Regular expression example — www.javamex.com — Readability
Regular expression example
•In this example, we'll use regular expressions to performing what is sometimes called HTML scraping or screen scraping. Namely, we want to extract some data from a web page. We'll concentrate on HTML data, but essentially similar expressions can actually be used to scrape XML data (for example, from an RSS feed). Using regular expressions to scrape data has the advantage that it is easy to make the expression cope flexibly with "broken" HTML. Many libraries designed to interpret HTML and/or XML (including the standard DOM API now part of the JDK) are often too "fussy" for the real world, where most web pages and XML documents are actually badly formed in some way or other.
As an example, we're going to scrape a page of Wikipedia to pull out a list of all the names of states in Mexico, along with the URLs of corresponding Wikipedia entries.
Step 1: Find where the data is!
This might be obvious, but the first stage is usually to "eyeball" the web page in question in our web browser to confirm where the data actually is on the page. In this case, if we look up Mexico in Wikipedia, a quick scroll down reveals that there is a table containing a list of Mexican states with links to their corresponding entries. In a moment, we'll need to tell our program to find the corresponding section of HTML and pull out the information we're interested in. Our browser address bar also tells us that the URL of the entry we're looking at is:
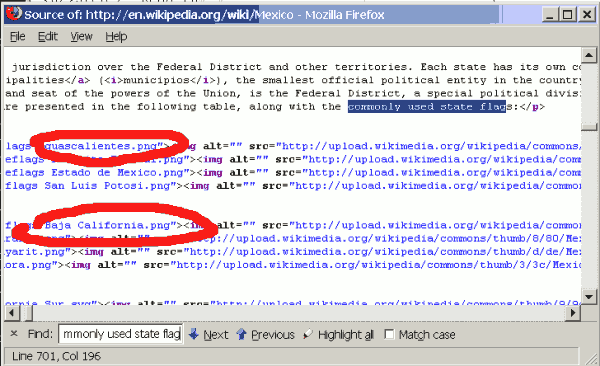
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MexicoAnd looking at the table, we see that the first names are Aguascalientes and Baja California. At the time of writing, the text directly before the table reads "...along with the commonly used state flags:". We probably want to take note of this text too, to help us find the data in the HTML source code.
Step 2: Identify "anchors" for your data
The next thing we will usually want to do is have a look at the HTML or XML pulled down from the URL we are interested in. We could make our program print this out, but the easiest way is probably to use the View Page Source option (or similar) of our web browser. Using Firefox's Find option to search for the text mentioned above, we quickly locate that text plus, below it, what appears to be some HTML code with the two state names we saw in the table (albeit names of image files):
Now we've honed in on the section of HTML that appears to contain the data, we need to look more closely at where the data lies. We need to:
- find some piece of HTML that will identify the "beginning" and "end" of a piece of data, and come up with subexpressions for those points;
- identify which pieces of HTML we can discard, and come up with suitable subexpressions which will "skip past" the data we're not interested in, probably using wildcard characters1;
- create a capturing groups2 for the pieces of data we're actually interested in.
In this case, we see that the table contains lines in the following format, where the text in bold is the data we are interested in:
<td><span class="flagicon"> <a href="/wiki/File:Mexico_stateflags_Aguascalientes.png" class="image" title="Mexico stateflags Aguascalientes.png"> <img alt="" src="http://upload.wikimedia.org/wikipedia/.../ 22px-Mexico_stateflags_Aguascalientes.png" width="22" height="13" border="0" class="thumbborder" /></a> </span><a href="/wiki/Aguascalientes" title="Aguascalientes">Aguascalientes</a> (Ags)</td>We list only one as an example, but it turns out that every row in the table starts with a span of class flagicon. So as a starting point, we'll use this to identify each row of data, and our expression will start by looking for (matching against):
String expr = "<td><span\\s+class=\"flagicon\"[^>]*>" + ...;Notice:
We've replaced a space inside a tag with \\s+, to match against any whitespace sequence, since we know that any sequence of spaces, newlines and tabs would actually be acceptable here. This is just good practice, in case there was variation in the HTML code (there actually isn't in this example).
- We use the sequence [^>]* to mean "anything between here and the end of the tag" (in actual fact, zero or more characters that are not close tag symbols): again this is just good practice, to cope with any unexpected additional attributes that we're not interested in.
The next thing that comes in the HTML code is a whole chunk of code inside the span that we're not interested in. So what we really want to do now is allow "anything between here and the close of the span". We can do so as follows:
String expr = "<td><span\\s+class=\"flagicon\"[^>]*>" + ".*?</span>" + ...;Here we use the dot3 followed by a star to mean "match any number of any character, provided the rest of the expression still matches". But we also add a question mark. This performs a reluctant match4: in other words, it will match the smallest number of characters possible, while still making the rest of the expression match. This effectively prevents .* from also matching against an instance of </span>: we want to find the first span close tag that comes next in the HTML sequence.
Finally, we're at a part of the HTML that contains the data we're interested in. The essential technique is to copy the piece of HTML containing the data into the expression, but (a) replace actual pieces of data with a bracketed expression (capturing group), and (b) try and make other parts of the expression more generic, for example using [^>]* and \\s+ as above. So we end up with the following:
String expr = "<td><span\\s+class=\"flagicon\"[^>]*>" + ".*?</span><a href=\"" + "([^\"]+)" // first piece of data goes up to quote + "\"[^>]*>" // end quote, then skip to end of tag + "([^<]+)" // name is data up to next tag + "</a>.*?</td>"; // end a tag, then skip to the td close tagNotice that we must escape (write \" for) quotes inside quotes, and subexpressions such as [^\"]* to mean "the next sequence of characters that does not include a quote".
Step 3: Read the web page or URL contents into a String
In order to run regular expressions over the web page or XML document in question, we need to pull it down from the URL. In the section on Java I/O5, we some sample code to read data from a URL6 and put the result in a String (or in fact, any old CharSequence— something like a StringBuilder or StringBuffer will also do). We're therefore going to assume that you have copied the following method from the aforementioned page:
Note that a slight issue you may need to deal with is that of character encoding. In our example getURLContent() method, we assumed a default encoding of ISO-8859-1, but in fact, Wikipedia appears to use UTF-8.
Step 4: Run the regular expression over the HTML data
Now we've pretty much done the hard work. We compile our regular expression into a Pattern object and use that to construct a Matcher around the HTML data pulled from the URL. A small detail is that we need to be careful about line endings in the HTML: we need to be flexible about what type of line endings to expect (Windows or UNIX), since web servers can run on either system. And we need to allow the dot character to match against line endings, since it doesn't matter if, say, a line ending occurs between HTML tag attributes. So we pass flags to the Pattern.compile() method as follows:
Pattern patt = Pattern.compile(expr, Pattern.DOTALL | Pattern.UNIX_LINES); URL url = new URL("http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Mexico"); Matcher m = patt.matcher(getURLContent(url)); while (m.find()) { String stateURL = m.group(1); String stateName = m.group(2); System.out.println(stateName + "," + stateURL); }