一、File 类
1、一个File类对象,表示了磁盘上的文件或目录
2、File类提供了与平台无关的方法对磁盘上文件或目录进行操作
3、File类直接处理文件和文件系统
4、File类没有指定信息怎样从文件读取或者向文件存储
二、File 创建文件
public class FileTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:/test.txt");
System.out.println(file.createNewFile());
}
}
显示
true
说明创建成功。
三、在文件夹下创建文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
File file = new File("c:/abc");
File file2 = new File(file, "hello.txt");
System.out.println(file2.createNewFile());
}
将在abc文件夹下创建hello.txt文件
四、InputStream和OutputStream类层次结构
1、InputStream的类层次结构
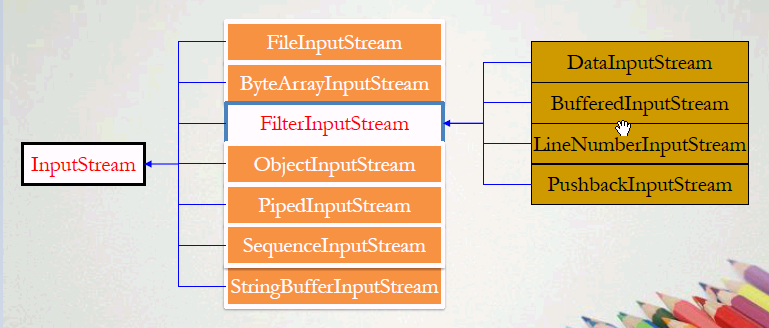
2、OutputStream的类层次结构
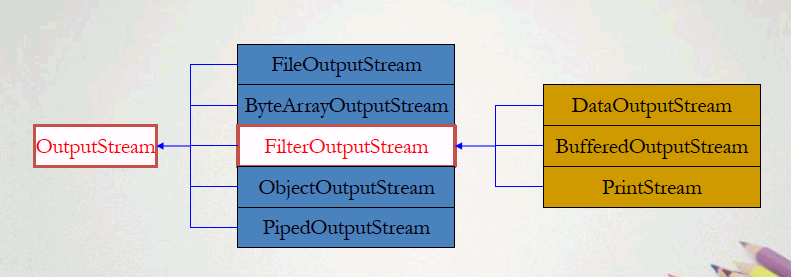
四、 FileInputStream读取文件数据
public class InputStreamTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("d:/temp/hello.txt");
byte[] buffer = new byte[200];
int length = 0;
while((length = is.read(buffer, 0, 200)) != -1){
System.out.println(length+"--------");
String str = new String(buffer, 0, length);
System.out.println(str);
}
is.close();
}
}
五、FileOutputStream写入文件
public class OutputStreamTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("d:/temp/out.txt");
String str = "hello world.";
byte[] buffer = str.getBytes();
os.write(buffer);
os.close();
}
}
六、过滤流
在InputStream类和OutStreame类子类中,FilterInputStream和FilterOutputStream过滤抽象类又派生出DataInputStream和DataOutputstram 数据输入和输出流等子类
七、缓冲输出流 BufferedOutStream
缓冲输出流 BufferedOutStream类提供了和FileOutputStream类同样的写操作方法,但是所有输出全部写入缓冲区中。当写满缓冲区或关闭输出流时,它再一次性输出到流,或者用flash()方法主动将缓冲区输出到流。
public class BufferedOutPutStreamTst1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("d:/temp/out2.txt");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(os);
String str = "cool hello world.";
byte[] buffer = str.getBytes();
bos.write(buffer);
bos.close();
os.close();
}
}
八、字节数组输入流 ByteArrayInputStream是把字节数组当成源的输入流。
public class ByteArrayInputStreamTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "abc";
byte[] b = str.getBytes();
ByteArrayInputStream in = new ByteArrayInputStream(b);
for(int i = 0; i < str.length(); i++){
int c;
while( (c = in.read()) != -1){
if(i == 0){
System.out.println((char)c);
}else {
System.out.println(Character.toUpperCase((char)c));
}
}
System.out.println();
in.reset();
}
}
}
显示结果
a b c A B C A B C
九、字节数组输出流 ByteArrayOutputStream
ByteArrayOutputStream是一个把字节数组当作输出流的实现。
public class ByteArrayInputStreamTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String str = "abc ef";
byte[] b = str.getBytes();
ByteArrayOutputStream f = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
f.write(b);
byte[] result = f.toByteArray();
for (int i = 0; i < result.length; i++) {
System.err.println((char)result[i]);
}
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("D:/temp/out3.txt");
//f里定义的字节数组写到os流中
f.writeTo(os);
f.close();
os.close();
}
}
显示效果
a b c e f
最后将f里定义的字节数组写到os流中,对应文件为D:/temp/out3.txt
十、数据输入流和输出流(DataInputStream和DataOutputStream)
提供了允许从流读写任意对象与基本数据类型功能的方法。
字节文件流FileInputStream和FileOutputStream只能提供纯字节或字节数组的输入/输出,如果需要进行基本数据类型如整数和浮点数的输入/输出。则要用到过滤流类的二进制数据文件流DataInputStram和DataOutputStream类。这两个类的对象必须和一个输入类或输出类联系起来,而不能直接用文件名或文件对象建立。
public class BufferedOutPutStreamTst1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("d:/temp/out3.txt");
BufferedOutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(os);
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(bos);
byte b = 3;
int i = 4;
char ch = 'a';
float f = 5.6f;
dos.writeByte(b);
dos.writeInt(i);
dos.writeChar(ch);
dos.writeFloat(f);
//关闭最外层的。里面的也关了。
dos.close();
//读和写的顺序要保持一致
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream("d:/temp/out3.txt")));
System.out.println(dis.readByte());
System.out.println(dis.readInt());
System.out.println(dis.readChar());
System.out.println(dis.readFloat());
dis.close();
}
}
写入的文件,是一个二进制文件

打印的效果
3 4 a 5.6
十三、手写InputStream
public class MyOwnStream1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
byte[] b = new byte[16];
for(int i = 0; i< b.length; i++){
b[i] = (byte)i;
}
MyByteArrayInputStream mybais = new MyByteArrayInputStream(b);
while (true) {
int c = mybais.read();
if(c < 0){
break;
}
System.out.print(c + " ");
}
}
}
class MyByteArrayInputStream extends InputStream{
protected byte[] data;
//当前读取的位置
protected int ptr = 0;
public MyByteArrayInputStream( byte[] b) {
this.data = b;
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
return (ptr < data.length ) ? (data[ptr++] ) : -1;
}
}
打印结果
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15
手写InputStram的完善版本
public class MyOwnStream2 extends InputStream {
protected byte[] data;
//当前读取的位置
protected int ptr = 0;
//从那一位开始读
protected int mark = 0;
public MyOwnStream2( byte[] b) {
this.data = b;
}
@Override
public int read() throws IOException {
return (ptr < data.length ) ? (data[ptr++] ) : -1;
}
@Override
public int available() throws IOException {
return data.length - ptr;
}
@Override
public void close() throws IOException {
ptr = data.length;
}
@Override
public synchronized void mark(int readlimit) {
this.mark = readlimit;
}
@Override
public synchronized void reset() throws IOException {
if(mark < 0 || mark >= data.length){
throw new IOException("the position is not valid");
}
ptr = mark;
}
@Override
public boolean markSupported() {
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
byte[] b = new byte[16];
for(int i = 0; i< b.length; i++){
b[i] = (byte)i;
}
}
@Override
public int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) throws IOException {
if(this.ptr >= data.length || len < 0){
return -1;
}
if((this.ptr +len) > data.length){
len = data.length - this.ptr;
}
if(len == 0){
return 0;
}
System.arraycopy(data, ptr, b, off, len);
ptr += len;
return len;
}
}