MySQL SELECT_LEX与subselect 执行 源码阅读笔记
Based on MySQL8.0 community version
JOIN::exec的细节不在此文中介绍。
SELECT_LEX
代码中常见简称为select。一个SELECT_LEX可以理解成一个SELECT FROM WHERE的query block(可能是subselect,可能是最外层最顶层outer_most query)。SELECT_LEX有prepare和optimize方法,没有execute方法,SELECT_LEX_UNIT在execute时是直接调用select->join->exec()的。
部分重要成员变量(一些parse相关的变量暂时跳过):
/**
Intrusive double-linked list of all query blocks within the same
query expression.
SELECT_LEX在union连接下从属于一个SELECT_LEX_UNIT,其链表链接在此维护。
*/
SELECT_LEX *next;
SELECT_LEX **prev;
/// The query expression containing this query block.
/// 即包含当前select的父对象SELECT_LEX_UNIT
SELECT_LEX_UNIT *master;
/// The first query expression contained within this query block.
/// 即当前query包含的第一个子select组SELECT_LEX_UNIT
SELECT_LEX_UNIT *slave;
/// SELECT_LEX和SELECT_LEX_UNIT的组合关系参考:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/internals/en/select-structure.html
/// Intrusive double-linked global list of query blocks.
/// 当前query下的全局select列表(方便遍历)
SELECT_LEX *link_next;
SELECT_LEX **link_prev;
/// Result of this query block
/// handle最后的query result的对象,发送给client或者写文件等
Query_result *m_query_result;
/// Describes context of this query block (e.g if it is a derived table).
/// 默认是UNSPECIFIED,parse阶段之后实际只有UNION_TYPE和DERIVED_TABLE_TYPE有用,一个是union select,另一个是当前select会生成derived_table。
enum sub_select_type linkage;
/**
Condition to be evaluated after all tables in a query block are joined.
After all permanent transformations have been conducted by
SELECT_LEX::prepare(), this condition is "frozen", any subsequent changes
to it must be done with change_item_tree(), unless they only modify AND/OR
items and use a copy created by SELECT_LEX::get_optimizable_conditions().
Same is true for 'having_cond'.
*/
/// where 条件
Item *m_where_cond;
/// Condition to be evaluated on grouped rows after grouping.
/// having 条件。TODO:部分having会转为where查询?
Item *m_having_cond;
/**
Saved values of the WHERE and HAVING clauses. Allowed values are:
- COND_UNDEF if the condition was not specified in the query or if it
has not been optimized yet
- COND_TRUE if the condition is always true
- COND_FALSE if the condition is impossible
- COND_OK otherwise
*/
Item::cond_result cond_value; // where cond result
Item::cond_result having_value; // having result
// 一般都是UNSPECIFIED_OLAP_TYPE, ROLLUP参见:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/group-by-modifiers.html
enum olap_type olap;
/**
After optimization it is pointer to corresponding JOIN. This member
should be changed only when THD::LOCK_query_plan mutex is taken.
*/
// 该select对应的join对象
JOIN *join;
/// join list of the top level
List<TABLE_LIST> top_join_list;
/// list for the currently parsed join
/// 主要作用于parse,但optimize等地方也有少量引用到它,感觉可能是误用?可能应当用top_join_list
List<TABLE_LIST> *join_list;
/// table embedding the above list
TABLE_LIST *embedding;
/// List of semi-join nests generated for this query block
List<TABLE_LIST> sj_nests;
/**
Points to first leaf table of query block. After setup_tables() is done,
this is a list of base tables and derived tables. After derived tables
processing is done, this is a list of base tables only.
Use TABLE_LIST::next_leaf to traverse the list.
*/
// 指向第一个真实表
TABLE_LIST *leaf_tables;
/**
If this query block is a recursive member of a recursive unit: the
TABLE_LIST, in this recursive member, referencing the query
name.
*/
// 指向要递归的表(in recursive CTE)
TABLE_LIST *recursive_reference;
/**
To pass the first steps of resolution, a recursive reference is made to
be a dummy derived table; after the temporary table is created based on
the non-recursive members' types, the recursive reference is made to be a
reference to the tmp table. Its dummy-derived-table unit is saved in this
member, so that when the statement's execution ends, the reference can be
restored to be a dummy derived table for the next execution, which is
necessary if we have a prepared statement.
WL#6570 should allow to remove this.
*/
SELECT_LEX_UNIT *recursive_dummy_unit;
SELECT_LEX_UNIT
代码中常见简称为unit。一个SELECT_LEX_UNIT表示一组由UNION / INTERSECT / EXCEPT等SELECT级别的逻辑操作组合成的一组SELECT结构,不过目前仅支持UNION,因此只是简单的列表结构。
部分重要成员变量:
/**
Intrusive double-linked list of all query expressions
immediately contained within the same query block.
SELECT_LEX_UNIT从属于一个SELECT_LEX,其链表链接在此维护。
*/
SELECT_LEX_UNIT *next;
SELECT_LEX_UNIT **prev;
/**
The query block wherein this query expression is contained,
NULL if the query block is the outer-most one.
*/
/// 即包含当前SELECT_LEX_UNIT的父对象SELECT_LEX
SELECT_LEX *master;
/// The first query block in this query expression.
/// 即当前query包含的第一个子select SELECT_LEX
SELECT_LEX *slave;
bool prepared; ///< All query blocks in query expression are prepared
bool optimized; ///< All query blocks in query expression are optimized
bool executed; ///< Query expression has been executed
TABLE_LIST result_table_list;
// A UNION B的结果
Query_result_union *union_result;
TABLE *table; /* temporary table using for appending UNION results */
/// Object to which the result for this query expression is sent
Query_result *m_query_result;
// list of fields which points to temporary table for union
List<Item> item_list;
/*
list of types of items inside union (used for union & derived tables)
Item_type_holders from which this list consist may have pointers to Field,
pointers is valid only after preparing SELECTS of this unit and before
any SELECT of this unit execution
TODO:
Possibly this member should be protected, and its direct use replaced
by get_unit_column_types(). Check the places where it is used.
*/
List<Item> types;
/* LIMIT clause runtime counters */
ha_rows select_limit_cnt, offset_limit_cnt;
/// Points to subquery if this query expression is used in one, otherwise NULL
// 包含当前UNIT的Item_subselect(如果是在WHERE/HAVING 的subselect中的话)
Item_subselect *item;
/**
Helper query block for query expression with UNION or multi-level
ORDER BY/LIMIT
*/
// 对于ORDER BY或UNION后的结果,需再借助一个fake的select将其发送出去
// SELECT A UNION SELECT B -->
// SELECT * FROM (SELECT A UNION SELECT B) AS UNION_RESULT
SELECT_LEX *fake_select_lex;
/**
SELECT_LEX that stores LIMIT and OFFSET for UNION ALL when no
fake_select_lex is used.
*/
SELECT_LEX *saved_fake_select_lex;
/**
Points to last query block which has UNION DISTINCT on its left.
In a list of UNIONed blocks, UNION is left-associative; so UNION DISTINCT
eliminates duplicates in all blocks up to the first one on its right
included. Which is why we only need to remember that query block.
*/
// 目前实际不支持 rec0 UNION ALL rec1 UNION DISTINCT rec2 UNION ALL rec3 的情况,即UNION DISTINCT后面不能再加UNION ALL。而且mixed UNION中DISTINCT会覆盖左边的ALL语义,所以不知道mix UNION有何用。
SELECT_LEX *union_distinct;
/**
The WITH clause which is the first part of this query expression. NULL if
none.
*/
// 即该查询是否一个当前层带WITH的CTE查询
PT_with_clause *m_with_clause;
/**
If this query expression is underlying of a derived table, the derived
table. NULL if none.
*/
// 当前SELECT将要生成的生成表(如果会生成derived_table的话)
TABLE_LIST *derived_table;
/**
First query block (in this UNION) which references the CTE.
NULL if not the query expression of a recursive CTE.
*/
// 对于当前UNIT,first_recursive表示第一个CTE select,first_recursive之后的都必然是recursive的select,之前的必然都是非recursive的select。
SELECT_LEX *first_recursive;
/**
True if the with-recursive algorithm has produced the complete result.
In a recursive CTE, a JOIN is executed several times in a loop, and
should not be cleaned up (e.g. by join_free()) before all iterations of
the loop are done (i.e. before the CTE's result is complete).
*/
// CTE recursive读的时候判断是否读结束
bool got_all_recursive_rows;
SELECT路径
以官方文档CTE中的employees表为例子
CREATE TABLE employees (
id INT PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
manager_id INT NULL
) ENGINE='innodb';
INSERT INTO employees VALUES
(333, "Yasmina", NULL), # Yasmina is the CEO (manager_id is NULL)
(198, "John", 333), # John has ID 198 and reports to 333 (Yasmina)
(692, "Tarek", 333),
(29, "Pedro", 198),
(4610, "Sarah", 29),
(72, "Pierre", 29),
(123, "Adil", 692);
1. 简单query
SELECT id FROM employees;
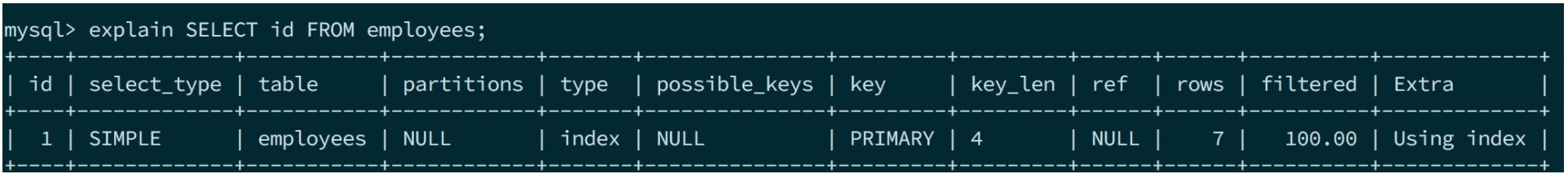
prepare首先会进入Sql_cmd_select::prepare_inner,对于非union的unit会直接调用当前唯一子节点 select的prepare;否则则调用unit->prepare,并且在unit->prepare里会遍历调用select->prepare。
/// @return true for a query expression without UNION or multi-level ORDER
bool SELECT_LEX_UNIT::is_simple() const { return !(is_union() || fake_select_lex); }
// bool Sql_cmd_select::prepare_inner(THD *thd)
if (unit->is_simple()) {
// unit的子节点只有一个select (此处不排斥select可能有subquery)
SELECT_LEX *const select = unit->first_select();
select->context.resolve_in_select_list = true;
select->set_query_result(result);
select->make_active_options(0, 0);
select->fields_list = select->item_list;
if (select->prepare(thd)) return true;
unit->set_prepared();
} else {
if (unit->prepare(thd, result, SELECT_NO_UNLOCK, 0)) return true;
}
execute会先进入Sql_cmd_dml::execute_inner,SELECT_LEX没有execute方法,直接调用join->exec(); unit->execute里会调用其子select的join->exec()。
/**
Execute a DML statement.
This is the default implementation for a DML statement and uses a
nested-loop join processor per outer-most query block.
The implementation is split in two: One for query expressions containing
a single query block and one for query expressions containing multiple
query blocks combined with UNION.
*/
bool Sql_cmd_dml::execute_inner(THD *thd) {
SELECT_LEX_UNIT *unit = lex->unit;
// optimize
if (unit->is_simple()) {
if (unit->set_limit(thd, unit->global_parameters()))
return true; /* purecov: inspected */
if (unit->first_select()->optimize(thd)) return true;
unit->set_optimized();
} else {
if (unit->optimize(thd)) return true;
}
// explain or execute
if (lex->is_explain()) {
if (explain_query(thd, unit)) return true; /* purecov: inspected */
} else {
if (unit->is_simple()) {
unit->first_select()->join->exec();
unit->set_executed();
if (thd->is_error()) return true;
} else {
if (unit->execute(thd)) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
2. union query
SELECT id from employees UNION SELECT manager_id from employees;
// in exec: SELECT id FROM (SELECT id from employees UNION SELECT manager_id from employees);
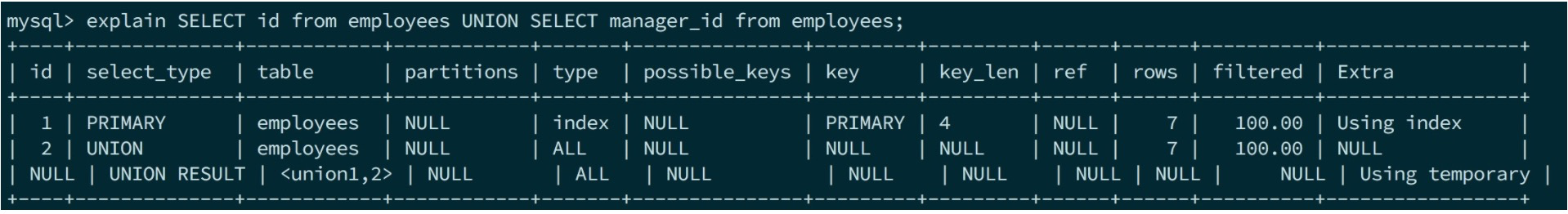
这一次进入上一节中的!unit->is_simple()的分支执行unit->prepare。但当两个子查询prepare完后,unit->prepare里会进入unit->prepare_fake_select_lex (fake_select_lex参考上面的成员变量说明) ,即实际执行时query会变成注释里的query,最外层的那个SELECT是mysql加上去的,称之为fake_select_lex。而fake_select_lex通常只是加个select从union临时表里取数,故不会有GROUP BY、WHERE、HAVING等问题。
execute阶段包括fake_select_lex的三个查询路径都是一样的:Sql_cmd_dml::execute_inner的!unit->is_simple()的分支。unit->optimize对真实的子节点 select和fake_select_lex是两套代码,但实际逻辑是一样的。
// three steps to optimize a select in SELECT_LEX_UNIT (including fake_select_lex)
thd->lex->set_current_select(select);
if (set_limit(thd, select)) DBUG_RETURN(true);
if (select->optimize(thd)) DBUG_RETURN(true);
3. subquery in WHERE clause
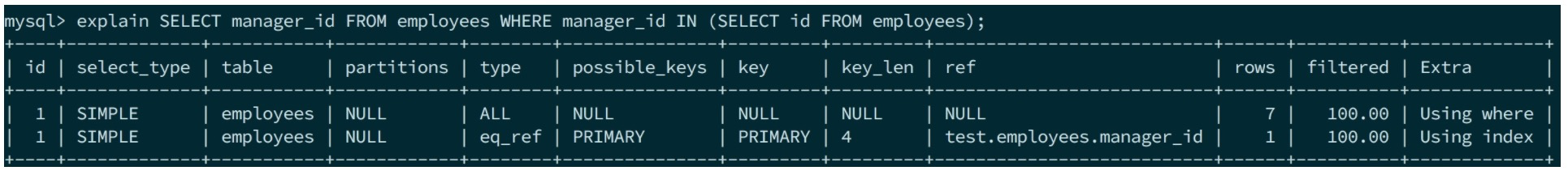
SELECT id FROM employees WHERE id IN (SELECT manager_id FROM employees);
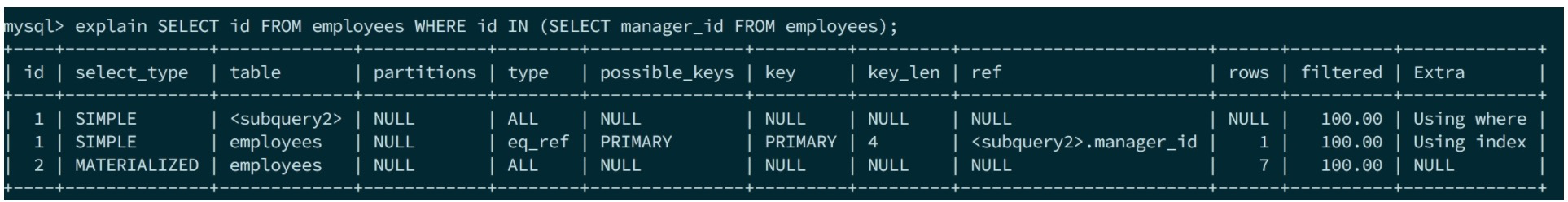
prepare阶段最外层select和上述介绍一致。subselect由于是处于WHERE中的,因此会转化成Item来表示,对应的对象是Item_subselect(Item_subselect下文会介绍细节)。因此WHERE中的subselect并不会在以上文与unit一起形成的hierachy structure存在,而是直接在parse直接传个subselect来自己管理。故subselect的prepare和execute都是受Item_subselect及其subselect_engine所调用。
题外话:
上面explain中的物化是因为manager_id没有索引,可以对比下面的explain output。因此IN在某些场景下会被优化成semi-join,因为和join的优化思路是一样的。
4. subquery in FROM clause
SELECT iid FROM (SELECT id + 10 AS iid, name FROM employees) t1;
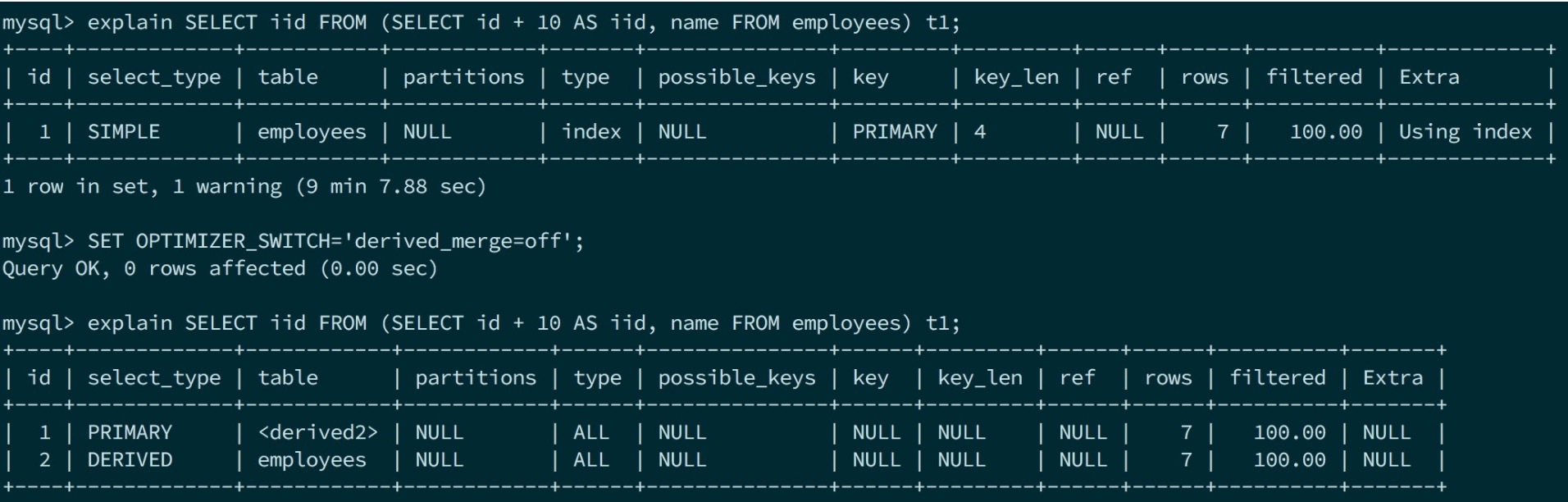
(默认会有一个提升到外层消除subquery derive table的优化)
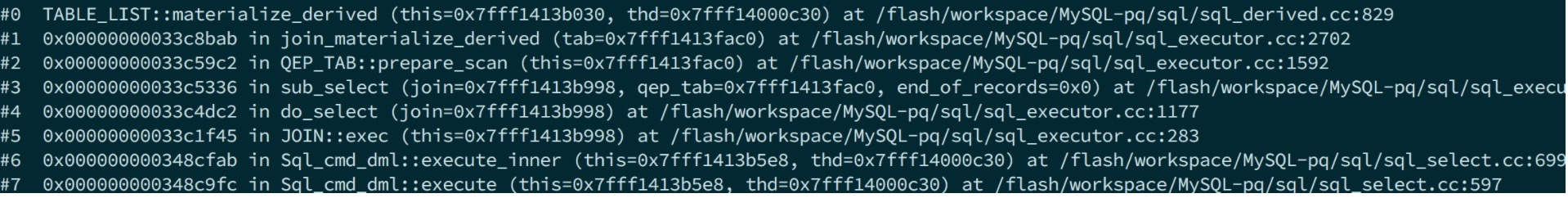
prepare阶段最外层select和上述介绍一致。这里的subselect会生成一个derived_table,所有的derived_table的subselect都会走如下图的调用链去prepare。

execute阶段最外层select和上述一致,执行到TABLE_LIST::materialize_derived的时候会直接调用相应的execute方法(和prepare类似,union的走unit->execute,否则直接join->exec)去生成derive table。
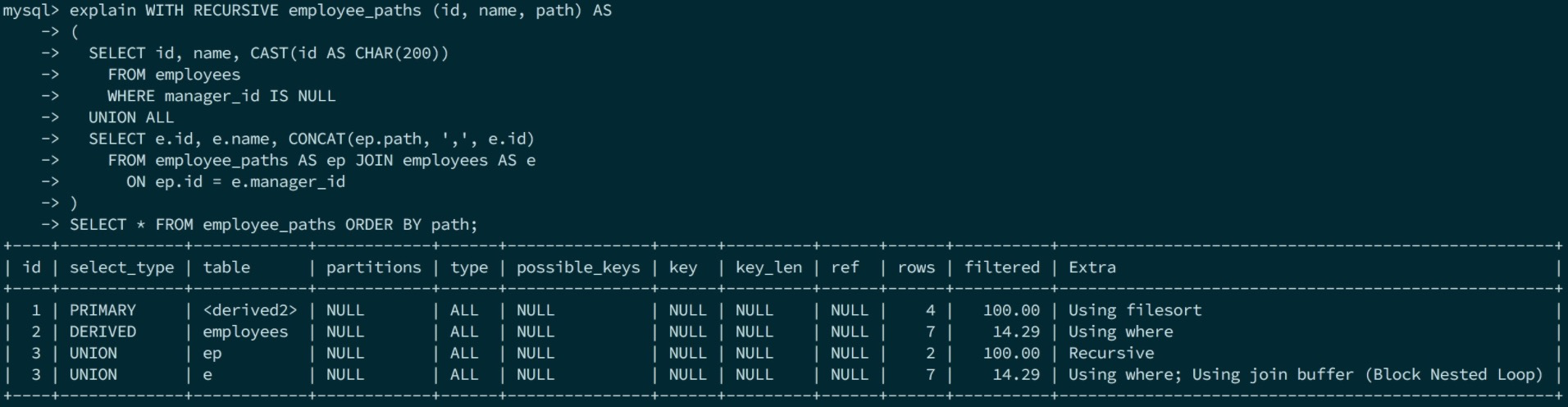
5. Recursive CTE
WITH RECURSIVE employee_paths (id, name, path) AS
(
SELECT id, name, CAST(id AS CHAR(200))
FROM employees
WHERE manager_id IS NULL
UNION ALL
SELECT e.id, e.name, CONCAT(ep.path, ',', e.id)
FROM employee_paths AS ep JOIN employees AS e
ON ep.id = e.manager_id
)
SELECT * FROM employee_paths ORDER BY path;
CTE介绍参见下文Common Table Expression小节。
prepare阶段最外层select和上述介绍一致。CTE会当成derive table去处理,因此和FROM subquery一样走TABLE_LIST::resolve_derived去调用SELECT_LEX::prepare。上面sql中共有三个会生成derived_table的sql,除了UNION的两个子查询外,第三个是union本身的查询。
execute阶段会在QEP_TAB::prepare_scan中预先生成物化的表(即CTE表),即explain中的step2,然后在exec里递归执行两个step3的UNION。
递归执行逻辑分散在sql_union.cc的Recursive_executor和 sql_executor.cc: sub_select的recursive判断中。对于示例sql A UNION B,recursive的发生在B中,执行顺序为先执行A结果写进临时表,执行B的时候employee_paths已经相当于有数据了。如此递归直至没有新的数据写入临时表(代码参见Recursive_executor::more_iterations()的if (row_count == new_row_count)判断)。
Item_subselect
子查询的执行入口在Item_subselect::val_int。
Item_subselect有如下继承关系的派生类:
-
Item_singlerow_subselect 。实际上应该叫Item_singlevalue_subselect,指返回值为一个常量的subselect。
-
Item_maxmin_subselect 。实际是服务于ALL/ANY的rewrite的。
-
/* If this is an ALL/ANY single-value subquery predicate, try to rewrite it with a MIN/MAX subquery. E.g. SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE b > ANY (SELECT a FROM t2) can be rewritten with SELECT * FROM t1 WHERE b > (SELECT MIN(a) FROM t2). A predicate may be transformed to use a MIN/MAX subquery if it: 1. has a greater than/less than comparison operator, and 2. is not correlated with the outer query, and 3. UNKNOWN results are treated as FALSE, or can never be generated, and */
-
-
Item_exists_subselect 。exists子查询的subselect,有可能会被如下方法处理:转换成semijoin、materialization、exists。
- Item_in_subselect 。in子查询的subselect。
- Item_allany_subselect 。ALL/ANY/SOME subselect.
- Item_in_subselect 。in子查询的subselect。
Item_subselect里会有个subselect_engine(简称engine),代表subselect的实际执行逻辑。subselect_engine有如下派生类:
- subselect_single_select_engine . 这里的single 指的是 single table,与union相对。exec的时候会直接执行JOIN的exec。
- subselect_union_engine . exec会调用SELECT_LEX_UNIT的exec,按顺序将UNION的每个select的JOIN都exec。
- subselect_indexquery_engine . 当IN subselect里的col是索引时可以使用索引查询。
- subselect_hash_sj_engine . Hash semi-join exec for IN predicate.
Item_subselect和subselect_engine的关系:相互都有对方的指针作为成员变量,但逻辑上是Item_subselect包含subselect_engine并负责其生命周期。
// Prepare phase:
Used inside Item_subselect::fix_fields() according to this scenario:
> Item_subselect::fix_fields {
> engine->prepare {
> query_block->prepare {
(Here we realize we need to do the rewrite and set
substitution= some new Item, eg. Item_in_optimizer )
}
}
*ref= substitution;
}
// Exec phase:
> Item_subselect::val_int {
> Item_subselect::exec() {
// 对于 Item_in_subselect,还会先计算left_expr的值。 (left_expr IN (subselect))
> SELECT_LEX_UNIT::optimize() { // iterate
> SELECT_LEX::optimize() {
JOIN::optimize();
}
}
> engine->exec() {
// subselect_single_select_engine
JOIN::exec();
// subselect_union engine
> SELECT_LEX_UNIT::exec() { // iterate
> SELECT_LEX::exec() {
JOIN::exec();
}
}
// subselect_indexquery_engine
query table by index by ha_index_read_map();
// subselect_hash_sj_engine
materialize_if_not_materialized(); // 内部是个 single_select_engine在做物化的exec
subselect_indexsubquery_engine::exec(); //对物化表进行索引读
}
}
}
// Cleanup phase
> Item_subselect::cleanup {
engine->cleanup();
}
Common Table Expression (CTE)
Ref: WITH syntax https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/8.0/en/with.html
CTE与subquery的不同是,CTE会提前物化成derive table,然后可以被多次或递归使用;subquery则是在遇到的时候才去做处理(可能是物化、消除、semi-join等),因此同样的subquery如果被多个地方调用,会有可能多次物化。CTE和view或临时表不同的是,CTE还是单个query下的概念,视图或临时表是可以跨query的。
CTE的表示类为table.h:Common_table_expr:
/**
After parsing, a Common Table Expression is accessed through a
TABLE_LIST. This class contains all information about the CTE which the
TABLE_LIST needs.
@note that before and during parsing, the CTE is described by a
PT_common_table_expr.
*/
class Common_table_expr {
public:
Common_table_expr(MEM_ROOT *mem_root)
: references(mem_root), recursive(false), tmp_tables(mem_root) {}
// 按照cte表的格式生成一个新的tmptable
TABLE *clone_tmp_table(THD *thd, TABLE_LIST *tl);
// clone tmp_tables[0]到sl->tl中,后面会用sl->tl->table来作为cte临时表的ref
bool substitute_recursive_reference(THD *thd, SELECT_LEX *sl);
/**
All references to this CTE in the statement, except those inside the
query expression defining this CTE.
In other words, all non-recursive references.
*/
// 即当前query 的cte部分ref的临时表(不包括正式表)
Mem_root_array<TABLE_LIST *> references;
/// True if it's a recursive CTE
bool recursive;
/**
List of all TABLE_LISTSs reading/writing to the tmp table created to
materialize this CTE. Due to shared materialization, only the first one
has a TABLE generated by create_tmp_table(); other ones have a TABLE
generated by open_table_from_share().
*/
// cte相关的tmptable对象的ref,同一个表可能由于recursive会产生多个shared ref
Mem_root_array<TABLE_LIST *> tmp_tables;
};
执行:
在TABLE_LIST::materialize_derived(THD *thd)函数中,会把CTE当成union select来去调用SELECT_LEX_UNIT->execute()去执行。SELECT_LEX_UNIT->execute里会调用Recursive_executor。
Recursive_executor initialize会打开从recursive_reference开始的所有tmp_table。 recursive_reference指的是第一个is_recursive的select (参见TABLE_LIST::resolve_derived),SELECT_LEX 数组的排列是non-recursive的在前,然后recursive的连续排在后。然后SELECT_LEX_UNIT->execute会按顺序执行对应SELECT_LEX->join->exec()。
执行和递归结束条件参见上面的Recursive CTE小节。
CTE其他相关代码:
-
SELECT_LEX_UNIT::prepare
-
// 如果是第一个引用CTE的select(query block),则将第一个select物化成临时表 if (sl == first_recursive) { // create_result_table() depends on current_select() save_select.restore(); /* All next query blocks will read the temporary table, which we must thus create now: */ if (derived_table->setup_materialized_derived_tmp_table(thd_arg)) goto err; /* purecov: inspected */ thd_arg->lex->set_current_select(sl); } // 如果是递归CTE,则将该SELECT_LEX涉及的cte子查询替换成clone出来的cte tmptable。 if (sl->recursive_reference) // Make tmp table known to query block: derived_table->common_table_expr()->substitute_recursive_reference( thd_arg, sl); -
sql_tmp_table.cc:create_ondisk_from_heap()
TABLE_LIST *const wtable_list = wtable->pos_in_table_list; Derived_refs_iterator ref_it(wtable_list); if (wtable_list) { Common_table_expr *cte = wtable_list->common_table_expr(); if (cte) { // 查找wtable在整个table数组中的位置 int i = 0, found = -1; TABLE *t; while ((t = ref_it.get_next())) { if (t == wtable) { found = i; break; } ++i; } DBUG_ASSERT(found >= 0); if (found > 0) // 为什么要把wtable放到最前面先处理呢? // 'wtable' is at position 'found', move it to 0 to convert it first std::swap(cte->tmp_tables[0], cte->tmp_tables[found]); ref_it.rewind(); } }