1.面向对象的标准库
2.多种IO标准库工具
- istream,提供输入操作
- ostream,提供输出操作
- cin:读入标准输入的istream对象.全局对象extern std::istream cin;定义于头文件
<iostream> - cout:写到标准输出的ostream对象
- cerr:输出标准错误的ostream对象。常用语程序错误信息
- >>,用于从istream对象中读入输入.从左到右
- <<,用于把输出写到ostream对象中
- getline,功能是从istream对象读取一个单词,然后写入string对象中
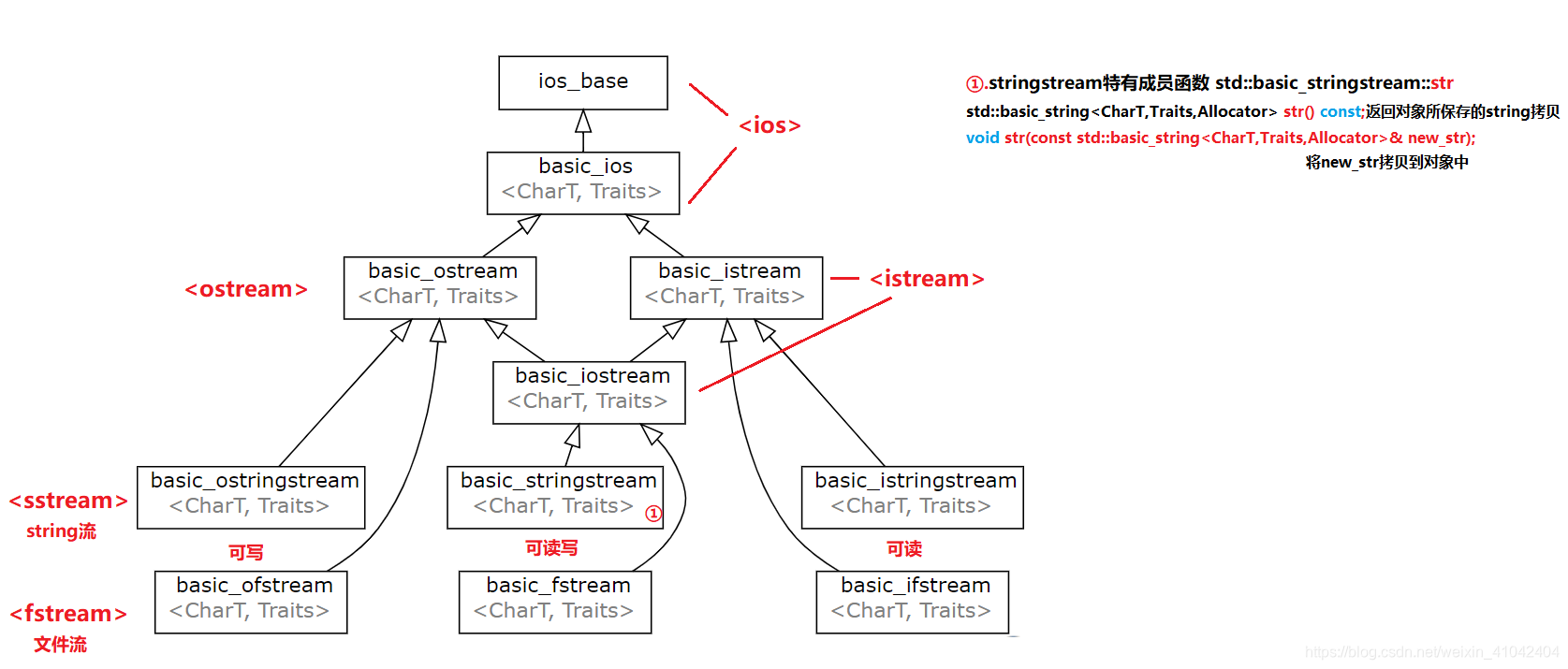
3.IO类之间的关系

4.IO对象不可复制或赋值
流对象不能存储在vector或其他容器中。
形参或返回类型也不能为流类型,如果需要,则必须传递或返回指向该对象的指针或引用,而且不能是const引用,因为读写一个IO对象会改变其状态。
5.IO库的条件状态
流的状态由bad,fail,eof,good操作揭示。
标志
- iostate:机器相关的类型,表达条件状态。
- badbit:系统级的故障
- failbit:可恢复的错误,比如 把字符输入到数值变量中。
- eofbit:遇到文件结束符,fail也置位
- goodbit:流未处于错误状态,保证为0.
函数(s表示流
- s.bad(): 若badbit置位,返回true
- s.fail(): 若failbit置位,返回true
- s.eof(): 若eofbit置位,返回true
- s.good(): 若goodbit置位,返回true
- s.clear():流的所有条件状态位复位,将流的状态设为有效,void
- s.clear(flag):指定位复位,void
- s.setstate(flag):指定位 置位,void
- s.rdstate(): 返回当前流的条件状态,s.iostate
《cpp primer》p280 :只有当一个流处于无错状态时,才能从他读写数据。在使用流之前,应该检查它的状态,通常用while循环来检查。>>表达式返回的是流的状态。
使用good()和fail()是检查流总体状态的正确方法。将流当作条件的代码等价:!fail();
if(cin)
//ok to use cin, it is in a valid state
while(cin >> word)
//ok:read operation successful…6.string流 <sstream>
公开成员函数 std::basic_stringstream::str
|
std::basic_string<CharT,Traits,Allocator> str() const; |
(1) | |
|
void str(const std::basic_string<CharT,Traits,Allocator>& new_str); |
(2) |
#include <sstream>
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int n;
std::istringstream in; // 亦可使用 in("1 2")
in.str("1 2");
in >> n;
std::cout << "after reading the first int from "1 2", the int is "
<< n << ", str() = "" << in.str() << ""
";
std::ostringstream out("1 2");
out << 3;
std::cout << "after writing the int '3' to output stream "1 2""
<< ", str() = "" << out.str() << ""
";
std::ostringstream ate("1 2", std::ios_base::ate);
ate << 3;
std::cout << "after writing the int '3' to append stream "1 2""
<< ", str() = "" << ate.str() << ""
";
}after reading the first int from "1 2", the int is 1, str() = "1 2" after writing the int '3' to output stream "1 2", str() = "3 2" after writing the int '3' to append stream "1 2", str() = "1 23"

读取输入流的个人信息
struct PersonInfo
{
/* data */
string name;
vector<string> phones;
};
string line,word;
vector<PersonInfo> people;
while(getline(cin,line)){
PersonInfo info;
istringstream record(line);//line拷贝到record中
record >>info.name;
while(record>>word)
info.phones.push_back(word);
people.push_back(info);
/* code */
}