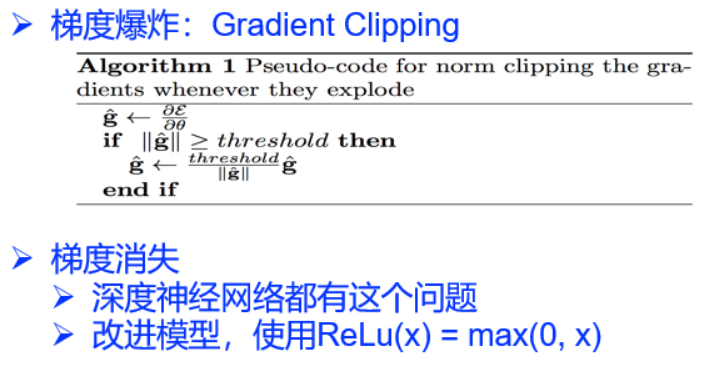

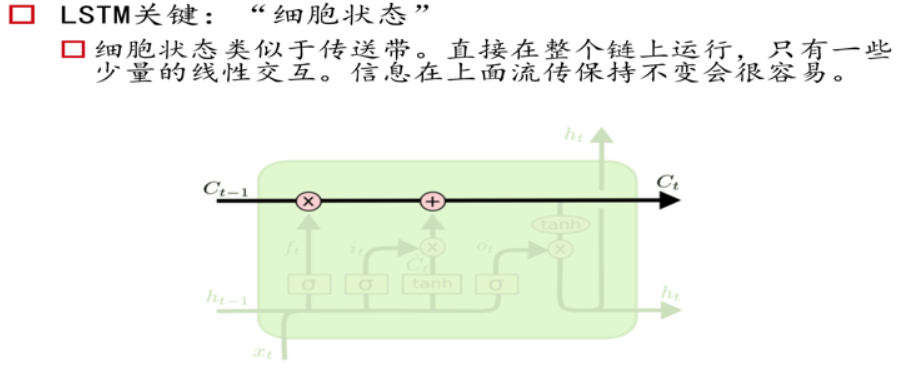
RNN记忆细胞
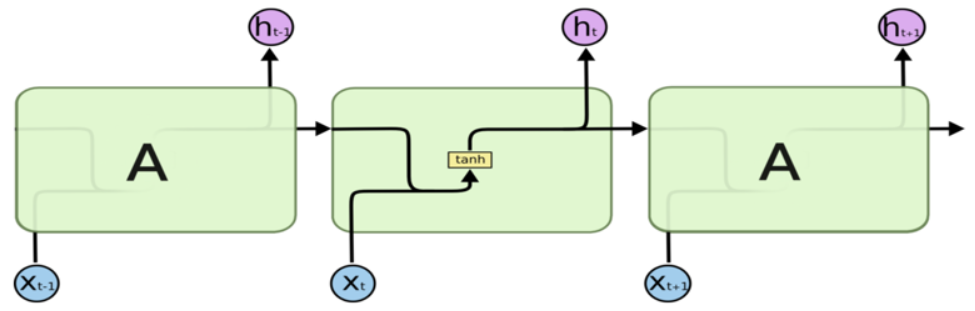
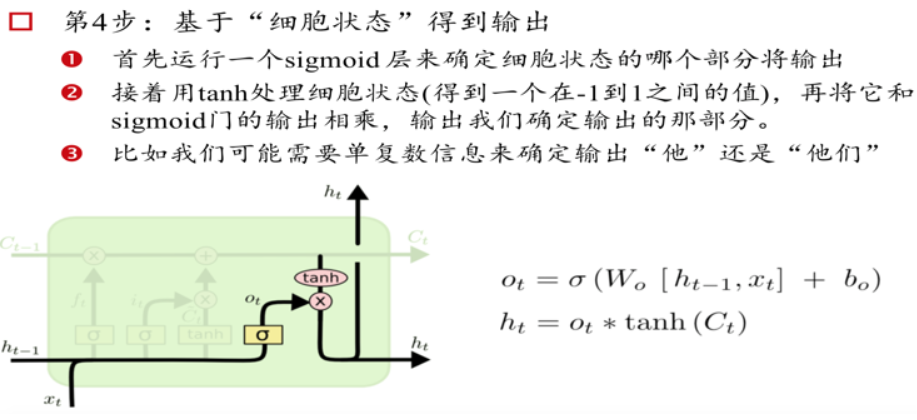
LSTM记忆细胞(Long Short-term Memory)
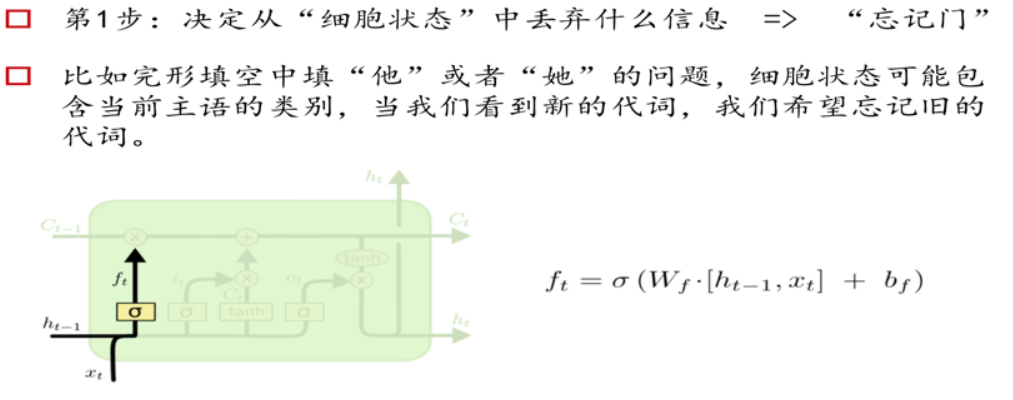
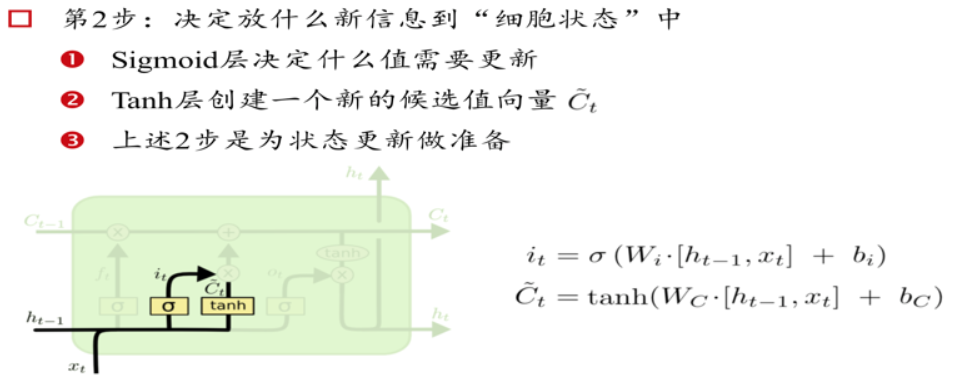
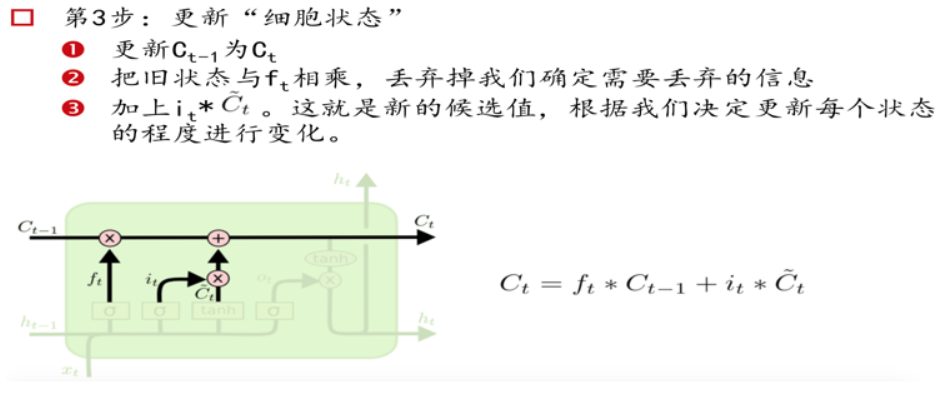
三个门Gate:输入门i;输出门o;遗忘门f。
三个输入:输入特征xt,上一时刻的隐状态ht-1, 上一时刻的Memory cell ct-1;
两个输出:但前的节点隐状态ht,和Memory cell ct;
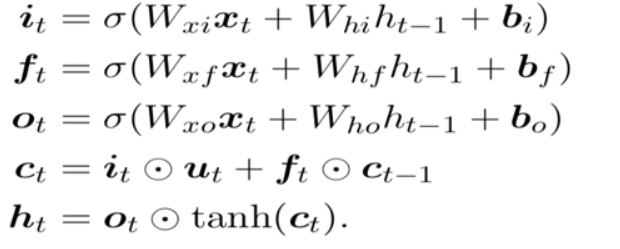
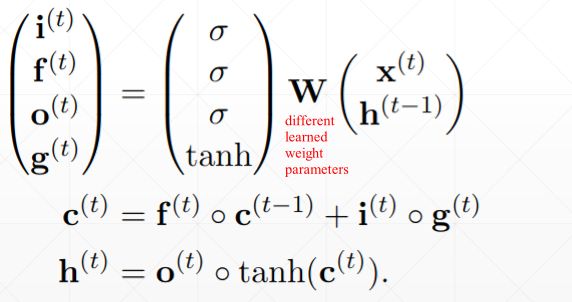
另一种简洁的表示:
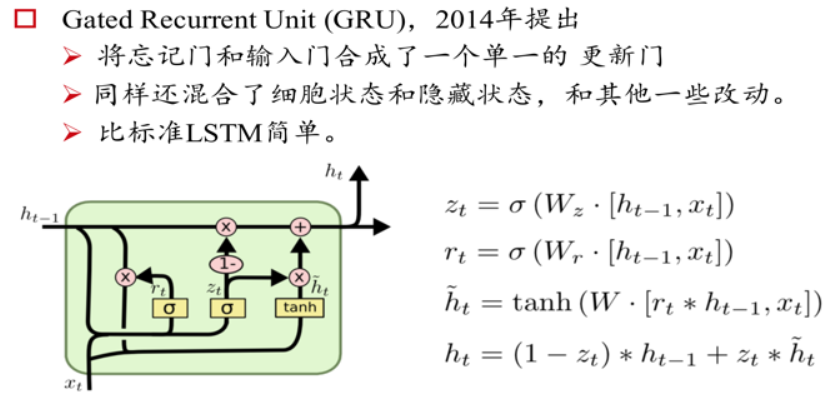
Gated Recurrent Unit
Pytorch中的: nn.RNN(input dim, hidden dim)
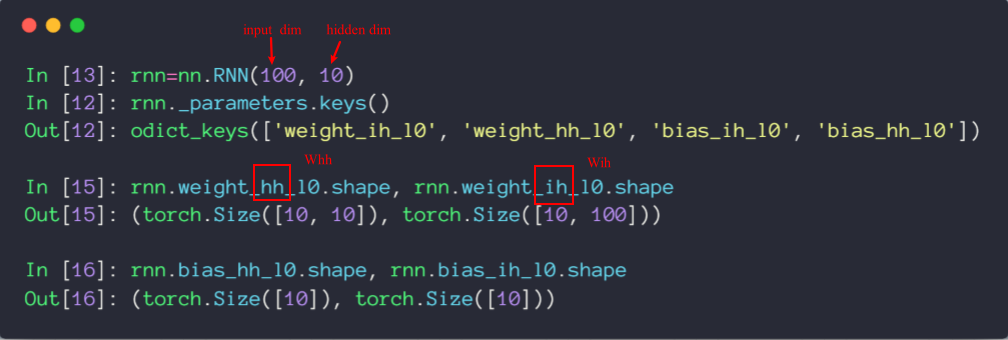


x: [seq len, b, word-vec] : b几句话,每句话的单词数为seq len, 每个单词的表示维度为 word vec; x为输入的语料,是整体输入的,不是一个一个输入的;
h0/ht: [num layers, b, h-dim]: RNN的层数num layers, b 为几句话(代表一次处理),h-dim为隐藏层的维度; ht为这句话的最终隐藏层状态;
out: [seq len, b, h-dim]: out为每个单词的隐状态的输出,h0, h1, ...;

Multi-layer RNN:
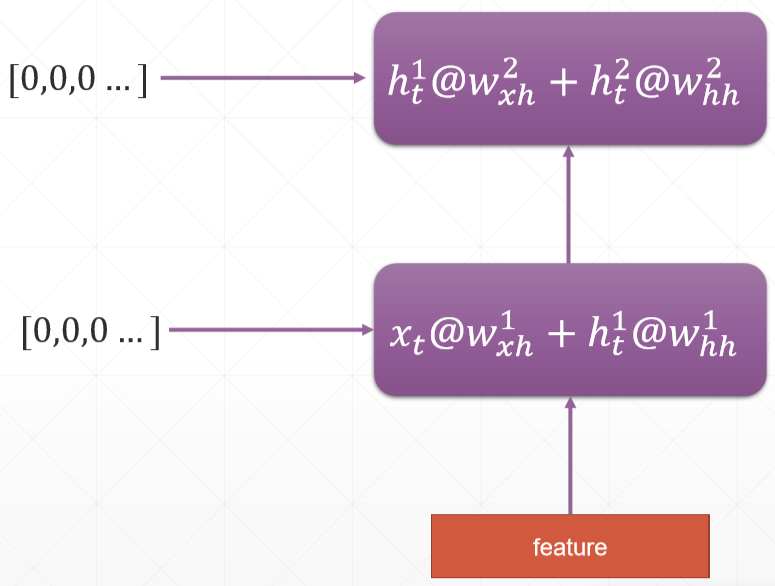



RNNCell 需要手动的循环








import torch from torch import nn from torch import optim from torch.nn import functional as F def main(): rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=100, hidden_size=20, num_layers=1) print(rnn) # RNN(100, 20) x = torch.randn(10, 3, 100) out, h = rnn(x, torch.zeros(1, 3, 20)) print(out.shape, h.shape) # torch.Size([10, 3, 20]) torch.Size([1, 3, 20])
# out: [10, 3, 20] 是所有时刻的隐状态的集合,所以维度和输入的单词个数是一致的,只不过每个隐状态的表示维度为20
# h: [1, 3, 20] 是最终的隐状态,和RNN的层数和输入的句子有关
rnn = nn.RNN(input_size=100, hidden_size=20, num_layers=4) print(rnn) # RNN(100, 20, num_layers=4) x = torch.randn(10, 3, 100) out, h = rnn(x, torch.zeros(4, 3, 20)) print(out.shape, h.shape)
# torch.Size([10, 3, 20]) torch.Size([4, 3, 20]) # print(vars(rnn)) print('rnn by cell') cell1 = nn.RNNCell(100, 20) h1 = torch.zeros(3, 20) for xt in x: h1 = cell1(xt, h1) print(h1.shape) cell1 = nn.RNNCell(100, 30) cell2 = nn.RNNCell(30, 20) h1 = torch.zeros(3, 30) h2 = torch.zeros(3, 20) for xt in x: h1 = cell1(xt, h1) h2 = cell2(h1, h2) print(h2.shape) print('Lstm') lstm = nn.LSTM(input_size=100, hidden_size=20, num_layers=4) print(lstm) x = torch.randn(10, 3, 100) out, (h, c) = lstm(x) print(out.shape, h.shape, c.shape)
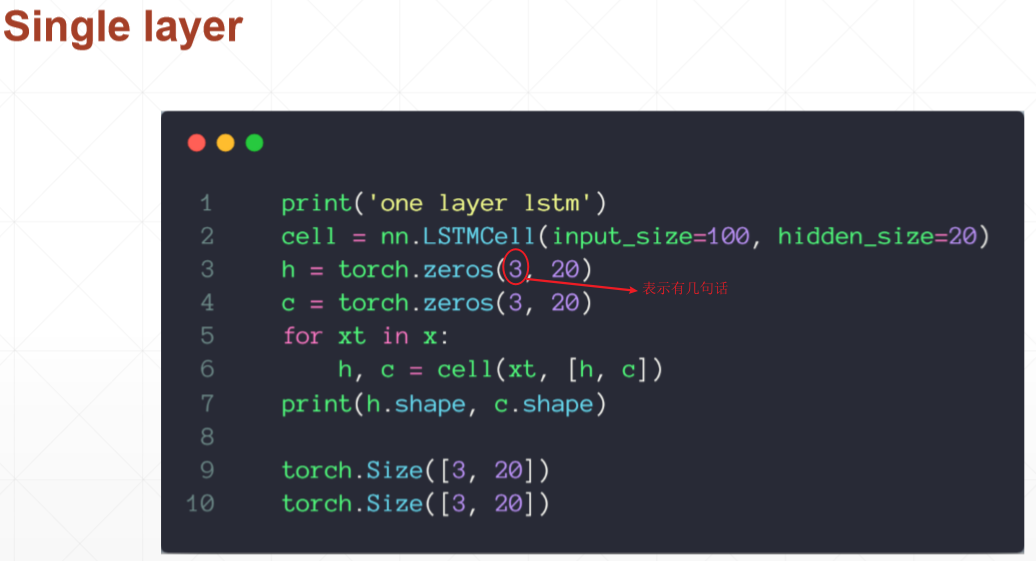
# torch.Size([10, 3, 20]) torch.Size([4, 3, 20]) torch.Size([4, 3, 20]) print('one layer lstm') cell = nn.LSTMCell(input_size=100, hidden_size=20) h = torch.zeros(3, 20) c = torch.zeros(3, 20) for xt in x: h, c = cell(xt, [h, c]) print(h.shape, c.shape)
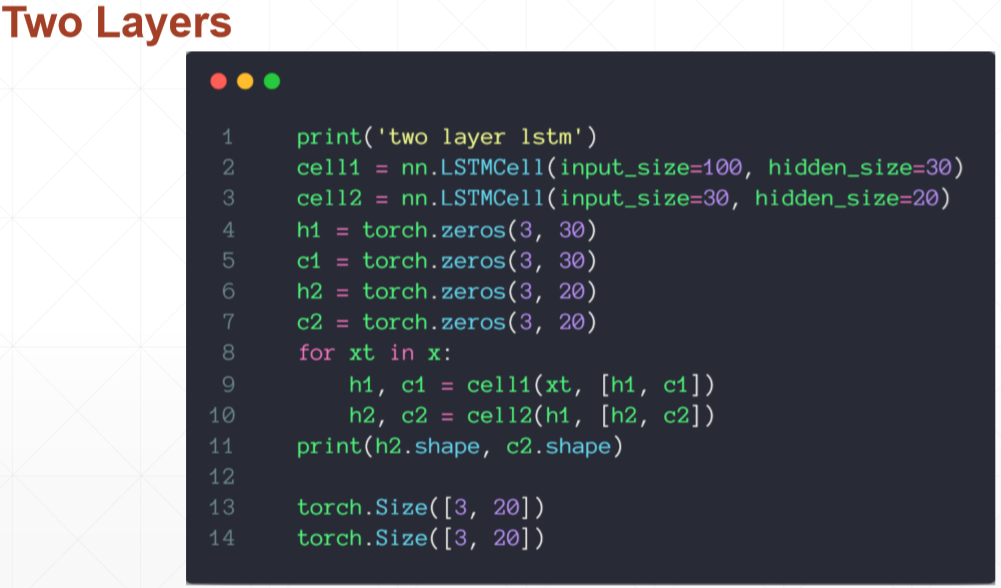
# torch.Size([3, 20]) torch.Size([3, 20]) print('two layer lstm') cell1 = nn.LSTMCell(input_size=100, hidden_size=30) cell2 = nn.LSTMCell(input_size=30, hidden_size=20) h1 = torch.zeros(3, 30) c1 = torch.zeros(3, 30) h2 = torch.zeros(3, 20) c2 = torch.zeros(3, 20) for xt in x: h1, c1 = cell1(xt, [h1, c1]) h2, c2 = cell2(h1, [h2, c2]) print(h2.shape, c2.shape) if __name__ == '__main__': main()
情感分类实例:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- """lstm Automatically generated by Colaboratory. Original file is located at https://colab.research.google.com/drive/1GX0Rqur8T45MSYhLU9MYWAbycfLH4-Fu """ !pip install torch !pip install torchtext !python -m spacy download en # K80 gpu for 12 hours import torch from torch import nn, optim from torchtext import data, datasets print('GPU:', torch.cuda.is_available()) torch.manual_seed(123) TEXT = data.Field(tokenize='spacy') LABEL = data.LabelField(dtype=torch.float) train_data, test_data = datasets.IMDB.splits(TEXT, LABEL) print('len of train data:', len(train_data)) print('len of test data:', len(test_data)) print(train_data.examples[15].text) print(train_data.examples[15].label) # word2vec, glove TEXT.build_vocab(train_data, max_size=10000, vectors='glove.6B.100d') LABEL.build_vocab(train_data) batchsz = 30 device = torch.device('cuda') train_iterator, test_iterator = data.BucketIterator.splits( (train_data, test_data), batch_size = batchsz, device=device ) class RNN(nn.Module): def __init__(self, vocab_size, embedding_dim, hidden_dim): """ """ super(RNN, self).__init__() # [0-10001] => [100] self.embedding = nn.Embedding(vocab_size, embedding_dim) # [100] => [256] self.rnn = nn.LSTM(embedding_dim, hidden_dim, num_layers=2, bidirectional=True, dropout=0.5) # [256*2] => [1] self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim*2, 1) self.dropout = nn.Dropout(0.5) def forward(self, x): """ x: [seq_len, b] vs [b, 3, 28, 28] """ # [seq, b, 1] => [seq, b, 100] embedding = self.dropout(self.embedding(x)) # output: [seq, b, hid_dim*2] # hidden/h: [num_layers*2, b, hid_dim] # cell/c: [num_layers*2, b, hid_di] output, (hidden, cell) = self.rnn(embedding) # [num_layers*2, b, hid_dim] => 2 of [b, hid_dim] => [b, hid_dim*2] hidden = torch.cat([hidden[-2], hidden[-1]], dim=1) # [b, hid_dim*2] => [b, 1] hidden = self.dropout(hidden) out = self.fc(hidden) return out rnn = RNN(len(TEXT.vocab), 100, 256) pretrained_embedding = TEXT.vocab.vectors print('pretrained_embedding:', pretrained_embedding.shape) rnn.embedding.weight.data.copy_(pretrained_embedding) print('embedding layer inited.') optimizer = optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), lr=1e-3) criteon = nn.BCEWithLogitsLoss().to(device) rnn.to(device) import numpy as np def binary_acc(preds, y): """ get accuracy """ preds = torch.round(torch.sigmoid(preds)) correct = torch.eq(preds, y).float() acc = correct.sum() / len(correct) return acc def train(rnn, iterator, optimizer, criteon): avg_acc = [] rnn.train() for i, batch in enumerate(iterator): # [seq, b] => [b, 1] => [b] pred = rnn(batch.text).squeeze(1) # loss = criteon(pred, batch.label) acc = binary_acc(pred, batch.label).item() avg_acc.append(acc) optimizer.zero_grad() loss.backward() optimizer.step() if i%10 == 0: print(i, acc) avg_acc = np.array(avg_acc).mean() print('avg acc:', avg_acc) def eval(rnn, iterator, criteon): avg_acc = [] rnn.eval() with torch.no_grad(): for batch in iterator: # [b, 1] => [b] pred = rnn(batch.text).squeeze(1) # loss = criteon(pred, batch.label) acc = binary_acc(pred, batch.label).item() avg_acc.append(acc) avg_acc = np.array(avg_acc).mean() print('>>test:', avg_acc) for epoch in range(10): eval(rnn, test_iterator, criteon) train(rnn, train_iterator, optimizer, criteon)