一、Mybatis环境搭建及简单实例
pom.xml
mybatis-config.xml
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> 2 <!DOCTYPE configuration 3 PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN" 4 "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd"> 5 <configuration> 6 7 <!-- 指定properties配置文件, 我这里面配置的是数据库相关 --> 8 <properties resource="dbConfig.properties"></properties> 9 10 <environments default="development"> 11 <environment id="development"> 12 <transactionManager type="JDBC"/> 13 <dataSource type="POOLED"> 14 <!-- 15 如果上面没有指定数据库配置的properties文件,那么此处可以这样直接配置 16 <property name="driver" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"/> 17 <property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test1"/> 18 <property name="username" value="root"/> 19 <property name="password" value="root"/> 20 --> 21 22 <!-- 上面指定了数据库配置文件, 配置文件里面也是对应的这四个属性 --> 23 <property name="driver" value="${driver}"/> 24 <property name="url" value="${url}"/> 25 <property name="username" value="${username}"/> 26 <property name="password" value="${password}"/> 27 28 </dataSource> 29 </environment> 30 </environments> 31 32 <!-- 映射文件,mybatis精髓, 后面才会细讲 --> 33 <mappers> 34 <mapper resource="com/dy/dao/userDao-mapping.xml"/> 35 </mappers> 36 37 </configuration>
1. configuration节点为根节点。
2. 在configuration节点之下,我们可以配置10个子节点, 分别为:properties、typeAliases、plugins、objectFactory、objectWrapperFactory、settings、environments、databaseIdProvider、typeHandlers、mappers。
实体类——User
properties的使用方法
envirements元素节点的使用方法
environments元素节点可以配置多个environment子节点, 怎么理解呢?
假如我们系统的开发环境和正式环境所用的数据库不一样(这是肯定的), 那么可以设置两个environment, 两个id分别对应开发环境(dev)和正式环境(final),那么通过配置environments的default属性就能选择对应的environment了, 例如,我将environments的deault属性的值配置为dev, 那么就会选择dev的environment。
typeAliases
typeHandler
Mybatis中的TypeHandler是什么?
无论是 MyBatis 在预处理语句(PreparedStatement)中设置一个参数时,还是从结果集中取出一个值时,都会用类型处理器将获取的值以合适的方式转换成 Java 类型。Mybatis默认为我们实现了许多TypeHandler, 当我们没有配置指定TypeHandler时,Mybatis会根据参数或者返回结果的不同,默认为我们选择合适的TypeHandler处理。
配置typeHandler
1 <configuration> 2 <typeHandlers> 3 <!-- 4 当配置package的时候,mybatis会去配置的package扫描TypeHandler 5 <package name="com.dy.demo"/> 6 --> 7 8 <!-- handler属性直接配置我们要指定的TypeHandler --> 9 <typeHandler handler=""/> 10 11 <!-- javaType 配置java类型,例如String, 如果配上javaType, 那么指定的typeHandler就只作用于指定的类型 --> 12 <typeHandler javaType="" handler=""/> 13 14 <!-- jdbcType 配置数据库基本数据类型,例如varchar, 如果配上jdbcType, 那么指定的typeHandler就只作用于指定的类型 --> 15 <typeHandler jdbcType="" handler=""/> 16 17 <!-- 也可两者都配置 --> 18 <typeHandler javaType="" jdbcType="" handler=""/> 19 20 </typeHandlers> 21 22 ...... 23 24 </configuration>
objectFactory是干什么的? 需要配置吗?
MyBatis 每次创建结果对象的新实例时,它都会使用一个对象工厂(ObjectFactory)实例来完成。默认的对象工厂需要做的仅仅是实例化目标类,要么通过默认构造方法,要么在参数映射存在的时候通过参数构造方法来实例化。默认情况下,我们不需要配置,mybatis会调用默认实现的objectFactory。 除非我们要自定义ObjectFactory的实现, 那么我们才需要去手动配置。
plugin有何作用? 需要配置吗?
plugins 是一个可选配置。mybatis中的plugin其实就是个interceptor, 它可以拦截Executor 、ParameterHandler 、ResultSetHandler 、StatementHandler 的部分方法,处理我们自己的逻辑。Executor就是真正执行sql语句的东西, ParameterHandler 是处理我们传入参数的,还记得前面讲TypeHandler的时候提到过,mybatis默认帮我们实现了不少的typeHandler, 当我们不显示配置typeHandler的时候,mybatis会根据参数类型自动选择合适的typeHandler执行,其实就是ParameterHandler 在选择。ResultSetHandler 就是处理返回结果的。
mappers作用 ? 需要配置吗?
mappers 节点下,配置我们的mapper映射文件, 所谓的mapper映射文件,就是让mybatis 用来建立数据表和javabean映射的一个桥梁。在我们实际开发中,通常一个mapper文件对应一个dao接口, 这个mapper可以看做是dao的实现。所以,mappers必须配置。
mapper映射文件配置之insert、update、delete
1 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> 2 <!DOCTYPE mapper 3 PUBLIC "-//ibatis.apache.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" 4 "http://ibatis.apache.org/dtd/ibatis-3-mapper.dtd"> 5 6 <!-- mapper 为根元素节点, 一个namespace对应一个dao --> 7 <mapper namespace="com.dy.dao.UserDao"> 8 9 <insert 10 <!-- 1. id (必须配置) 11 id是命名空间中的唯一标识符,可被用来代表这条语句。 12 一个命名空间(namespace) 对应一个dao接口, 13 这个id也应该对应dao里面的某个方法(相当于方法的实现),因此id 应该与方法名一致 --> 14 15 id="insertUser" 16 17 <!-- 2. parameterType (可选配置, 默认为mybatis自动选择处理) 18 将要传入语句的参数的完全限定类名或别名, 如果不配置,mybatis会通过ParameterHandler 根据参数类型默认选择合适的typeHandler进行处理 19 parameterType 主要指定参数类型,可以是int, short, long, string等类型,也可以是复杂类型(如对象) --> 20 21 parameterType="com.demo.User" 22 23 <!-- 3. flushCache (可选配置,默认配置为true) 24 将其设置为 true,任何时候只要语句被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存都会被清空,默认值:true(对应插入、更新和删除语句) --> 25 26 flushCache="true" 27 28 <!-- 4. statementType (可选配置,默认配置为PREPARED) 29 STATEMENT,PREPARED 或 CALLABLE 的一个。这会让 MyBatis 分别使用 Statement,PreparedStatement 或 CallableStatement,默认值:PREPARED。 --> 30 31 statementType="PREPARED" 32 33 <!-- 5. keyProperty (可选配置, 默认为unset) 34 (仅对 insert 和 update 有用)唯一标记一个属性,MyBatis 会通过 getGeneratedKeys 的返回值或者通过 insert 语句的 selectKey 子元素设置它的键值,默认:unset。如果希望得到多个生成的列,也可以是逗号分隔的属性名称列表。 --> 35 36 keyProperty="" 37 38 <!-- 6. keyColumn (可选配置) 39 (仅对 insert 和 update 有用)通过生成的键值设置表中的列名,这个设置仅在某些数据库(像 PostgreSQL)是必须的,当主键列不是表中的第一列的时候需要设置。如果希望得到多个生成的列,也可以是逗号分隔的属性名称列表。 --> 40 41 keyColumn="" 42 43 <!-- 7. useGeneratedKeys (可选配置, 默认为false) 44 (仅对 insert 和 update 有用)这会令 MyBatis 使用 JDBC 的 getGeneratedKeys 方法来取出由数据库内部生成的主键(比如:像 MySQL 和 SQL Server 这样的关系数据库管理系统的自动递增字段),默认值:false。 --> 45 46 useGeneratedKeys="false" 47 48 <!-- 8. timeout (可选配置, 默认为unset, 依赖驱动) 49 这个设置是在抛出异常之前,驱动程序等待数据库返回请求结果的秒数。默认值为 unset(依赖驱动)。 --> 50 timeout="20"> 51 52 <update 53 id="updateUser" 54 parameterType="com.demo.User" 55 flushCache="true" 56 statementType="PREPARED" 57 timeout="20"> 58 59 <delete 60 id="deleteUser" 61 parameterType="com.demo.User" 62 flushCache="true" 63 statementType="PREPARED" 64 timeout="20"> 65 </mapper>
如果我们在使用mysql的时候,想在数据插入后返回插入的id, 我们也可以使用 selectKey 这个元素:
1 <!-- 对应userDao中的insertUser方法, --> 2 <insert id="insertUser" parameterType="com.dy.entity.User"> 3 <!-- oracle等不支持id自增长的,可根据其id生成策略,先获取id 4 5 <selectKey resultType="int" order="BEFORE" keyProperty="id"> 6 select seq_user_id.nextval as id from dual 7 </selectKey> 8 9 --> 10 11 <!-- mysql插入数据后,获取id --> 12 <selectKey keyProperty="id" resultType="int" order="AFTER" > 13 SELECT LAST_INSERT_ID() as id 14 </selectKey> 15 16 insert into user(id, name, password, age, deleteFlag) 17 values(#{id}, #{name}, #{password}, #{age}, #{deleteFlag}) 18 </insert>
select配置
1 <select 2 <!-- 1. id (必须配置) 3 id是命名空间中的唯一标识符,可被用来代表这条语句。 4 一个命名空间(namespace) 对应一个dao接口, 5 这个id也应该对应dao里面的某个方法(相当于方法的实现),因此id 应该与方法名一致 --> 6 7 id="selectPerson" 8 9 <!-- 2. parameterType (可选配置, 默认为mybatis自动选择处理) 10 将要传入语句的参数的完全限定类名或别名, 如果不配置,mybatis会通过ParameterHandler 根据参数类型默认选择合适的typeHandler进行处理 11 parameterType 主要指定参数类型,可以是int, short, long, string等类型,也可以是复杂类型(如对象) --> 12 parameterType="int" 13 14 <!-- 3. resultType (resultType 与 resultMap 二选一配置) 15 resultType用以指定返回类型,指定的类型可以是基本类型,可以是java容器,也可以是javabean --> 16 resultType="hashmap" 17 18 <!-- 4. resultMap (resultType 与 resultMap 二选一配置) 19 resultMap用于引用我们通过 resultMap标签定义的映射类型,这也是mybatis组件高级复杂映射的关键 --> 20 resultMap="personResultMap" 21 22 <!-- 5. flushCache (可选配置) 23 将其设置为 true,任何时候只要语句被调用,都会导致本地缓存和二级缓存都会被清空,默认值:false --> 24 flushCache="false" 25 26 <!-- 6. useCache (可选配置) 27 将其设置为 true,将会导致本条语句的结果被二级缓存,默认值:对 select 元素为 true --> 28 useCache="true" 29 30 <!-- 7. timeout (可选配置) 31 这个设置是在抛出异常之前,驱动程序等待数据库返回请求结果的秒数。默认值为 unset(依赖驱动)--> 32 timeout="10000" 33 34 <!-- 8. fetchSize (可选配置) 35 这是尝试影响驱动程序每次批量返回的结果行数和这个设置值相等。默认值为 unset(依赖驱动)--> 36 fetchSize="256" 37 38 <!-- 9. statementType (可选配置) 39 STATEMENT,PREPARED 或 CALLABLE 的一个。这会让 MyBatis 分别使用 Statement,PreparedStatement 或 CallableStatement,默认值:PREPARED--> 40 statementType="PREPARED" 41 42 <!-- 10. resultSetType (可选配置) 43 FORWARD_ONLY,SCROLL_SENSITIVE 或 SCROLL_INSENSITIVE 中的一个,默认值为 unset (依赖驱动)--> 44 resultSetType="FORWARD_ONLY">
resultMap配置
1 <!-- 2 1.type 对应类型,可以是javabean, 也可以是其它 3 2.id 必须唯一, 用于标示这个resultMap的唯一性,在使用resultMap的时候,就是通过id指定 4 --> 5 <resultMap type="" id=""> 6 7 <!-- id, 唯一性,注意啦,这个id用于标示这个javabean对象的唯一性, 不一定会是数据库的主键(不要把它理解为数据库对应表的主键) 8 property属性对应javabean的属性名,column对应数据库表的列名 9 (这样,当javabean的属性与数据库对应表的列名不一致的时候,就能通过指定这个保持正常映射了) 10 --> 11 <id property="" column=""/> 12 13 <!-- result与id相比, 对应普通属性 --> 14 <result property="" column=""/> 15 16 <!-- 17 constructor对应javabean中的构造方法 18 --> 19 <constructor> 20 <!-- idArg 对应构造方法中的id参数 --> 21 <idArg column=""/> 22 <!-- arg 对应构造方法中的普通参数 --> 23 <arg column=""/> 24 </constructor> 25 26 <!-- 27 collection,对应javabean中容器类型, 是实现一对多的关键 28 property 为javabean中容器对应字段名 29 column 为体现在数据库中列名 30 ofType 就是指定javabean中容器指定的类型 31 --> 32 <collection property="" column="" ofType=""></collection> 33 34 <!-- 35 association 为关联关系,是实现N对一的关键。 36 property 为javabean中容器对应字段名 37 column 为体现在数据库中列名 38 javaType 指定关联的类型 39 --> 40 <association property="" column="" javaType=""></association> 41 </resultMap>
那么,问题来了: 什么是动态SQL? 动态SQL有什么作用?
传统的使用JDBC的方法,相信大家在组合复杂的的SQL语句的时候,需要去拼接,稍不注意哪怕少了个空格,都会导致错误。Mybatis的动态SQL功能正是为了解决这种问题, 其通过 if, choose, when, otherwise, trim, where, set, foreach标签,可组合成非常灵活的SQL语句,从而提高开发人员的效率。
if
1 <select id="findUserById" resultType="user"> 2 select * from user where 3 <if test="id != null"> 4 id=#{id} 5 </if> 6 and deleteFlag=0; 7 </select>
有问题?
where
1 <select id="findUserById" resultType="user"> 2 select * from user 3 <where> 4 <if test="id != null"> 5 id=#{id} 6 </if> 7 and deleteFlag=0; 8 </where> 9 </select>
从表面上来看,就是多了个where标签而已, 不过实质上, mybatis是对它做了处理,当它遇到AND或者OR这些,它知道怎么处理。其实我们可以通过 trim 标签去自定义这种处理规则。
trim
上面的where标签,其实可以用trim表示:
<trim prefix="WHERE" prefixOverrides="AND |OR "> ... </trim>
set
1 <update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.dy.entity.User"> 2 update user set 3 <if test="name != null"> 4 name = #{name}, 5 </if> 6 <if test="password != null"> 7 password = #{password}, 8 </if> 9 <if test="age != null"> 10 age = #{age} 11 </if> 12 <where> 13 <if test="id != null"> 14 id = #{id} 15 </if> 16 and deleteFlag = 0; 17 </where> 18 </update>
1 <update id="updateUser" parameterType="com.dy.entity.User"> 2 update user 3 <set> 4 <if test="name != null">name = #{name},</if> 5 <if test="password != null">password = #{password},</if> 6 <if test="age != null">age = #{age},</if> 7 </set> 8 <where> 9 <if test="id != null"> 10 id = #{id} 11 </if> 12 and deleteFlag = 0; 13 </where> 14 </update>
这个用trim 可表示为:
<trim prefix="SET" suffixOverrides=","> ... </trim>
foreach
1 <select id="selectPostIn" resultType="domain.blog.Post"> 2 SELECT * 3 FROM POST P 4 WHERE ID in 5 <foreach item="item" index="index" collection="list" 6 open="(" separator="," close=")"> 7 #{item} 8 </foreach> 9 </select>
choose
<select id="findActiveBlogLike" resultType="Blog"> SELECT * FROM BLOG WHERE state = ‘ACTIVE’ <choose> <when test="title != null"> AND title like #{title} </when> <when test="author != null and author.name != null"> AND author_name like #{author.name} </when> <otherwise> AND featured = 1 </otherwise> </choose> </select>
SqlSessionFactory与sqlsession
从表面上来看,咱们都是通过SqlSession去执行sql语句。那么咱们就先看看是怎么获取SqlSession的吧:
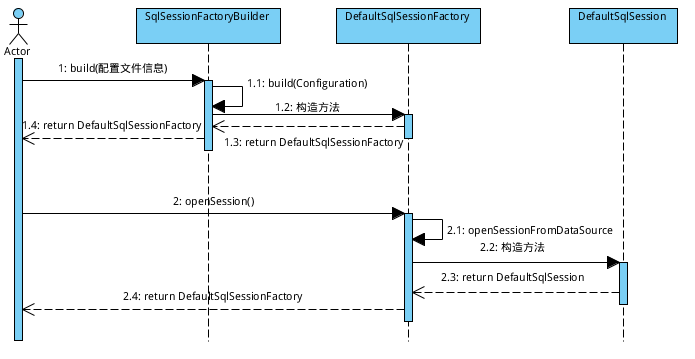
1 SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory = null; 2 String resource = "mybatis-conf.xml"; 3 try { 4 //SqlSessionFactoryBuilder读取配置文件 5 sessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(Resources 6 .getResourceAsReader(resource)); 7 } catch (IOException e) { 8 e.printStackTrace(); 9 } 10 //通过SqlSessionFactory获取SqlSession 11 SqlSession sqlSession = sessionFactory.openSession();
SqlSession咱们也拿到了,咱们可以调用SqlSession中一系列的select..., insert..., update..., delete...方法轻松自如的进行CRUD操作了。 就这样? 那咱配置的映射文件去哪儿了? 别急, 咱们接着往下看:
2. 利器之MapperProxy:
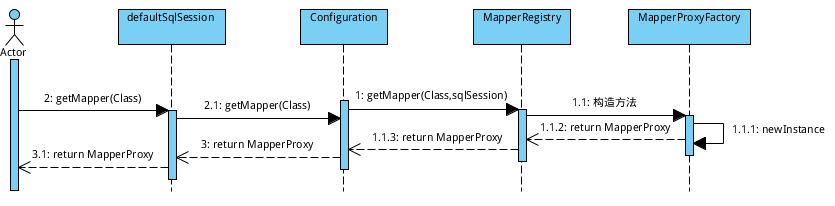
在mybatis中,通过MapperProxy动态代理咱们的dao, 也就是说, 当咱们执行自己写的dao里面的方法的时候,其实是对应的mapperProxy在代理。