Classify structured data using Keras Preprocessing Layers
对于既有数值特征,又有类别特征的输入情况,使用 keras的预处理层进行转换。
https://colab.research.google.com/github/tensorflow/docs/blob/master/site/en/tutorials/structured_data/preprocessing_layers.ipynb?hl=ar-bh#scrollTo=sMYQvJuBi7MS
This tutorial demonstrates how to classify structured data (e.g. tabular data in a CSV). You will use Keras to define the model, and preprocessing layers as a bridge to map from columns in a CSV to features used to train the model. This tutorial contains complete code to:
Note: This tutorial is similar to Classify structured data with feature columns. This version uses new experimental Keras Preprocessing Layers instead of
tf.feature_column. Keras Preprocessing Layers are more intuitive, and can be easily included inside your model to simplify deployment.
处理效果
数值型 , 定义输入, 进行正规化变换。
类别性, 转换为整数, 对整数进行类别编码, one-hot-code
CategoryEncoding
https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/experimental/preprocessing/CategoryEncoding
This layer provides options for condensing data into a categorical encoding. It accepts integer values as inputs and outputs a dense representation (one sample = 1-index tensor of float values representing data about the sample's tokens) of those inputs.
类别编码对应的CODE
index -- 字符查询表, 根据字符,查到index
encoder-- 根据index查询到的index,生成one-hot码
def get_category_encoding_layer(name, dataset, dtype, max_tokens=None): # Create a StringLookup layer which will turn strings into integer indices if dtype == 'string': index = preprocessing.StringLookup(max_tokens=max_tokens) else: index = preprocessing.IntegerLookup(max_values=max_tokens) # Prepare a Dataset that only yields our feature feature_ds = dataset.map(lambda x, y: x[name]) # Learn the set of possible values and assign them a fixed integer index. index.adapt(feature_ds) # Create a Discretization for our integer indices. encoder = preprocessing.CategoryEncoding(max_tokens=index.vocab_size()) # Apply one-hot encoding to our indices. The lambda function captures the # layer so we can use them, or include them in the functional model later. return lambda feature: encoder(index(feature))
测试输出
type_col = train_features['Type'] layer = get_category_encoding_layer('Type', train_ds, 'string') layer(type_col)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(5, 4), dtype=float32, numpy=
array([[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 1., 0.],
[0., 0., 0., 1.]], dtype=float32)>
数值型处理
生成一个正则转换器。
def get_normalization_layer(name, dataset): # Create a Normalization layer for our feature. normalizer = preprocessing.Normalization() # Prepare a Dataset that only yields our feature. feature_ds = dataset.map(lambda x, y: x[name]) # Learn the statistics of the data. normalizer.adapt(feature_ds) return normalizer
例子,将对应特征,做正规化处理。
photo_count_col = train_features['PhotoAmt'] layer = get_normalization_layer('PhotoAmt', train_ds) layer(photo_count_col)
<tf.Tensor: shape=(5, 1), dtype=float32, numpy= array([[ 1.3705449 ], [ 0.74395925], [-0.19591942], [-0.8225052 ], [-0.8225052 ]], dtype=float32)>
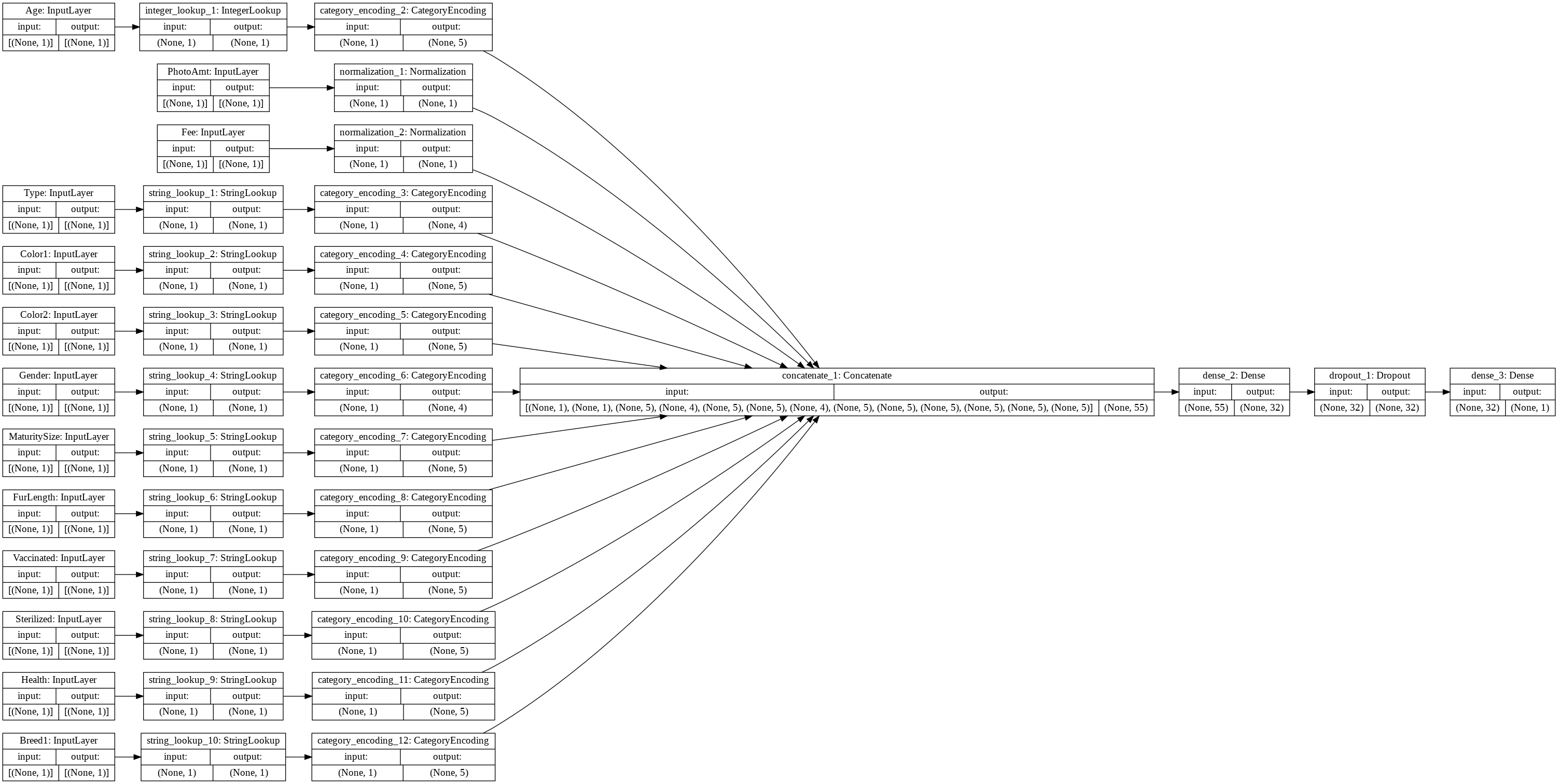
预处理管线定义
all_input 存储 所有的输入层单元
encoded_features 存储 所有的输入层单元, 经过预处理管线后的 逻辑单元, 例如 正规化对象, 和 ONE-HOT 编码对象。
all_inputs = [] encoded_features = [] # Numeric features. for header in ['PhotoAmt', 'Fee']: numeric_col = tf.keras.Input(shape=(1,), name=header) normalization_layer = get_normalization_layer(header, train_ds) encoded_numeric_col = normalization_layer(numeric_col) all_inputs.append(numeric_col) encoded_features.append(encoded_numeric_col) # Categorical features encoded as string. categorical_cols = ['Type', 'Color1', 'Color2', 'Gender', 'MaturitySize', 'FurLength', 'Vaccinated', 'Sterilized', 'Health', 'Breed1'] for header in categorical_cols: categorical_col = tf.keras.Input(shape=(1,), name=header, dtype='string') encoding_layer = get_category_encoding_layer(header, train_ds, dtype='string', max_tokens=5) encoded_categorical_col = encoding_layer(categorical_col) all_inputs.append(categorical_col) encoded_features.append(encoded_categorical_col)
使用 concatenate 接口,将所有的 编码特征, 连接起来。
构成统一的特征向量输出。
然后,将统一的特征向量输出, 连接到 第一层稠密层单元, 然后连接到第二层稠密层单元。
第二层稠密层单元,就是作为模型输出。
tf.keras.Model 模型的一个参数,是对所有输入输出的 规约;
第二个参数,是经过一些列预处理和模型本身的管线输出, 模型输出的规约。
all_features = tf.keras.layers.concatenate(encoded_features)
x = tf.keras.layers.Dense(32, activation="relu")(all_features) x = tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5)(x) output = tf.keras.layers.Dense(1)(x)
model = tf.keras.Model(all_inputs, output)
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss=tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True), metrics=["accuracy"])
tf.keras.layers.concatenate
https://www.tensorflow.org/api_docs/python/tf/keras/layers/concatenate
tensor
https://www.tensorflow.org/guide/tensor
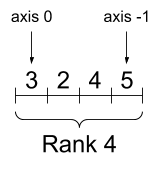
print("Type of every element:", rank_4_tensor.dtype)
print("Number of axes:", rank_4_tensor.ndim)
print("Shape of tensor:", rank_4_tensor.shape)
print("Elements along axis 0 of tensor:", rank_4_tensor.shape[0])
print("Elements along the last axis of tensor:", rank_4_tensor.shape[-1])
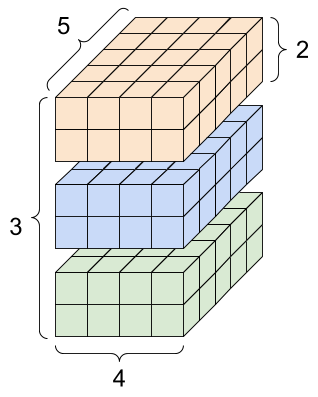
print("Total number of elements (3*2*4*5): ", tf.size(rank_4_tensor).numpy())Type of every element: <dtype: 'float32'> Number of axes: 4 Shape of tensor: (3, 2, 4, 5) Elements along axis 0 of tensor: 3 Elements along the last axis of tensor: 5 Total number of elements (3*2*4*5): 120
A rank-4 tensor, shape: [3, 2, 4, 5]