Java线程池在实际的应用开发中十分广泛。虽然Java1.5之后在JUC包中提供了内置线程池可以拿来就用,但是这之前仍有许多老的应用和系统是需要程序员自己开发的。因此,基于线程池的需求背景、技术要求了解线程池原理和实现,一方面可以更为深刻理解Java多线程开发,有助于解决业务系统中因为线程问题所产生的bug;另一方面也有利于对遗留代码的重构。
如果需要先行了解Java并发编程的基础知识,可参考以下随笔:
1. Java并发编程之线程创建和启动(Thread、Runnable、Callable和Future)
2. Java并发编程之线程生命周期、守护线程、优先级、关闭和join、sleep、yield、interrupt
线程池原理
所谓的线程池,跟JDBC连接池、代理池等一样,属于一种“池”的设计模式。在设计好的数据结构中存放一定数量的线程,并且根据任务需要自动调整线程数量的多少,直到峰值。具体说来,线程池需要满足若干条件:
1. 任务队列:用于缓存提交的任务
2. QueueSize:任务队列存放的Runnable任务实例的数量,需要有限制值防止内存溢出。
3. 线程数量管理:创建线程时初始的数量init;线程池自动扩充时最大的线程数量max;空闲时的活跃线程或核心线程数量core。三者满足init<=core<=max
4. 工作线程队列:用于存储工作线程,并统计工作线程的数量。
5. 任务拒绝策略:如果线程数量达到上限且任务队列已满,需要有拒绝策略通知任务提交者,这个在工程实践中非常重要。
6. 线程工厂:用于个性化定制线程,如设置守护线程、线程名称等。
7. Keepedalive时间:线程各个重要参数自动维护的时间间隔。
线程池原理图如下:
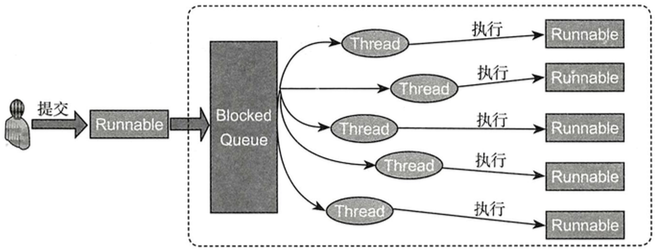
线程池实现
“模块设计,类图先行”。明确了线程池需要实现的功能之后,就可以画出线程池的草图了,核心接口及实现类如下:
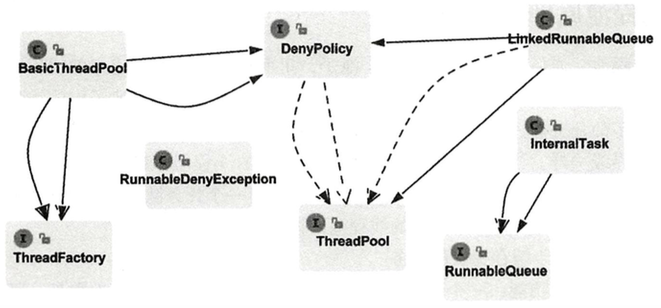
ThreadPool接口
ThreadPool接口主要定义一个线程池的基本属性,如任务提交、初始容量、最大容量、核心容量等。实现代码如下:
1 public interface ThreadPool { 2 3 //submit tasks to thread pool 4 void execute(Runnable runnable); 5 //close pool 6 void shutdown(); 7 //get the initial size of pool 8 int getInitSize(); 9 //get the max size of pool 10 int getMaxSize(); 11 //get the core size of pool 12 int getCoreSize(); 13 //get the cache tasks queue of pool 14 int getQueueSize(); 15 //get the active thread volume of pool 16 int getActiveCount(); 17 //check if pool has been shutdown 18 boolean isShutdown(); 19 }
RunnableQueue接口
这个接口的作用与BlockingQueue接口一样,用于存储提交的Runnable实现类任务。
1 public interface RunnableQueue { 2 //提交任务到队列 3 void offer(Runnable runnable); 4 //从队列中获取任务 5 Runnable take() throws InterruptedException; 6 //返回队列中任务数 7 int size(); 8 }
ThreadFactory接口
定义了个性化创建线程的工厂方法
1 @FunctionalInterface 2 public interface ThreadFactory { 3 4 Thread createThread(Runnable runnable); 5 6 }
DenyPolicy接口
定义了线程池的拒绝策略,即当任务队列达到上限时,采取何种措施拒绝。注意接口内定义了内部类作为外围接口的实现类(该类自动为public和static,像这种嵌套类的实现,可查询《Java编程思想》)。
1 @FunctionalInterface 2 public interface DenyPolicy { 3 4 void reject(Runnable runnable, ThreadPool threadPool); 5 //定义嵌套类作为拒绝策略的实现类 6 //1.拒绝并丢弃任务 7 class DiscardDenyPolicy implements DenyPolicy{ 8 9 @Override 10 public void reject(Runnable runnable, ThreadPool threadPool) { 11 12 } 13 } 14 15 //2.拒绝并抛出自定义异常 16 class AbortDenyPolicy implements DenyPolicy{ 17 18 @Override 19 public void reject(Runnable runnable, ThreadPool threadPool) { 20 throw new RunnableDenyException("The runnable " + runnable + " will abort."); 21 } 22 } 23 24 //3.拒绝, 使用提交者所在线程来完成线程任务. 25 class RunnerDenyPolicy implements DenyPolicy{ 26 27 @Override 28 public void reject(Runnable runnable, ThreadPool threadPool) { 29 30 if(!threadPool.isShutdown()) { 31 runnable.run(); 32 } 33 } 34 } 35 }
其实实现了自定义异常类RunnableDenyException:
1 public class RunnableDenyException extends RuntimeException { 2 3 private static final long serialVersionUID = 112311231231412L; 4 5 public RunnableDenyException(String message) { 6 super(message); 7 } 8 }
InternalTask实现类
Runnable的实现类,会使用到RunnableQueue,它的作用其实是封装了一个任务实例,把Runnable任务的run方法封装到自己的Run方法实现中,并且提供了一个stop方法,用于在线程池销毁或数量维护时停止当前线程。
1 public class InternalTask implements Runnable { 2 //组合一个RunnableQueue的引用 3 private final RunnableQueue runnableQueue; 4 //使用volatile关键字修饰开关变量 5 private volatile boolean running = true; 6 7 public InternalTask(RunnableQueue runnableQueue) { 8 this.runnableQueue = runnableQueue; 9 } 10 @Override 11 public void run() { 12 // if current task match "both running and isInterrupt" are true 13 // continue to take runnable from queue and run 14 while(running && !Thread.currentThread().isInterrupted()) { 15 try { 16 Runnable task = runnableQueue.take(); 17 task.run(); 18 } catch (Exception e) { 19 running = false; 20 break; 21 } 22 } 23 24 } 25 //停止线程的开关方法 26 public void stop() { 27 this.running = false; 28 } 29 }
到这里,一个基本线程池的骨架就搭好了,接下来主要是实现各接口,实现具体的方法。
1. 队列的实现类LinkedRunnableQueue
1 public class LinkedRunnableQueue implements RunnableQueue { 2 //设置队列上限 3 private final int limit; 4 //设置拒绝策略的引用 5 private final DenyPolicy denyPolicy; 6 //使用LinkedList作为队列的具体实现类 7 private final LinkedList<Runnable> runnableList = new LinkedList<>(); 8 //设置线程池的引用 9 private final ThreadPool threadPool; 10 //构造方法时赋初始值 11 public LinkedRunnableQueue(int limit, DenyPolicy denyPolicy, ThreadPool threadPool) { 12 this.limit = limit; 13 this.denyPolicy = denyPolicy; 14 this.threadPool = threadPool; 15 } 16 17 @Override 18 public void offer(Runnable runnable) { 19 //使用同步锁, 确保入队的线程安全 20 synchronized (runnableList) { 21 //当达到队列上限, 调用拒绝策略;否则加入队尾, 并唤醒阻塞中的线程. 22 if(runnableList.size() >= limit) { 23 denyPolicy.reject(runnable, threadPool); 24 }else { 25 runnableList.addLast(runnable); 26 runnableList.notifyAll(); 27 } 28 } 29 } 30 31 @Override 32 public Runnable take() throws InterruptedException { 33 synchronized (runnableList) { 34 35 while(runnableList.isEmpty()) { 36 try { 37 //如果队列中没有可执行任务, 线程挂起, 进入runnableList关联的monitor waitset中等待被唤醒 38 runnableList.wait(); 39 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 40 //如果被中断, 需要抛出异常 41 throw e; 42 } 43 } 44 return runnableList.removeFirst(); 45 } 46 } 47 48 @Override 49 public int size() { 50 synchronized (runnableList) { 51 //返回队列中的任务数量 52 return runnableList.size(); 53 } 54 } 55 }
2. 线程工厂的实现
1 public class DefaultThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory { 2 //定义原子类的Integer作为线程组的计数 3 private static final AtomicInteger GROUP_COUNTER = new AtomicInteger(1); 4 //定义线程组对象 5 private static final ThreadGroup group = new ThreadGroup("MyThreadPool-"+ GROUP_COUNTER.getAndDecrement()); 6 //定义生产的线程计数 7 private static final AtomicInteger COUNTER = new AtomicInteger(0); 8 9 @Override 10 public Thread createThread(Runnable runnable) { 11 return new Thread(group, runnable, "thread-pool-" + COUNTER.getAndDecrement()); 12 } 13 }
3. 线程池的实现
线程池的实现相对比较复杂, 运用了多种设计模式的思想,核心的要点包括:
1. 使用私有内部类的方式来复用Thread类,防止向外暴露Thread类的方法;
2. 核心组成部分主要是LinkedList实现的任务队列和ArrayDeque实现的工作线程队列,构成了主要的存储主体。
3. 核心的扩容机制需要RunnableQueue + InternalTask + ThreadFactory的结合, 简单说来就是通过判定任务数是否达到阈值,然后增加工作线程的数量。
1 public class BasicThreadPool implements ThreadPool { 2 //为了不暴露Thread类的方法, 使用私有内部类WorkThread来继承Thread类 3 private WorkThread workThread; 4 //线程池的基本属性 5 private final int initSize; 6 private final int maxSize; 7 private final int coreSize; 8 private int activeCount; 9 //线程工厂引用 10 private final ThreadFactory threadFactory; 11 //队列引用 12 private final RunnableQueue runnableQueue; 13 //线程池销毁标识 14 private volatile boolean isShutdown = false; 15 //工作线程的队列, 使用ArrayDeque实现 16 private final Queue<ThreadTask> threadQueue = new ArrayDeque<>(); 17 //定义了一个默认的拒绝策略 18 private final static DenyPolicy DEFAULT_DENY_POLICY = new DenyPolicy.DiscardDenyPolicy(); 19 //定义了一个默认的工厂对象 20 private final static ThreadFactory DEFAULT_THREAD_FACTORY = new DefaultThreadFactory(); 21 22 private final long keepAliveTime; 23 private final TimeUnit timeUnit; 24 //默认的构造器, 只需要传入初始容量, 最大容量, 核心容量和队列上限 25 public BasicThreadPool(int initSize, int maxSize, int coreSize, int queueSize) { 26 this(initSize, maxSize, coreSize, queueSize, DEFAULT_THREAD_FACTORY, 27 DEFAULT_DENY_POLICY,10,TimeUnit.SECONDS); 28 } 29 //完整构造器 30 public BasicThreadPool(int initSize, int maxSize, int coreSize, int queueSize, ThreadFactory threadFactory, 31 DenyPolicy denyPolicy,long keepAliveTime, TimeUnit timeUnit) { 32 this.workThread = new WorkThread(); 33 this.initSize = initSize; 34 this.maxSize = maxSize; 35 this.coreSize = coreSize; 36 this.threadFactory = threadFactory; 37 this.runnableQueue = new LinkedRunnableQueue(queueSize, denyPolicy, this); 38 this.keepAliveTime = keepAliveTime; 39 this.timeUnit = timeUnit; 40 this.init(); 41 } 42 //线程池的初始化方法, 在构造器中被调用, 用于启动工作线程 43 private void init() { 44 workThread.start(); 45 for(int i = 0; i < initSize; i++) { 46 newThread(); 47 } 48 } 49 //封装了工作线程的启动方法: 50 //1. 使用InternalTask封装RunnableQueue对象 51 //2. 通过工厂方法制造工作线程并启动 52 //3. 工作线程入队, 工作线程队列计数器+1 53 private void newThread() { 54 InternalTask internalTask = new InternalTask(runnableQueue); 55 Thread thread = this.threadFactory.createThread(internalTask); 56 ThreadTask threadTask = new ThreadTask(thread, internalTask); 57 threadQueue.offer(threadTask); 58 this.activeCount++; 59 thread.start(); 60 } 61 //工作线程出队的方法 62 private void removeThread() { 63 ThreadTask threadTask = threadQueue.remove(); 64 threadTask.internalTask.stop(); 65 this.activeCount--; 66 } 67 //核心:通过内部类继承Thread方法, 设计了自动扩容的机制. 68 //为了防止过快增加到Max容量, 使用continue来退出循环 69 private class WorkThread extends Thread{ 70 @Override 71 public void run() { 72 while(!isShutdown && !isInterrupted()) { 73 try { 74 timeUnit.sleep(keepAliveTime); 75 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 76 isShutdown = true; 77 break; 78 } 79 synchronized (this) { 80 if(isShutdown) { 81 break; 82 } 83 if(runnableQueue.size() > 0 && activeCount < coreSize) { 84 for(int i = initSize; i<coreSize;i++) { 85 newThread(); 86 } 87 continue; 88 } 89 if(runnableQueue.size() > 0 && activeCount < maxSize) { 90 for(int i = coreSize; i<maxSize;i++) { 91 newThread(); 92 } 93 } 94 if(runnableQueue.size()==0 && activeCount > coreSize) { 95 for(int i = coreSize; i < activeCount; i++) { 96 removeThread(); 97 } 98 } 99 100 } 101 } 102 } 103 } 104 105 @Override 106 public void execute(Runnable runnable) { 107 //如果线程池已经销毁, 将抛出异常 108 if(this.isShutdown) { 109 throw new IllegalStateException("the thread pool is destoried"); 110 } 111 this.runnableQueue.offer(runnable); 112 } 113 114 @Override 115 public void shutdown() { 116 synchronized(this) { 117 //防止重复销毁 118 if(isShutdown) { 119 return; 120 } 121 //重置关闭标识 122 isShutdown = true; 123 //关闭任务工作线程 124 threadQueue.forEach(threadTask -> { 125 threadTask.internalTask.stop(); 126 threadTask.thread.interrupt(); 127 }); 128 //关闭线程池的工作线程 129 this.workThread.interrupt(); 130 } 131 } 132 133 @Override 134 public int getInitSize() { 135 if(isShutdown) { 136 throw new IllegalStateException("The thread pool is destroy"); 137 } 138 return this.initSize; 139 } 140 141 @Override 142 public int getMaxSize() { 143 if(isShutdown) { 144 throw new IllegalStateException("The thread pool is destroy"); 145 } 146 return this.maxSize; 147 } 148 149 @Override 150 public int getCoreSize() { 151 if(isShutdown) { 152 throw new IllegalStateException("The thread pool is destroy"); 153 } 154 return this.coreSize; 155 } 156 157 @Override 158 public int getQueueSize() { 159 if(isShutdown) { 160 throw new IllegalStateException("The thread pool is destroy"); 161 } 162 return runnableQueue.size(); 163 } 164 165 @Override 166 public int getActiveCount() { 167 synchronized(this) { 168 return this.activeCount; 169 } 170 } 171 172 @Override 173 public boolean isShutdown() { 174 return this.isShutdown; 175 } 176 }
线程池的测试
编写一个简单的测试类,同时启动20个任务,测试线程池的活动状态:
1 public class ThreadPoolTest { 2 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { 4 5 final ThreadPool threadPool = new BasicThreadPool(2, 6, 4, 1000); 6 7 for(int i = 0; i < 20; i++) { 8 threadPool.execute(() -> { 9 try { 10 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(10); 11 System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "is Running and done"); 12 } catch (InterruptedException e) { 13 e.printStackTrace(); 14 } 15 }); 16 } 17 while(true) { 18 System.out.println("getActiveCount: " + threadPool.getActiveCount()); 19 System.out.println("getQueueSize: " + threadPool.getQueueSize()); 20 System.out.println("getCoreSize: " + threadPool.getCoreSize()); 21 System.out.println("getMaxSize: " + threadPool.getMaxSize()); 22 System.out.println("================================================"); 23 TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(5); 24 } 25 } 26 }
输出结果如下
thread-pool--1is Running and done thread-pool-0is Running and done getActiveCount: 4 getQueueSize: 14 getCoreSize: 4 getMaxSize: 6 ================================================ getActiveCount: 4 getQueueSize: 14 getCoreSize: 4 getMaxSize: 6 ================================================ thread-pool--3is Running and done thread-pool--2is Running and done thread-pool--1is Running and done thread-pool-0is Running and done getActiveCount: 6 getQueueSize: 8 getCoreSize: 4 getMaxSize: 6