线程是在进程中独立运行的子任务。
什么场景使用多线程技术?
1.阻塞。一旦系统中出现了阻塞现象,则可以根据实际情况来使用多线程技术提高运行效率。
2.依赖。业务分为两个执行过程,A和B,A业务发生阻塞时,B业务不需要A业务的执行结果,这时B业务可以使用多线程技术提高运行效率。
多线程是异步的。多线程随即执行,是因为CPU将时间片(时间片是CPU分配给各个程序的时间)分给不同的线程,线程获得时间片后才能执行任务。
CPU在不同的线程上进行切换是需要耗时的,所以并不是创建的线程越多,软件运行效率就越高,相反,线程过多反而会降低软件的执行效率。
实现多线程技术的两种方式: 1.继承Thread类,2.实现Running接口。
说明 :1.Thread 类实现了Running接口。 2.使用继承Thread类的方式创建新线程时,就不支持多继承了。
public class Thread implements Runnable
继承Thread类创建线程。
MyThread.java
package thread;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
System.out.println("运行了MyThread");
}
}
MyThreadRun.java
package thread;
public class MyThreadRun {
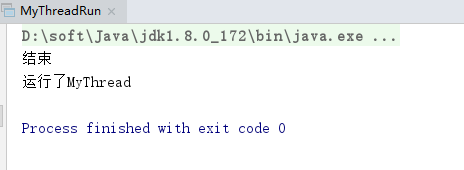
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();// 耗时大
System.out.println("结束");//耗时小
}
}
运行结果
实现Running接口创建线程。
MyRunning.java
package thread;
public class MyRunning implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("运行了MyRuning");
}
}
MyRunningRun.java
package thread;
public class MyRunningRun {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new MyRunning();
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
thread.start();
System.out.println("运行结束");
}
}
运行结果

共享数据 : 多个线程可以访问同一个变量。例如购票。
使用synchronized 关键字,使多个线程在执行run方法时,以排队的方式进行处理。
synchronized可以对任何对象及方法加锁,而加锁的这段代码称为“互斥区”或"临界区"。
synchronized关键字实现同步的原因是:使用了flag标记ACC_SYNCHRONIZED,当调用方法时,调用指令会检查方法的ACC_SYNCHRONIZED访问标志是否设置,如果设置了,执行线程会持有同步锁,然后执行方法,最后扎起方法完成时释放锁。
MyThread.java
package thread;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
private int count = 5; //总票数
@Override
synchronized public void run() {
super.run();
count--;
System.out.println("由 " + Thread.currentThread().getName() +" 售票, 现在剩余票count = " + count );
}
}
MyThreadRun.java
package thread;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
private int count = 5; //总票数
@Override
synchronized public void run() {
super.run();
count--;
System.out.println("由 " + Thread.currentThread().getName() +" 售票, 现在剩余票count = " + count );
}
}
运行结果 可以看到运行结果并不是按照ABCDE 进行执行的,说明执行start()的顺序不代表执行run()的顺序

非线程安全问题主要是指多个线程对同一个对象中的同一个实例变量进行操作时会出现值被更改、值不同步的情况。进而影响程序执行流程。
run() :立即执行run()方法。不启动新的线程。
start() :执行run()方法时间不定,启动新的线程。
异常法 停止线程
MyThread.java
package thread;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
super.run();
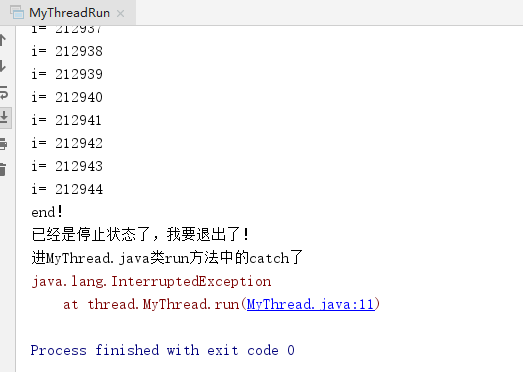
try {
for (int i=0;i<500000;i++) {
if(this.isInterrupted()) {
System.out.println("已经是停止状态了,我要退出了!");
throw new InterruptedException();
}
System.out.println("i= "+ i);
}
System.out.println("我在for下面");
}catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("进MyThread.java类run方法中的catch了");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
MyThreadRun.java
package thread;
public class MyThreadRun {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
MyThread thread = new MyThread();
thread.start();
Thread.sleep(2000); //当前正在执行的线程休眠2秒
thread.interrupt();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("mian catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end!");
}
}
运行结果
Java中有两种线程:一种是用户线程,也就是非守护线程;另一种是守护线程。
守护线程是一种特殊的线程,当进程中不需要非守护线程了,则守护线程自动销毁。典型的守护线程是垃圾回收线程。
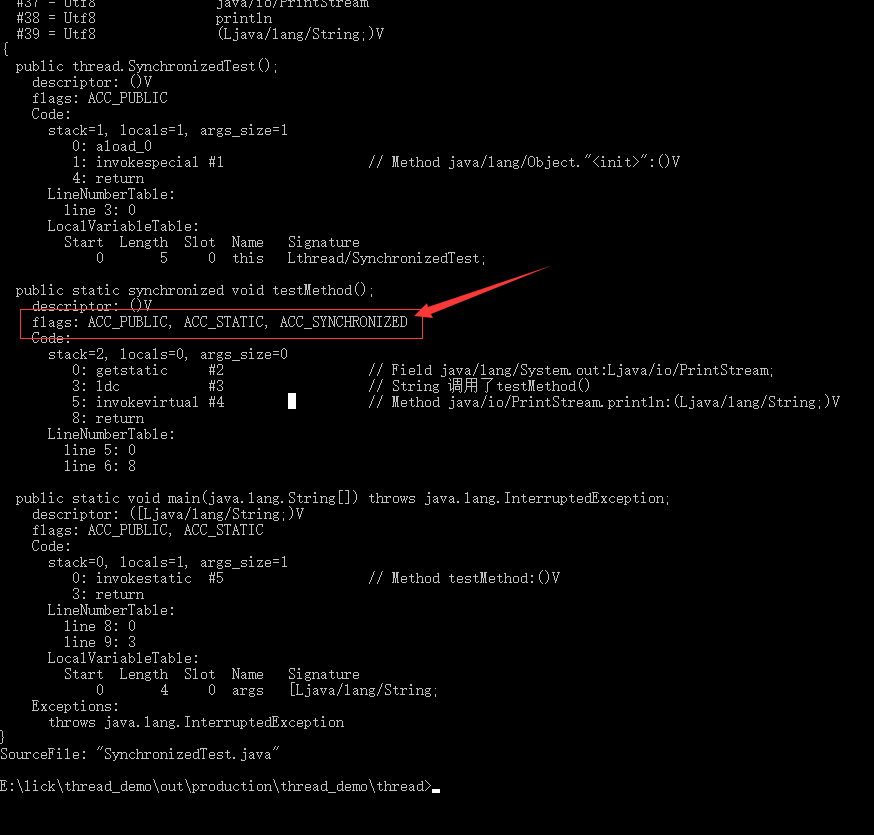
synchronized 关键字
SynchronizedTest.java
package thread;
public class SynchronizedTest {
synchronized public static void testMethod() {
System.out.println("调用了testMethod()");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
testMethod();
}
}
在cmd中使用javap命令将class文件转换成字节码指令,参数-v用户输出附属信息,参数-c用户对代码进行反汇编。
Microsoft Windows [版本 10.0.17134.345]
(c) 2018 Microsoft Corporation。保留所有权利。
E:lick hread_demooutproduction hread_demo hread>javap -c -v SynchronizedTest.class
Classfile /E:/lick/thread_demo/out/production/thread_demo/thread/SynchronizedTest.class
Last modified 2019-8-4; size 703 bytes
MD5 checksum 3a9258d31bf2b018c71c4d7c9cb1ecb0
Compiled from "SynchronizedTest.java"
public class thread.SynchronizedTest
minor version: 0
major version: 50
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_SUPER
Constant pool:
#1 = Methodref #7.#24 // java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
#2 = Fieldref #25.#26 // java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#3 = String #27 // 调用了testMethod()
#4 = Methodref #28.#29 // java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
#5 = Methodref #6.#30 // thread/SynchronizedTest.testMethod:()V
#6 = Class #31 // thread/SynchronizedTest
#7 = Class #32 // java/lang/Object
#8 = Utf8 <init>
#9 = Utf8 ()V
#10 = Utf8 Code
#11 = Utf8 LineNumberTable
#12 = Utf8 LocalVariableTable
#13 = Utf8 this
#14 = Utf8 Lthread/SynchronizedTest;
#15 = Utf8 testMethod
#16 = Utf8 main
#17 = Utf8 ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
#18 = Utf8 args
#19 = Utf8 [Ljava/lang/String;
#20 = Utf8 Exceptions
#21 = Class #33 // java/lang/InterruptedException
#22 = Utf8 SourceFile
#23 = Utf8 SynchronizedTest.java
#24 = NameAndType #8:#9 // "<init>":()V
#25 = Class #34 // java/lang/System
#26 = NameAndType #35:#36 // out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#27 = Utf8 调用了testMethod()
#28 = Class #37 // java/io/PrintStream
#29 = NameAndType #38:#39 // println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
#30 = NameAndType #15:#9 // testMethod:()V
#31 = Utf8 thread/SynchronizedTest
#32 = Utf8 java/lang/Object
#33 = Utf8 java/lang/InterruptedException
#34 = Utf8 java/lang/System
#35 = Utf8 out
#36 = Utf8 Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#37 = Utf8 java/io/PrintStream
#38 = Utf8 println
#39 = Utf8 (Ljava/lang/String;)V
{
public thread.SynchronizedTest();
descriptor: ()V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC
Code:
stack=1, locals=1, args_size=1
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
4: return
LineNumberTable:
line 3: 0
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 5 0 this Lthread/SynchronizedTest;
public static synchronized void testMethod();
descriptor: ()V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATIC, ACC_SYNCHRONIZED
Code:
stack=2, locals=0, args_size=0
0: getstatic #2 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
3: ldc #3 // String 调用了testMethod()
5: invokevirtual #4 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
8: return
LineNumberTable:
line 5: 0
line 6: 8
public static void main(java.lang.String[]) throws java.lang.InterruptedException;
descriptor: ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATIC
Code:
stack=0, locals=1, args_size=1
0: invokestatic #5 // Method testMethod:()V
3: return
LineNumberTable:
line 8: 0
line 9: 3
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 4 0 args [Ljava/lang/String;
Exceptions:
throws java.lang.InterruptedException
}
SourceFile: "SynchronizedTest.java"
E:lick hread_demooutproduction hread_demo hread>
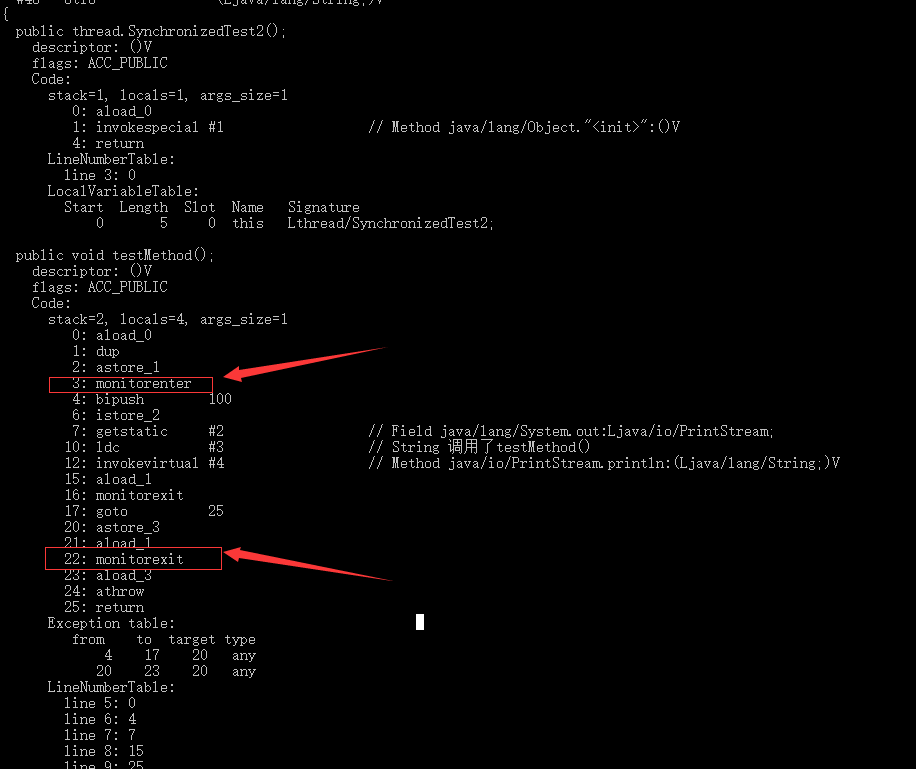
如果使用synchronized同步代码块,则使用monitorenter和monitorexit指令进行同步处理。
SynchronizedTest2 .java
package thread;
public class SynchronizedTest2 {
public void testMethod() {
synchronized (this) {
int age = 100;
System.out.println("调用了testMethod()");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
SynchronizedTest2 test = new SynchronizedTest2();
test.testMethod();
}
}
Microsoft Windows [版本 10.0.17134.345]
(c) 2018 Microsoft Corporation。保留所有权利。
E:lick hread_demooutproduction hread_demo hread>javap -c -v SynchronizedTest2.class
Classfile /E:/lick/thread_demo/out/production/thread_demo/thread/SynchronizedTest2.class
Last modified 2019-8-4; size 898 bytes
MD5 checksum fdab454b47c6b381b641631535b6a367
Compiled from "SynchronizedTest2.java"
public class thread.SynchronizedTest2
minor version: 0
major version: 50
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_SUPER
Constant pool:
#1 = Methodref #8.#32 // java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
#2 = Fieldref #33.#34 // java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#3 = String #35 // 调用了testMethod()
#4 = Methodref #36.#37 // java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
#5 = Class #38 // thread/SynchronizedTest2
#6 = Methodref #5.#32 // thread/SynchronizedTest2."<init>":()V
#7 = Methodref #5.#39 // thread/SynchronizedTest2.testMethod:()V
#8 = Class #40 // java/lang/Object
#9 = Utf8 <init>
#10 = Utf8 ()V
#11 = Utf8 Code
#12 = Utf8 LineNumberTable
#13 = Utf8 LocalVariableTable
#14 = Utf8 this
#15 = Utf8 Lthread/SynchronizedTest2;
#16 = Utf8 testMethod
#17 = Utf8 age
#18 = Utf8 I
#19 = Utf8 StackMapTable
#20 = Class #38 // thread/SynchronizedTest2
#21 = Class #40 // java/lang/Object
#22 = Class #41 // java/lang/Throwable
#23 = Utf8 main
#24 = Utf8 ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
#25 = Utf8 args
#26 = Utf8 [Ljava/lang/String;
#27 = Utf8 test
#28 = Utf8 Exceptions
#29 = Class #42 // java/lang/InterruptedException
#30 = Utf8 SourceFile
#31 = Utf8 SynchronizedTest2.java
#32 = NameAndType #9:#10 // "<init>":()V
#33 = Class #43 // java/lang/System
#34 = NameAndType #44:#45 // out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#35 = Utf8 调用了testMethod()
#36 = Class #46 // java/io/PrintStream
#37 = NameAndType #47:#48 // println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
#38 = Utf8 thread/SynchronizedTest2
#39 = NameAndType #16:#10 // testMethod:()V
#40 = Utf8 java/lang/Object
#41 = Utf8 java/lang/Throwable
#42 = Utf8 java/lang/InterruptedException
#43 = Utf8 java/lang/System
#44 = Utf8 out
#45 = Utf8 Ljava/io/PrintStream;
#46 = Utf8 java/io/PrintStream
#47 = Utf8 println
#48 = Utf8 (Ljava/lang/String;)V
{
public thread.SynchronizedTest2();
descriptor: ()V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC
Code:
stack=1, locals=1, args_size=1
0: aload_0
1: invokespecial #1 // Method java/lang/Object."<init>":()V
4: return
LineNumberTable:
line 3: 0
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 5 0 this Lthread/SynchronizedTest2;
public void testMethod();
descriptor: ()V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC
Code:
stack=2, locals=4, args_size=1
0: aload_0
1: dup
2: astore_1
3: monitorenter
4: bipush 100
6: istore_2
7: getstatic #2 // Field java/lang/System.out:Ljava/io/PrintStream;
10: ldc #3 // String 调用了testMethod()
12: invokevirtual #4 // Method java/io/PrintStream.println:(Ljava/lang/String;)V
15: aload_1
16: monitorexit
17: goto 25
20: astore_3
21: aload_1
22: monitorexit
23: aload_3
24: athrow
25: return
Exception table:
from to target type
4 17 20 any
20 23 20 any
LineNumberTable:
line 5: 0
line 6: 4
line 7: 7
line 8: 15
line 9: 25
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
7 8 2 age I
0 26 0 this Lthread/SynchronizedTest2;
StackMapTable: number_of_entries = 2
frame_type = 255 /* full_frame */
offset_delta = 20
locals = [ class thread/SynchronizedTest2, class java/lang/Object ]
stack = [ class java/lang/Throwable ]
frame_type = 250 /* chop */
offset_delta = 4
public static void main(java.lang.String[]) throws java.lang.InterruptedException;
descriptor: ([Ljava/lang/String;)V
flags: ACC_PUBLIC, ACC_STATIC
Code:
stack=2, locals=2, args_size=1
0: new #5 // class thread/SynchronizedTest2
3: dup
4: invokespecial #6 // Method "<init>":()V
7: astore_1
8: aload_1
9: invokevirtual #7 // Method testMethod:()V
12: return
LineNumberTable:
line 11: 0
line 12: 8
line 13: 12
LocalVariableTable:
Start Length Slot Name Signature
0 13 0 args [Ljava/lang/String;
8 5 1 test Lthread/SynchronizedTest2;
Exceptions:
throws java.lang.InterruptedException
}
SourceFile: "SynchronizedTest2.java"
E:lick hread_demooutproduction hread_demo hread>
线程出现异常,会释放所有持有的锁。注意:类Thread.java中的suspend()和sleep(mills)方法被调用后并不释放锁。
volatile关键字,具有三个特性:
1.可见性: B线程能立马看到A线程更改的数据。
2.原子性:
3.禁止代码重排序。
synchronized关键字的三个特征:
1.可见性:synchronized关键字具有可见性。
2.原子性:使用synchronized实现了同步,同步实现了原子性,保证被同步的代码段在同一时间段只有一个线程在执行。
3.禁止代码重排序。
关键字synchronized和关键字volatile的使用场景总结:
1、当想实现一个变量的值被更改时,让其他线程能取得最新的值时,就要对变量使用volatile.
2、当多个线程对同一对象的同一实例变量进行操作时,为了避免出现非线程安全问题,就要使用synchronized.