问题
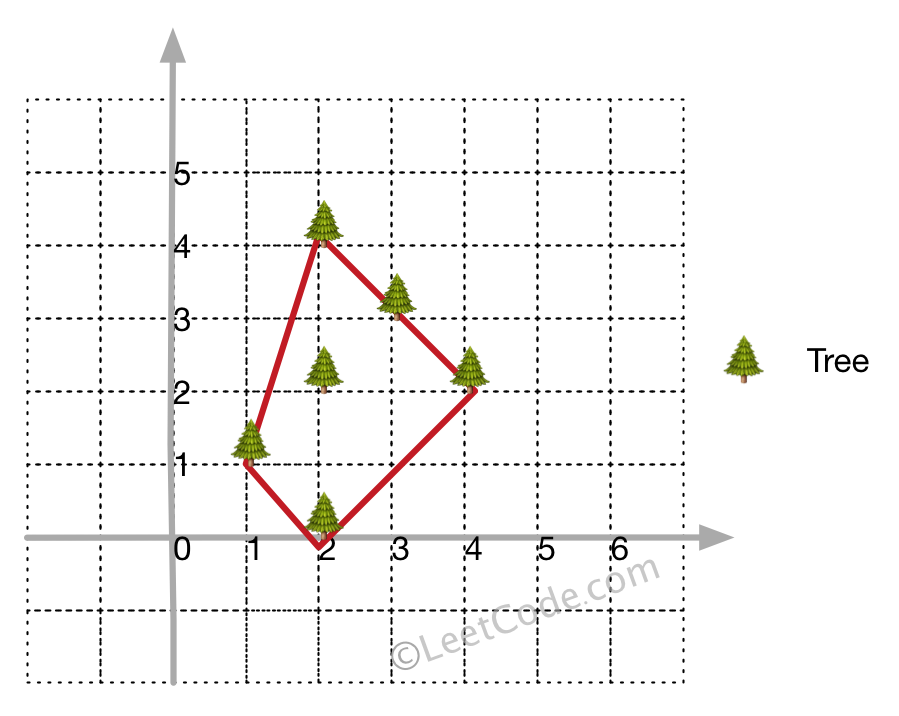
给定一群树的坐标点,画个围栏把所有树围起来(凸包)。
至少有一棵树,输入和输出没有顺序。
Input: [[1,1],[2,2],[2,0],[2,4],[3,3],[4,2]]
Output: [[1,1],[2,0],[4,2],[3,3],[2,4]]
思路和代码
1. 暴力法(超时)
对于任意两点连成的一条直线,如果其它所有点都在这条直线的一侧,则这两个点为解集中的两个点。
怎么判断点在直线的同一侧呢?
假设确定直线的两点为p1(x1, y1)和p2(x2, y2),方向从p1到p2,两点代入直线方程Ax+By+C=0,得到
A = y2 - y1;
B = x1 - x2;
C = x2 * y1 - x1 * y2.
将其它所有点p代入直线方程Ax + By + C,大于0说明在直线右侧,小于0说明在直线左侧,等于0说明在直线上。
时间复杂度O(n^3),空间复杂度O(n)
# Definition for a point.
# class Point(object):
# def __init__(self, a=0, b=0):
# self.x = a
# self.y = b
class Solution(object):
def outerTrees(self, points):
"""
:type points: List[Point]
:rtype: List[Point]
"""
n = len(points)
if n < 4:
return points
convex_index = [0] * n
for i in range(n):
for j in range(i + 1, n):
x1, y1 = points[i].x, points[i].y
x2, y2 = points[j].x, points[j].y
first = same_direct = True
first_direct = 0
for k in range(n):
if (k != i and k != j):
x3, y3 = points[k].x, points[k].y
direct = (y2 - y1) * x3 + (x1 - x2) * y3 + x2 * y1 - x1 * y2
if first and direct != 0:
first_direct = direct
first = False
if first == False and first_direct * direct < 0:
same_direct = False
break
if (same_direct):
convex_index[i] = convex_index[j] = 1
return [points[i] for i in range(n) if convex_index[i]]
2. 分治法
(1)横坐标最小和最大的点一定在解集中,记为P1和P2,直线P1P2把所有点分成了两部分,上包和下包。如下图所示(图源见参考资料)
(2)对上包,求距离直线P1P2最远的点,记为Pmax。
(3)点到直线的距离公式为(Ax+By+C) / 根号(A^2+B^2),如果是比较大小的话可以忽略分母直接计算分子,同时考虑直线方向是从左往后,Pmax在直线的左侧,距离求出来是负的,需要取一个负号。
(4)连接P1Pmax直线,以左侧为上包,执行上述操作
(5)连接PmaxP2直线,也以左侧为上包,执行上述操作。
(6)对下包也执行类似的操作。
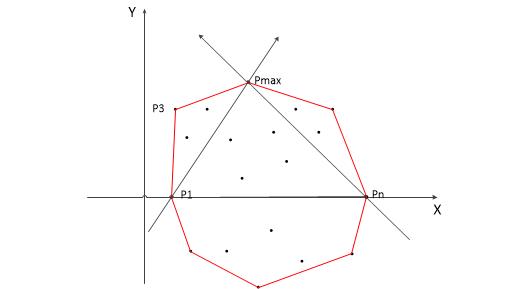
时间复杂度O(N*logN),空间复杂度O(N)
class Solution(object):
def outerTrees(self, points):
"""
:type points: List[Point]
:rtype: List[Point]
"""
n = len(points)
if n < 4:
return points
self.convex_index = [0] * n
points = sorted(points, key = lambda p: (p.x, p.y))
self.convex_index[0] = 1
self.convex_index[n-1] = 1
self.div(points, 0, n-1)
self.div(points, n-1, 0)
return [points[i] for i in range(n) if self.convex_index[i]]
def div(self, points, left, right):
if(left < right and right - left <= 1 or left > right and left - right <= 1):
return
x1, y1 = points[left].x, points[left].y
x2, y2 = points[right].x, points[right].y
max_distance = 0
max_index = -1
i = min(left, right)
i += 1
while True:
x3, y3 = points[i].x, points[i].y
distance = - ((y2 - y1) * x3 + (x1 - x2) * y3 + x2 * y1 - x1 * y2)
if distance >= max_distance:
max_distance = distance
max_index = i
i += 1
if( left < right and i == right or right < left and i == left):
break
if max_index != -1:
self.convex_index[max_index] = 1
self.div(points, left, max_index)
self.div(points, max_index, right)
3. Jarvis算法
(1)横坐标最小的点一定是凸包上的点,记为p,从p开始按逆时针方向找点,每次找最靠近外侧的点。
(2)先假设数组中的下一个点为点q,然后遍历剩余的点r,如果存在点r位于向量pq的右侧,则更新q(q=r),这样遍历完后就可以找到q。在暴力法中我们用直线方程的公式来判断点所处的位置,其实可以使用叉积的方式(相关解释见第5点),如果pq x qr的模小于0,说明pq转向qr(0到180度以内)是顺时针,r位于pq的右侧,此时把q更新为r(q = r)。
(3)然后更新p(p = q),继续第二步的操作,直到p等于(1)中的初始点(横坐标最小的点)。
(4)第二步中找到点q后,可能存在点r,位于向量pq中的某一点,这个时候点r也是凸包上的点,应该加上这样的点。
(5)叉积(外积,向量积)的模,以及叉积的计算公式,如下所示。
对于二维向量,(a_z, b_z)都为0,可以得到叉积模的计算方式为(a_x * b_y - a_y * b_x),这个值小于0则表示a转向b(转向角度在0到180度以内)的方向为顺时针。其实这个符号就是sin的符号,决定着叉积的方向,根据右手螺旋法则,四指为向量的旋转方向,大拇指为叉积的方向,四指逆时针时,大拇指方向为正,即sin符号为正。
时间复杂度O(nH),空间复杂度O(n),H表示凸包上的点的个数
class Solution(object):
def cross_product_norm(self, p, q, r):
return (q.x - p.x) * (r.y - q.y) - (q.y - p.y) * (r.x - q.x)
def between(self, p, q, r):
a = q.x >= p.x and q.x <= r.x or q.x >= r.x and q.x <= p.x
b = q.y >= p.y and q.y <= r.y or q.y >= r.y and q.y <= p.y
return a and b
def outerTrees(self, points):
"""
:type points: List[Point]
:rtype: List[Point]
"""
n = len(points)
if n < 4:
return points
left_most = 0
convex_index = [0] * n
for i in range(n):
if points[i].x < points[left_most].x:
left_most = i
p = left_most
while True:
q = (p+1)%n
for r in range(n):
if(self.cross_product_norm(points[p], points[q], points[r])<0):
q = r
for r in range(n):
if(r != p and r != q and self.cross_product_norm(points[p], points[q], points[r]) == 0 and self.between(points[p], points[r], points[q])):
convex_index[r] = 1
convex_index[q] = 1
p = q
if (p == left_most):
break
return [points[i] for i in range(n) if convex_index[i]]
4. Graham扫描法
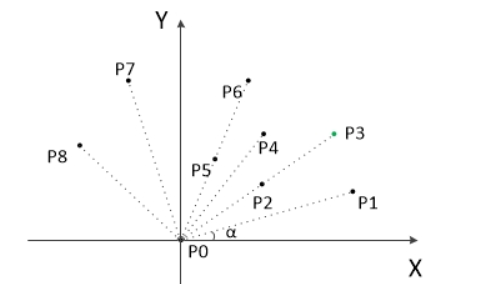
(1)纵坐标最小的点一定是凸包上的点,记为P0,以P0为原点,计算各个点相对于P0的幅角,从小到大排序,幅角相同时,距离近的排在前面。
(2)如下图所示(图源见参考资料),此时第一个点P1和最后一个点P8一定是凸包上的点。先将P0和P1放入栈中,然后以P2作为“当前点”开始扫描,重复以下的扫描策略,直到遇到P8时停止。
(3)扫描策略:连接栈顶的下一个点和栈顶的点构成向量(初始时连接的是P0和P1)。
如果“当前点”在向量的左边,把当前点压栈,然后“当前点”变成下一个点。
如果“当前点”在向量的右边,出栈栈顶元素。
(4)以下图所示,对算法举个例子。
连接P0和P1,发现P2在左侧,P2入栈。
连接P1和P2,发现P3在右侧,P2出栈。
连接P0和P1,发现P3在左侧,P3入栈。
连接P1和P3,发现P4在左侧,P4入栈。
连接P3和P4,发现P5在左侧,P5入栈。
连接P4和P5,发现P6在右侧,P5出栈。
连接P3和P4,发现P6在右侧,P4出栈。
连接P1和P3,发现P6在左侧,P6入栈。
连接P3和P6,发现P7在左侧,P7入栈。
连接P6和P7,发现P8在左侧,P8入栈。
遇到最后一个点P8,终止迭代。
(5)如果P0P8向量中间还有一个点,比如有个P75,那么这个P75会在P8之前被出栈,而这个点也是凸包上的点,所以要把最后一条射线上共线的那些点也加入凸包中。
时间复杂度O(N*logN),空间复杂度O(N)
class Solution(object):
def cross_product_norm(self, p, q, r):
return (q.x - p.x) * (r.y - q.y) - (q.y - p.y) * (r.x - q.x)
def cos_square(self, p0, p):
x_value = p.x - p0.x
y_value = p.y - p0.y
cos_value = x_value * x_value * 1.0 / (x_value * x_value + y_value * y_value)
if x_value < 0:
cos_value = - cos_value
return cos_value
def norm(self, p0, p):
x_value = p.x - p0.x
y_value = p.y - p0.y
return x_value * x_value + y_value * y_value
def outerTrees(self, points):
"""
:type points: List[Point]
:rtype: List[Point]
"""
n = len(points)
if n < 4:
return points
bottom_most = 0
for i in range(n):
if points[i].y < points[bottom_most].y:
bottom_most = i
p0 = points[bottom_most]
del points[bottom_most]
n -= 1
points.sort(key = lambda p: (- self.cos_square(p0, p), self.norm(p0, p)))
stack_points = []
stack_points.append(p0)
stack_points.append(points[0])
i = 1
while True:
if(self.cross_product_norm(stack_points[-2], stack_points[-1], points[i]) >= 0):
stack_points.append(points[i])
i += 1
else:
stack_points.pop()
if(i == n):
for j in range(n-1)[::-1]:
if(self.cross_product_norm(p0, points[n-1], points[j]) == 0):
stack_points.append(points[j])
else:
break
break
return stack_points