引入
1 在开发的过程中,我们经常遇到某些耗时很长的javascript操作,并且伴随着大量的异步。
2 比如我们有一个ajax的操作,这个ajax从发出请求到接收响应需要5秒,在这5秒内我们可以运行其他代码段,当响应到达后,我们需要判断响应的结果(无非就是成功或者失败),并根据不同的结果 添加回调函数。
3 为了有效的简洁的添加回调函数jQuery引入了Callbacks。
4 而为了方便的 根据不同的结果(或者根据各种跟结果有关的逻辑,比如不管是成功或者失败) 添加回调函数,jQuery引入了Deferred。
$.ajax("test.html")
.done(function(){ alert("success"); })
.fail(function(){ alert("error"); });
5 因而Deferred与Callbacks是密不可分的,事实上,Callbacks也是从Deferred中分离出去的
回顾Callbacks
1 Callbacks大体架构

2 Callbacks源码分析:
define([
"./core",
"./var/rnotwhite"
], function( jQuery, rnotwhite ) {
// String to Object options format cache
var optionsCache = {};
// Convert String-formatted options into Object-formatted ones and store in cache
/*
如果: var a = $.Callback('once memory')
则 optionsCache中会有这么一项:"once memory":{memory:true,once:true}
*/
function createOptions( options ) {
var object = optionsCache[ options ] = {};
jQuery.each( options.match( rnotwhite ) || [], function( _, flag ) {
object[ flag ] = true;
});
return object;
}
/*
* Create a callback list using the following parameters:
*
* options: an optional list of space-separated options that will change how
* the callback list behaves or a more traditional option object
*
* By default a callback list will act like an event callback list and can be
* "fired" multiple times.
*
* Possible options:
*
* once: will ensure the callback list can only be fired once (like a Deferred)
*
* memory: will keep track of previous values and will call any callback added
* after the list has been fired right away with the latest "memorized"
* values (like a Deferred)
*
* unique: will ensure a callback can only be added once (no duplicate in the list)
*
* stopOnFalse: interrupt callings when a callback returns false
*
*/
jQuery.Callbacks = function( options ) {
// Convert options from String-formatted to Object-formatted if needed
// (we check in cache first)
options = typeof options === "string" ?
( optionsCache[ options ] || createOptions( options ) ) :
jQuery.extend( {}, options );
var // Last fire value (for non-forgettable lists)
memory,
// Flag to know if list was already fired list是否已经被fire函数调用过
fired,
// Flag to know if list is currently firing 当前是否正在调用fire函数
firing,
// First callback to fire (used internally by add and fireWith) 第一个被执行的回调函数在list的位置
firingStart,
// End of the loop when firing fire函数要运行的回调函数的个数
firingLength,
// Index of currently firing callback (modified by remove if needed) 当前正在执行的回调函数的索引
firingIndex,
//回调函数数组
list = [],
// Stack of fire calls for repeatable lists 可重复的回调函数栈。我们可能会短时间内执行多次fire(),若当前的fire()正在迭代执行回调函数,而紧接着又执行了一次fire()时,会将下一次的fire()参数等保存至stack中,等待当前的fire()执行完成后,将stack中的fire()进行执行
stack = !options.once && [],
// Fire callbacks
fire = function( data ) {
// data[0] 是一个对象,data[1]则是回调函数的参数
memory = options.memory && data; // 很精妙,仔细体会一下这句代码,如果调用Calbacks时传入了memory,则memory = data,否则memory = false
fired = true; // 在调用本函数时,将fired状态进行修改
firingIndex = firingStart || 0;
firingStart = 0;
firingLength = list.length;
firing = true; // 迭代回调函数之前,将firing状态进行修改
for ( ; list && firingIndex < firingLength; firingIndex++ ) {
if ( list[ firingIndex ].apply( data[ 0 ], data[ 1 ] ) === false &&
options.stopOnFalse ) { // 运行回调函数的同时,检测回调函数是否返回false,若返回false,且调用Callbacks时传入stopOnFalse参数,则终止迭代
memory = false; // To prevent further calls using add 既然终止迭代了,那么之后添加的回调函数都不应该被调用,将memory设置为false
break;
}
}
firing = false; // 迭代回调函数完成后,将firing状态进行修改
if ( list ) {
if ( stack ) { // 没有使用once参数
if ( stack.length ) {
fire( stack.shift() );
}
} else if ( memory ) { // 使用了once memory参数,则在迭代完回调函数之后清空list
list = [];
} else { // 其他
self.disable();
}
}
},
// Actual Callbacks object
self = {
// 将一个新的回调函数添加至list
add: function() {
if ( list ) {
// First, we save the current length 首先,我们将当前的长度进行保存
var start = list.length;
(function add( args ) { // 自执行函数
jQuery.each( args, function( _, arg ) {
var type = jQuery.type( arg );
if ( type === "function" ) {
if ( !options.unique || !self.has( arg ) ) {
list.push( arg ); // 若参数中的元素为函数且(无unique参数或者list中没有该函数),则将该函数添加至list末尾
}
} else if ( arg && arg.length && type !== "string" ) { // arg的长度不为0且每项的类型不为字符串,也就是args为这种情况:[[fun1,fun2...],[fun3,fun4]](不仅限于这种情况)
// Inspect recursively
add( arg );
}
});
})( arguments );
// Do we need to add the callbacks to the
// current firing batch?
// 当Callback中的firingLength变为 动态的! 也就是:只要我们向list中添加了一个新的回调函数,即使在fire()运行过程中,改变也能立即体现出来
if ( firing ) {
firingLength = list.length;
// With memory, if we're not firing then
// we should call right away
} else if ( memory ) { // 如果当前没有执行回调函数,且存在memory参数,则执行新添加的回调函数
firingStart = start;
fire( memory );
}
}
return this;
},
// Remove a callback from the list 将一个回调函数从list中移除
remove: function() {
if ( list ) {
jQuery.each( arguments, function( _, arg ) {
var index;
while ( ( index = jQuery.inArray( arg, list, index ) ) > -1 ) {
list.splice( index, 1 );
// Handle firing indexes
if ( firing ) {
if ( index <= firingLength ) {
firingLength--;
}
if ( index <= firingIndex ) {
firingIndex--;
}
}
}
});
}
return this;
},
// Check if a given callback is in the list.
// If no argument is given, return whether or not list has callbacks attached.
has: function( fn ) {
return fn ? jQuery.inArray( fn, list ) > -1 : !!( list && list.length );
},
// Remove all callbacks from the list 清空数组
empty: function() {
list = [];
firingLength = 0;
return this;
},
// Have the list do nothing anymore 使用了这个方法,则意味着该回调对象失效了。
disable: function() {
list = stack = memory = undefined;
return this;
},
// Is it disabled?
disabled: function() {
return !list;
},
// Lock the list in its current state 给数组上锁
lock: function() {
stack = undefined;
if ( !memory ) {
self.disable();
}
return this;
},
// Is it locked?
locked: function() {
return !stack;
},
// Call all callbacks with the given context and arguments
// 使用传入的context作为当前函数的执行上下文
fireWith: function( context, args ) {
if ( list && ( !fired || stack ) ) {
args = args || [];
args = [ context, args.slice ? args.slice() : args ];
if ( firing ) {
stack.push( args ); // 如果当前正在迭代执行回调函数,则将新的fire参数推入stack中
} else {
fire( args );
}
}
return this;
},
// Call all the callbacks with the given arguments
fire: function() {
self.fireWith( this, arguments );
return this;
},
// To know if the callbacks have already been called at least once
// 用来确定当前callback对象是否被fire()过
fired: function() {
return !!fired;
}
};
return self;
};
return jQuery;
});
源码讲解
另外要注意下面两个参数:
once:如果创建Callbacks时加入该参数,则运行数组中的所有回调函数之后,也就是fire()之后,会清空数组。
memory:会保存上一次运行fire(args)时的参数args,每当添加一个新的回调函数到数组中,会立即使用args作为参数调用新加的函数一次
Deferred讲解:
Deferred大体架构:
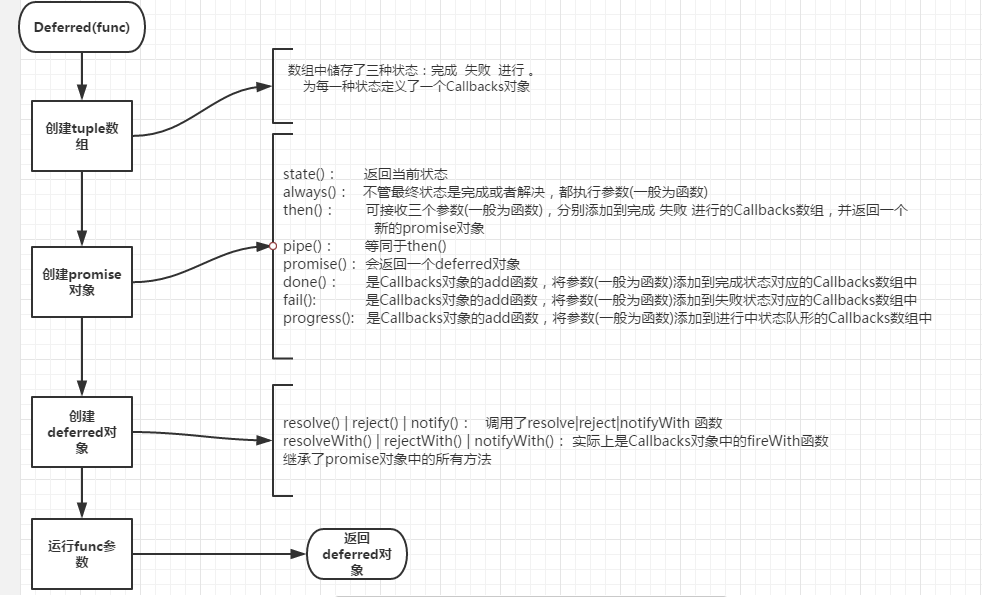
1 先来看一看tuple数组:
var tuples = [
// action, add listener, listener list, final state
[ "resolve", "done", jQuery.Callbacks("once memory"), "resolved" ],// 解决 操作成功 Callbacks对象 最终状态为解决
[ "reject", "fail", jQuery.Callbacks("once memory"), "rejected" ], // 拒绝 操作失败 Callbacks对象 最终状态为拒绝
[ "notify", "progress", jQuery.Callbacks("memory") ] // 通知 操作进行中 Callbacks对象 最终状态无(操作进行中的最终状态就是操作完成,完成无非就是转变为上面两种 成功或者失败)
]
jQuery的设计理念是这样的:
1 deferred对象有三种执行状态----完成 失败 进行中。
2 每种状态对应一个Callbacks实例
3 如果执行状态是"完成"(resolved),deferred对象立刻调用done()方法指定的回调函数(也就是执行已完成状态对应的Callbacks实例的fire方法);如果执行状态是"失败",调用fail()方法指定的回调函数;如果执行状态是"进行中",则继续等待,或者调用progress()方法指定的回调函数。
2 promise对象和deferred对象
一个是deferred外部接口对象,一个是内部promise对象。
promise对象是一个受限的对象, 这就是所谓的受限制的deferred对象,因为相比deferred对象, promise对象没有resolve(With), reject(With), notify(With)这些能改变deferred对象状态并且执行callbacklist的方法了,只能是then、done、fali等方法。
3 done fail progress 方法 与 resolve reject notify方法
在上图中我们已经说明了前三个方法就是Callbacks中的add方法。后三个调用了Callbacks中的fireWith()方法。
所以,我们可以总结出:
1 三种状态各对应一个Callbacks实例
2 使用done 或fail 或progress时,实际上就是往各自对应的Callbacks实例中的list数组添加回调函数
3 使用resolve 或reject 或notify时,则就是运行各自对应Callbacks实例中的list数组中的回调函数
4 then方法
then方法创建了一个新的promise对象,then就是pipe,我们可以想象是一个管道。管道就是能 ‘承上启下’(更贴切的来说,在Deferred中的then只做了承上,仅仅是个人观点)
var a = $.Deferred();
a.then(function(val){
console.log(val); // 2
return val * 2
}).then(function(val){
console.log(val); // 4
});
a.resolve(2)
如案例所示,下一个回调对象都能取到上一个回调对象的值,这样一直可以叠加往后传递。
关于then可能看了非常迷糊,不要紧,上面说的是then的高级特性,平时我们基本不怎么使用的。
平时我们大部分是使用then来代替done以及fail:
$.when($.ajax( "test.php" )) .then(successFunction, failureFunction );
deferred源码分析
define([
"./core",
"./var/slice",
"./callbacks"
], function( jQuery, slice ) {
jQuery.extend({
Deferred: function( func ) {
// 创建一个tuples数组,一个promise对象,一个deferred对象,一个state变量
var tuples = [
// action, add listener, listener list, final state
[ "resolve", "done", jQuery.Callbacks("once memory"), "resolved" ],// 解决 操作成功 Callbacks对象 最终状态为解决
[ "reject", "fail", jQuery.Callbacks("once memory"), "rejected" ], // 拒绝 操作失败 Callbacks对象 最终状态为拒绝
[ "notify", "progress", jQuery.Callbacks("memory") ] // 通知 操作进行中 Callbacks对象 最终状态无(操作进行中的最终状态就是操作完成,完成无非就是转变为上面两种 成功或者失败)
],
state = "pending",
promise = {
state: function() { // 返回当前状态
return state;
},
always: function() {
deferred.done( arguments ).fail( arguments );
return this;
},
then: function( /* fnDone, fnFail, fnProgress */ ) {
var fns = arguments;
return jQuery.Deferred(function( newDefer ) {
jQuery.each( tuples, function( i, tuple ) {
var fn = jQuery.isFunction( fns[ i ] ) && fns[ i ];
// deferred[ done | fail | progress ] for forwarding actions to newDefer
deferred[ tuple[1] ](function() { // 注意,这里的deferred指的不是新Deferred对象中的deferred(也就是不是指的newDefer)
var returned = fn && fn.apply( this, arguments );
// 若returned是一个deferred对象,则为returned添加一个回调函数,这个回调函数运行后使newDefer能够接收到returned的fire()参数
if ( returned && jQuery.isFunction( returned.promise ) ) {
returned.promise()
.done( newDefer.resolve )
.fail( newDefer.reject )
.progress( newDefer.notify );
} else {
newDefer[ tuple[ 0 ] + "With" ](
this === promise ? newDefer.promise() : this,
fn ? [ returned ] : arguments
);
}
});
});
fns = null;
}).promise();
},
// Get a promise for this deferred
// If obj is provided, the promise aspect is added to the object
promise: function( obj ) { // 若obj非null,则将obj与promise对象结合并返回,否则返回promise对象
return obj != null ? jQuery.extend( obj, promise ) : promise;
}
},
deferred = {};
// Keep pipe for back-compat 和之前的版本兼容
promise.pipe = promise.then;
// Add list-specific methods
jQuery.each( tuples, function( i, tuple ) {
var list = tuple[ 2 ], // 这是一个Callbacks 对象
stateString = tuple[ 3 ]; // 用字符串表示的状态
// promise[ done | fail | progress ] = list.add
promise[ tuple[1] ] = list.add; // Callbacks对象的add函数
// Handle state 处理状态
if ( stateString ) {
list.add(function() {
// state = [ resolved | rejected ]
state = stateString; // Callbacks对象中的回调函数列表第一项:改变状态
// [ reject_list | resolve_list ].disable; progress_list.lock
},
tuples[ i ^ 1 ][ 2 ].disable, // 因为reject,resolve是对立的,当行为为reject,那么resolve的Callbacks就无用了,将其回调函数列表清空即可
tuples[ 2 ][ 2 ].lock ); // 当行为为reject或者resolve时,即"结果已确定",那么就不允许再调用 "操作进行中" 的Callbacks对象的fire()了
}
// deferred[ resolve | reject | notify ]
deferred[ tuple[0] ] = function() {
deferred[ tuple[0] + "With" ]( this === deferred ? promise : this, arguments );
return this;
};
deferred[ tuple[0] + "With" ] = list.fireWith;
});
// Make the deferred a promise 将promise合并至deferred
promise.promise( deferred );
// Call given func if any 在初始化完deferred对象后,会立即运行func函数,并把deferred作为第一个参数传入
if ( func ) {
func.call( deferred, deferred );
}
// All done!
return deferred;
},
// Deferred helper
when: function( subordinate /* , ..., subordinateN */ ) {
/* 大体思路:
* 若参数(参数必需是deferred对象)只有一个,则返回这个参数的promise对象
* 若参数有多个,则生成一个新的deferred对象,并返回deferred对象的promise对象
* 当所有参数的状态为完成时,使新deferred对象的状态变为完成,
* 若有一个参数的状态为失败,则使新deferred对象的状态变为失败
*
* */
var i = 0,
resolveValues = slice.call( arguments ),//slice是数组的slice方法,一般情况下:resolveValues就是一个由deferred组成的数组
length = resolveValues.length,
// the count of uncompleted subordinates 没有运行完成的deferred对象的数量
// 如果length长度不为1或者subordinate是一个deferred对象则,remaining=length,否则remaining为0
remaining = length !== 1 ||
( subordinate && jQuery.isFunction( subordinate.promise ) ) ? length : 0,//运算符优先级: 逻辑与逻辑或 优先级高于 ? :
// the master Deferred.
// If resolveValues consist of only a single Deferred, just use that.
// 如果remaining为1,则使用subordinate(这是一个deferred对象)即可,否则创建一个新的deferred对象
deferred = remaining === 1 ? subordinate : jQuery.Deferred(),
// Update function for both resolve and progress values
updateFunc = function( i, contexts, values ) {
return function( value ) {
contexts[ i ] = this;
values[ i ] = arguments.length > 1 ? slice.call( arguments ) : value;
if ( values === progressValues ) {
deferred.notifyWith( contexts, values );
} else if ( !( --remaining ) ) {
deferred.resolveWith( contexts, values );
}
};
},
progressValues, progressContexts, resolveContexts;
// Add listeners to Deferred subordinates; treat others as resolved
if ( length > 1 ) {
progressValues = new Array( length );
progressContexts = new Array( length );
resolveContexts = new Array( length );
// 迭代resolveValues中的每一个deferred对象,为其添加不同状态下的回调函数
for ( ; i < length; i++ ) {
if ( resolveValues[ i ] && jQuery.isFunction( resolveValues[ i ].promise ) ) {
resolveValues[ i ].promise()
.done( updateFunc( i, resolveContexts, resolveValues ) )
.fail( deferred.reject )
.progress( updateFunc( i, progressContexts, progressValues ) );
} else {
--remaining;
}
}
}
// If we're not waiting on anything, resolve the master
if ( !remaining ) {
deferred.resolveWith( resolveContexts, resolveValues );
}
return deferred.promise();
}
});
return jQuery;
});
