20182320 2019-2020-1 《数据结构与面向对象程序设计》实验5报告
课程:《程序设计与数据结构》
班级: 1823
姓名: 郑力元
学号:20182320
实验教师:王志强
实验日期:2019年10月18日
必修/选修: 必修
1.实验内容
1.1 Android Stuidio的安装测试
参考《Java和Android开发学习指南(第二版)(EPUBIT,Java for Android 2nd)》第二十四章:
参考http://www.cnblogs.com/rocedu/p/6371315.html#SECANDROID,安装 Android Stuidio
完成Hello World, 要求修改res目录中的内容,Hello World后要显示自己的学号,自己学号前后一名同学的学号,提交代码运行截图和码云Git链接,截图没有学号要扣分
学习Android Stuidio调试应用程序
1.2 Activity测试
参考《Java和Android开发学习指南(第二版)(EPUBIT,Java for Android 2nd)》第二十五章:
构建项目,运行教材相关代码
创建 ThirdActivity, 在ThirdActivity中显示自己的学号,修改代码让MainActivity启动ThirdActivity
1.3 UI测试
参考《Java和Android开发学习指南(第二版)(EPUBIT,Java for Android 2nd)》第二十六章:
构建项目,运行教材相关代码
修改代码让Toast消息中显示自己的学号信息
1.4 布局测试
参考《Java和Android开发学习指南(第二版)(EPUBIT,Java for Android 2nd)》第二十七章:
构建项目,运行教材相关代码
修改布局让P290页的界面与教材不同
1.5 事件处理测试
参考《Java和Android开发学习指南(第二版)(EPUBIT,Java for Android 2nd)》第二十八章:
构建项目,运行教材相关代码
提交代码运行截图和码云Git链接,截图要有学号水印,否则会扣分
2. 实验过程及结果
2.1 Android Stuidio的安装测试
第一步:参考教材的第24章,进行Android Studio的下载和安装
第二步:安装Android Studio中的模拟器
第三步:创建Project,会自动生成程序“Hello World”,选择在虚拟机上运行,如下

2.2 Activity测试
第一步:学习教材第25章,了解Android程序单元的结构和代码结构,再参考树上的SecondActivityDemo程序,学习如何通过一个活动启动另一个活动。
第二步:编写程序的清单,其中要包含两个活动的注册。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.thirdactivity">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
//第一个活动MainActivity的注册
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
//第二个活动ThirdActivity的注册
<activity android:name="ThirdActivity"
android:label="@string/thirdActivity">
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
第三步:编写、设计两个活动的布局文件
第一个活动的布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
//创建TextView来在第一个界面上显示文字
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="@string/start_thirdactivity"
app:layout_constraintBottom_toBottomOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintLeft_toLeftOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintRight_toRightOf="parent"
app:layout_constraintTop_toTopOf="parent" />
</RelativeLayout>
第二个活动的布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
//创建一个TextView来在第二个界面显示学号
<TextView
android:id="@+id/textView1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
//这里输入学号
android:text="20182320"
android:textAppearance="@style/TextAppearance.AppCompat.Display4"
android:visibility="visible"
tools:visibility="visible" />
</RelativeLayout>
第四步:编写主活动和被启动的活动的活动类
主活动的类代码
package com.example.thirdactivity;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.MotionEvent;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.TextView;
//在这里我们需要让主活动类实现OnTouchListener接口,监听触碰这个活动,才能实现通过这个触碰行为启动另一个活动
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements View.OnTouchListener {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
TextView tv=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView1);
tv.setOnTouchListener(this);
}
//实现OnTouchListener接口需要实现它里面的onTouch方法
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
//这里比较重要,分步解析:
//1.创建一个Intent类并实例化,存入这个类和需要启动的ThirdActivity类
Intent intent=new Intent(this,ThirdActivity.class);
//2.通过Intent类的putExtra方法放入要传给下个界面的字符串
intent.putExtra("message","20182320");
//3.通过startActivity方法启动
startActivity(intent);
return true;
}
}
被启动活动的类代码
package com.example.thirdactivity;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.TextView;
import androidx.annotation.Nullable;
public class ThirdActivity extends Activity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(@Nullable Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_third);
Intent intent=getIntent();
String message=intent.getStringExtra("message");
//通过findViewById来查找在第二个界面中显示文本的textView并设置它的值为主活动传过来的message
((TextView)findViewById(R.id.textView1)).setText(message);
}
}
第五步:若上面代码中有调用资源文件夹下的资源但是标红的,需要检查一下资源文件夹中是否有这个资源,若没有需要对string等文件进行修改和添加。
第六步:运行
第一个界面:

点击第一个界面中的文本后,启动第二个活动,弹出第二个界面:

2.3 UI测试
我设计的是使用一个button来使toast弹出。
第一步:进行布局文件的编写
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
//如下,创建一个button
<Button
android:id="@+id/button"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center"
android:layout_marginTop="255dp"
android:paddingLeft="32dp"
android:paddingRight="32dp"
android:text="Button" />
</LinearLayout>
第二步:编写清单
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.uitest">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:roundIcon="@mipmap/ic_launcher_round"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
第三步:编写主活动(重点)
public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity{
TextView textView;
Button button;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
/*在onCreat中设置一个Button类的对象bt,并用
findViewById将它指向我们在布局中创建好的button*/
Button bt=(Button)findViewById(R.id.button);
//调用Button类的setOnClickListener方法来创建一个监听器
bt.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
//重写onClick方法来定义点击button后的活动
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
//直接用Toast和它的makeText方法来创建一个Toast弹窗
Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this,"20182320",Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
});
}
}
第四步:运行
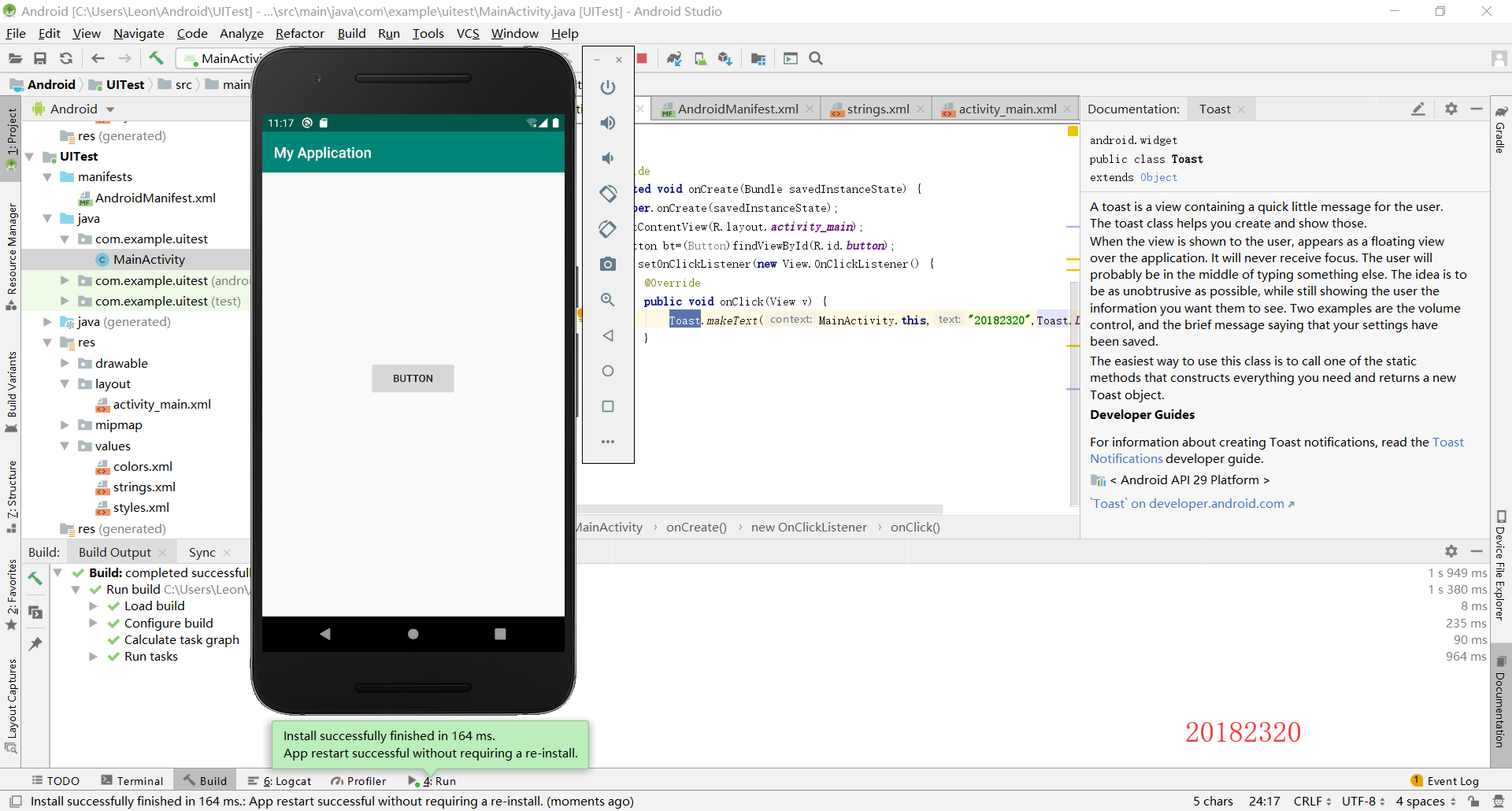
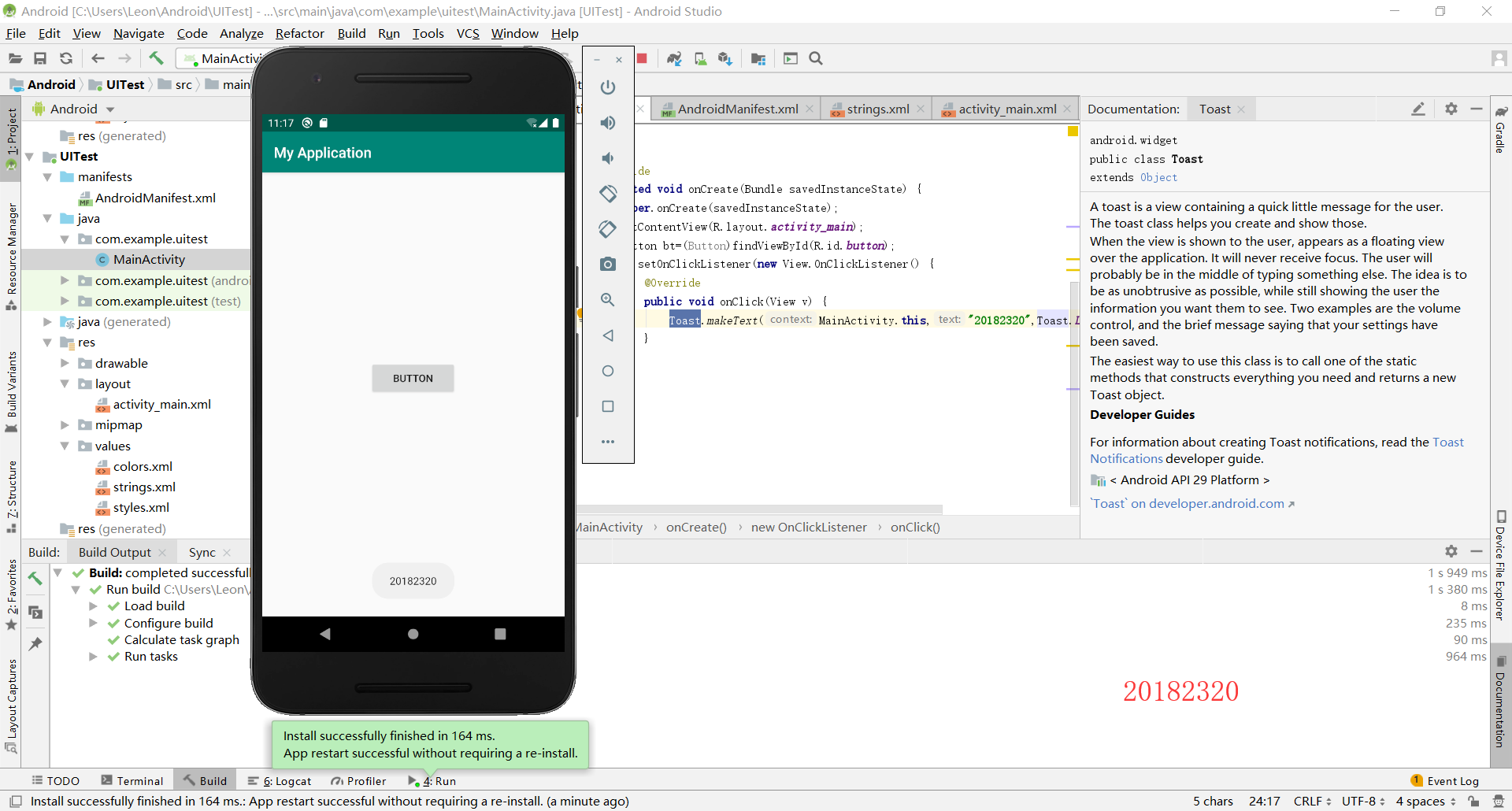
2.4 布局测试
这一个实验主要涉及布局的设计和使用方法,包括用design界面设计和用代码设计。
2.4 Clock
第一步:修改layout
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity=""
android:orientation="vertical"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
<Button
android:id="@+id/cancelButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerInParent="true"
android:text="Cancel" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/saveButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_below="@id/cancelButton"
android:text="Save" />
<ImageView
android:layout_width="150dp"
android:layout_height="150dp"
android:layout_below="@id/cancelButton"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="120dp"
android:padding="4dp"
android:src="@android:drawable/ic_btn_speak_now" />
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/filter_button_container"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:background="@android:color/black"
android:gravity="center"
android:orientation="vertical">
<Button
android:id="@+id/filterButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:text="Filter" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/shareButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:text="Share" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/deleteButton"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:text="Delete" />
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
第二步:运行
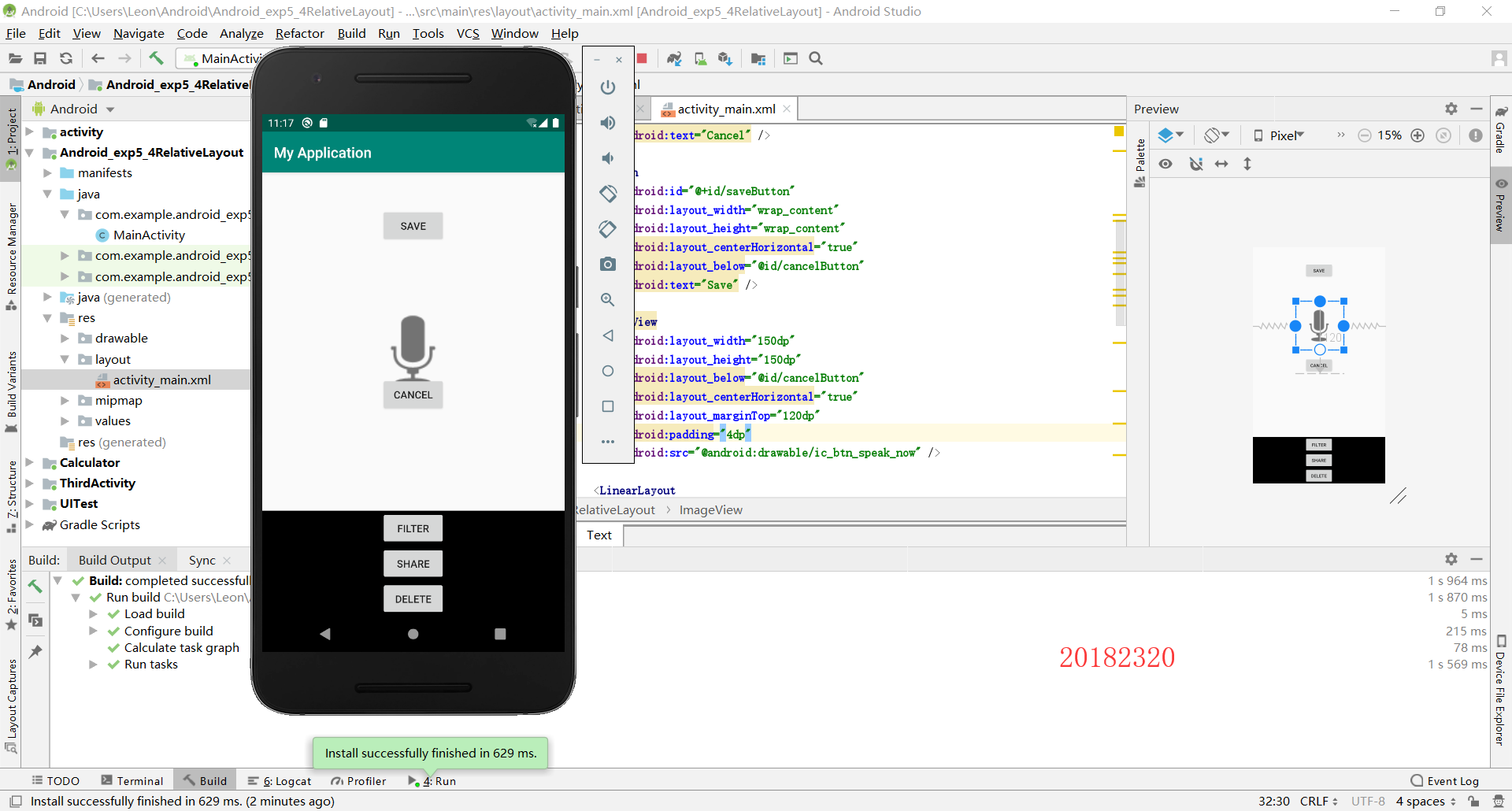
2.5 事件处理测试
2.5.1 Clock
第一步:编写layout
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context=".MainActivity">
//创建一个AnalogClock微件
<AnalogClock
android:id="@+id/analogClock1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentTop="true"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="90dp"
//这里的onClick属性使我们不需要再额外创建监听器
android:onClick="changeColor"
/>
</RelativeLayout>
第二步:编写清单
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.android_exp5_5multicolorclock">
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.example.android_exp5_5multicolorclock.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
第三步:编写主活动类
package com.example.android_exp5_5multicolorclock;
import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.graphics.Color;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
int counter = 0;
//定义颜色
int[] colors = { Color.BLACK, Color.BLUE, Color.CYAN,
Color.DKGRAY, Color.GRAY, Color.GREEN, Color.LTGRAY,
Color.MAGENTA, Color.RED, Color.WHITE, Color.YELLOW };
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it
// is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.menu_main, menu);
return true;
}
//更换颜色的方法
public void changeColor(View view) {
if (counter == colors.length) {
counter = 0;
}
view.setBackgroundColor(colors[counter++]);
}
}
第四步:运行

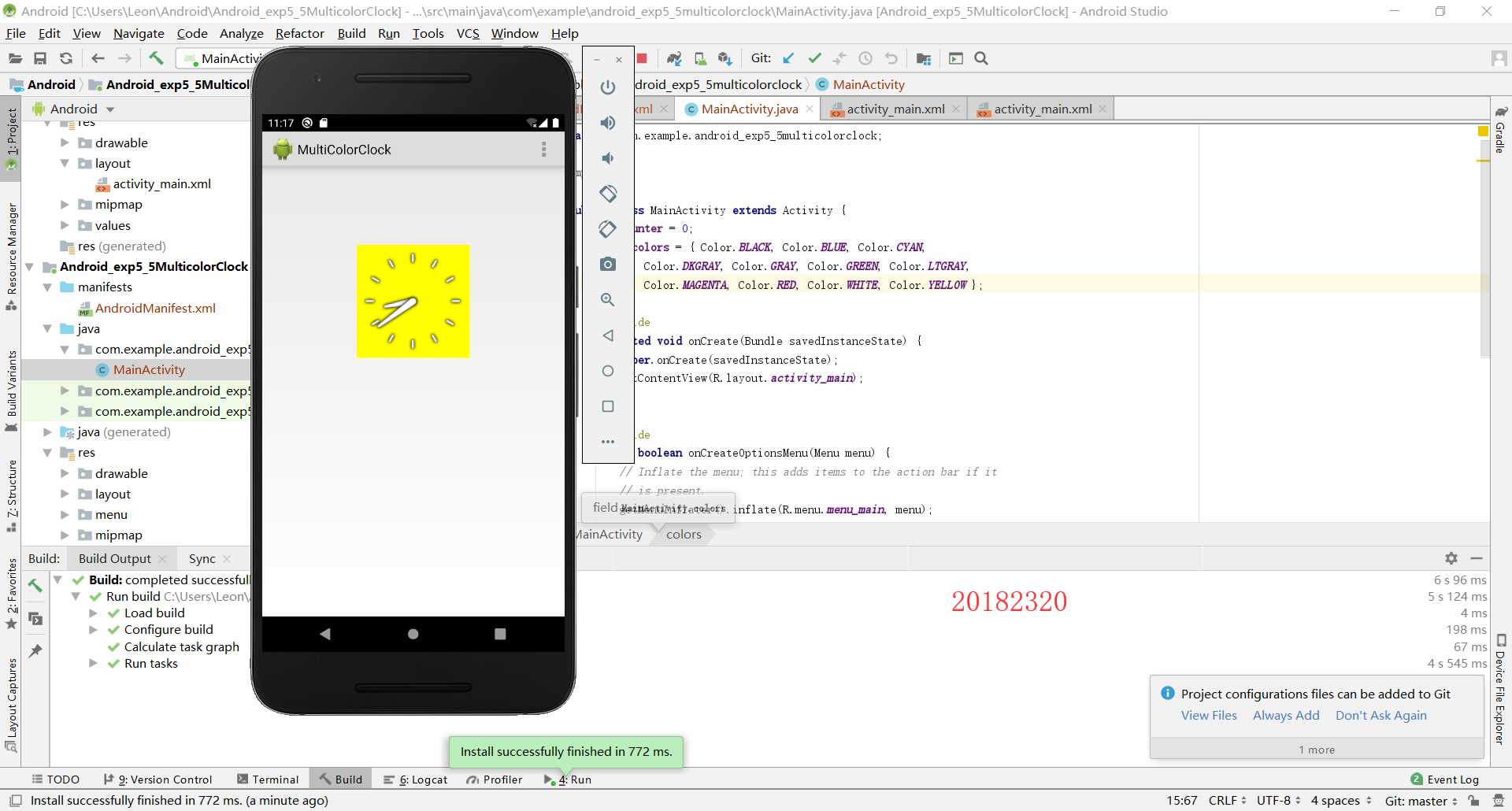
2.5.2 CellView
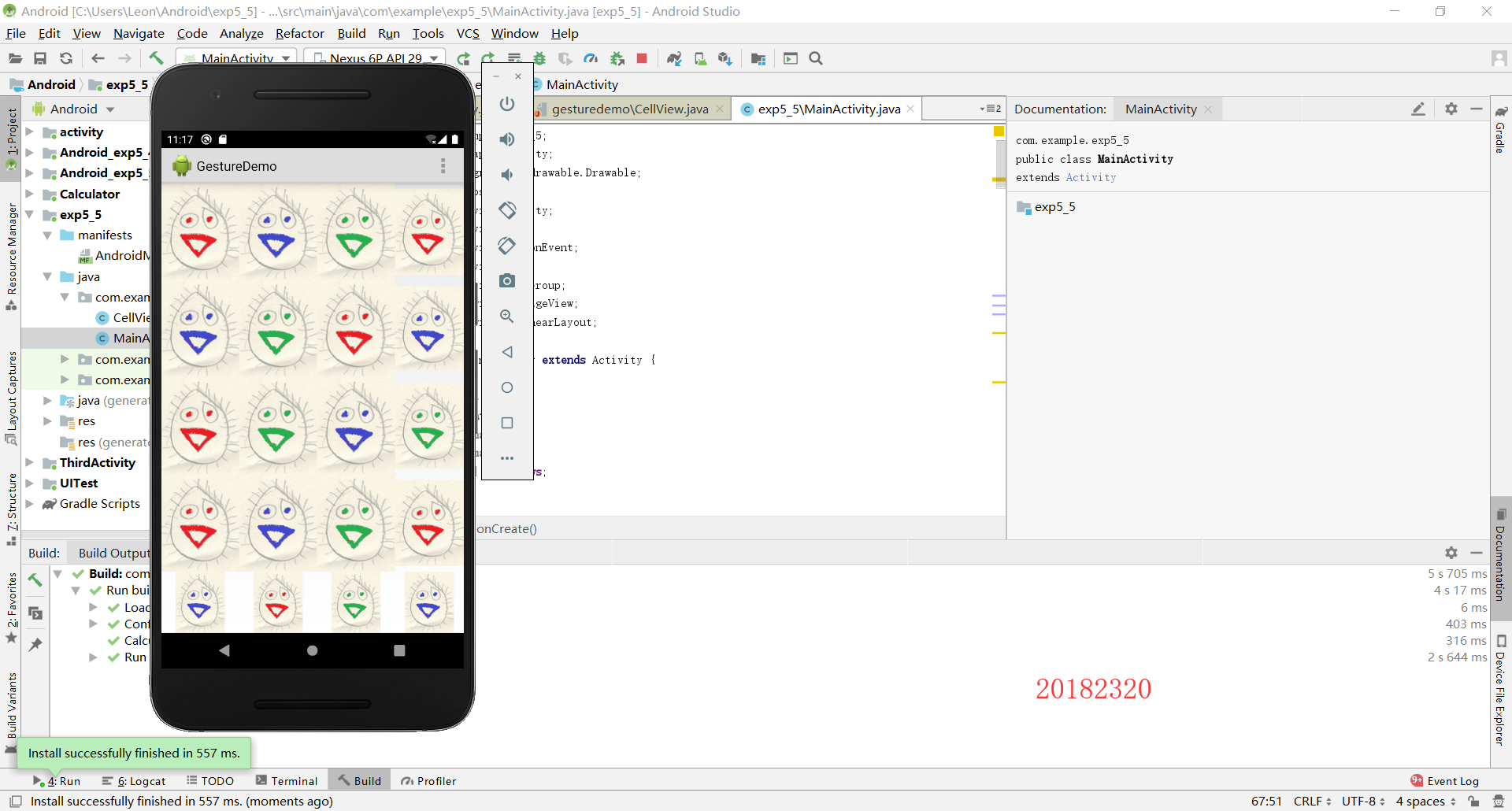
3. 实验过程中遇到的问题和解决过程
问题1:
一个安卓单元的结构和组成是什么样的?
解决1:
重要的部分有三个:清单、布局、活动类
(1)清单:为使用的资源和元素进行提前声明
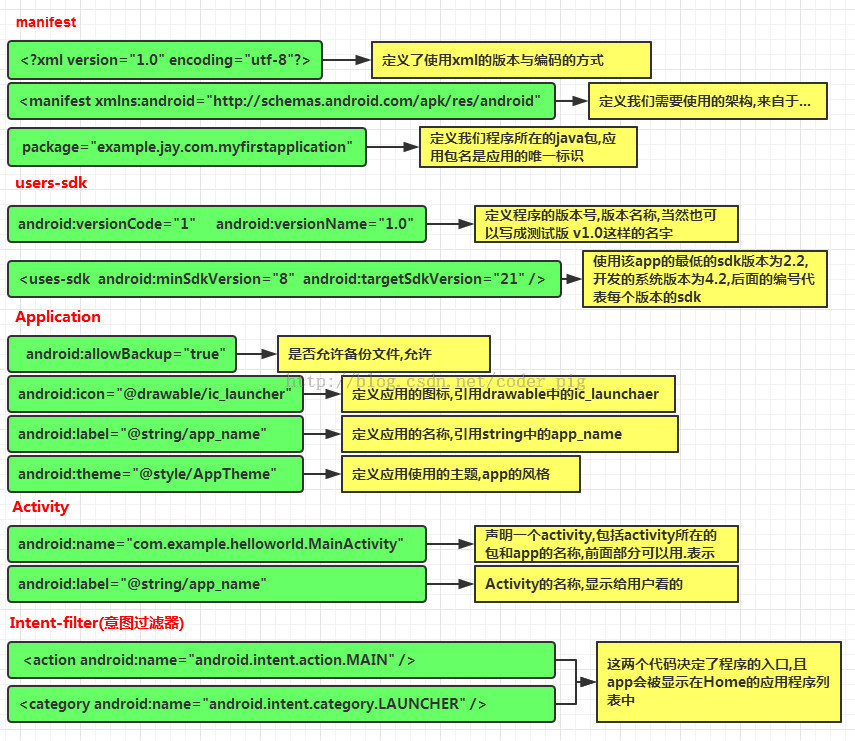
(2)布局:程序的界面设计
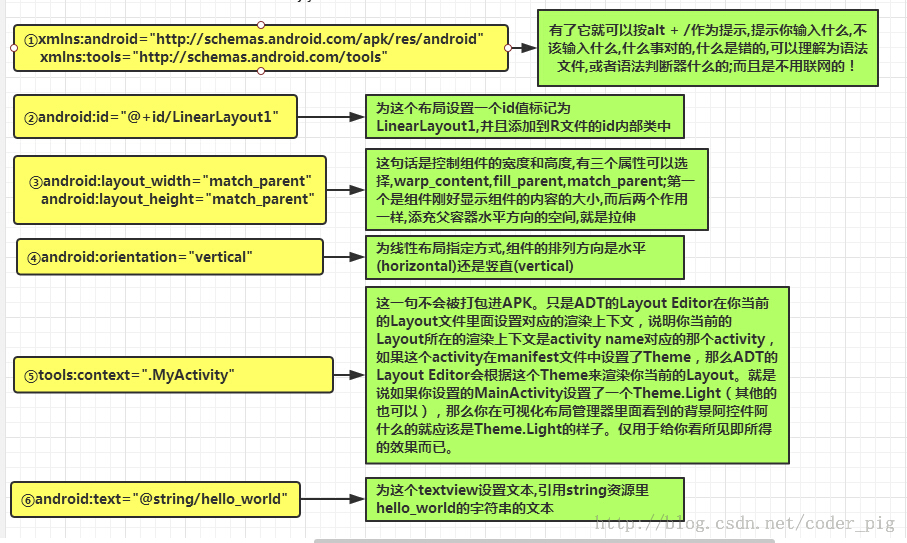
(3)活动类:具体实现程序的功能

参考:CSDN
其他(感悟、思考等)
Android Studio虽然是基于Java的,但是还是多了一些资源包、清单等额外需要学习、掌握的内容,在这些内容的学习中,了解每个代码的结构和每个部分的功能,能使我们尽快上手。